Podcast
Questions and Answers
Match the following soil horizons with their characteristics:
Match the following soil horizons with their characteristics:
A – Horizon = Top layer of soil rich in minerals and humus B – Horizon = Sub-soil with larger rock particles and less humus C – Horizon = Sub-stratum made of broken rocks from weathering Bed – rock = Unweathered solid rock beneath soil layers
Match the following descriptions with the correct soil horizon:
Match the following descriptions with the correct soil horizon:
A – Horizon = Soft, porous, and holds more water B – Horizon = Lighter in color and harder than top soil C – Horizon = Formation from the partial weathering of bed-rock Bed – rock = Source of soil produced over a long period
Match the following soil horizons with their alternate names:
Match the following soil horizons with their alternate names:
A – Horizon = Top soil B – Horizon = Sub-soil C – Horizon = Sub-stratum Bed – rock = Parent rock
Match the following soil horizons with their fertility levels:
Match the following soil horizons with their fertility levels:
Match the following soil horizons with the living organisms they contain:
Match the following soil horizons with the living organisms they contain:
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
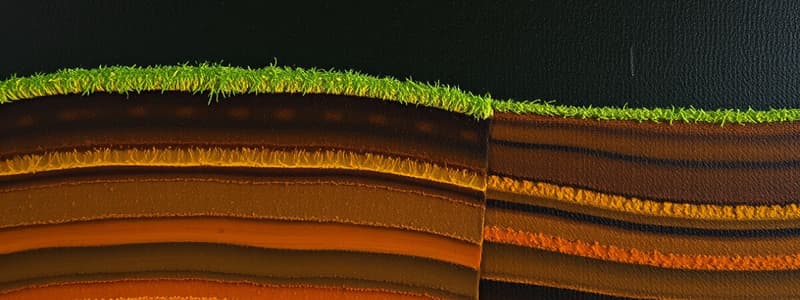
Soil Profile Overview
- A vertical section through soil layers is referred to as a Soil Profile.
- Soil Profile contains three distinct layers, known as Horizons: A, B, and C.
A – Horizon (Top Soil)
- The topmost layer, known as A – Horizon or Top Soil.
- Characterized by dark color, rich in minerals and humus.
- Essential for plant roots; it supports their growth.
- Hosts diverse living organisms, including insects (ants, beetles), earthworms, rodents, and microbial life (bacteria and fungi).
- Contains decayed organic matter from dead plants and animals, adding to its fertility.
- Soft and porous texture allows it to retain moisture effectively.
- Provides essential nutrients and minerals, making it the most valuable soil layer for plants.
B – Horizon (Sub-Soil)
- Located directly beneath the A – Horizon, this layer is known as B – Horizon or Sub-Soil.
- Composed of larger rock particles compared to A – Horizon.
- Typically lighter in color, harder, and more compact.
- Has a limited presence of living organisms.
- Some tree roots can extend into this layer, though it is much less fertile than the top soil.
- Contains minimal humus, contributing to its lower fertility.
C – Horizon (Sub-Stratum)
- Positioned below the B – Horizon, referred to as C – Horizon or Sub-Stratum.
- Made of small lumps of broken rock created by the partial weathering of bedrock (parent rock).
- The rock in this layer continues to break down into finer particles.
- Beneath the C – Horizon lies unweathered Solid Rock known as Bed-Rock, which has formed soil over long periods.
Influential Climatic Factors
- Key climatic factors include wind, temperature, rainfall, light, and humidity.
- These factors play a significant role in affecting soil profiles and impacting soil structure.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.