Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the structure of simple columnar epithelium?
What is the structure of simple columnar epithelium?
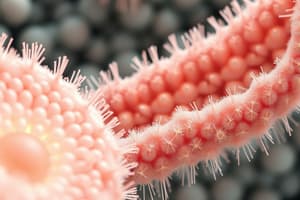
Single layer of cells that are taller than wide; oval shaped nucleus in basal region of cell; apical region of cells have microvilli; may contain goblet cells that secrete mucin.
What is the function of microvilli in simple columnar epithelium?
What is the function of microvilli in simple columnar epithelium?
Absorption
What is a location where simple columnar epithelium is found?
What is a location where simple columnar epithelium is found?
Lining of most of the digestive tract except for the lining of the stomach.
What are goblet cells and their location?
What are goblet cells and their location?
Study Notes
Simple Columnar Epithelium - Structure
- Composed of a single layer of cells characterized by a height greater than width.
- Features oval-shaped nuclei located in the basal region of the cells.
- Apical cell surface has microvilli, enhancing surface area for absorption.
- Contains goblet cells that produce and secrete mucin, a glycoprotein component of mucus.
Simple Columnar Epithelium - Function
- Microvilli on the apical surface facilitate the absorption of nutrients and other substances.
- Goblet cells within the epithelium aid in mucin secretion, contributing to protective mucus formation.
Simple Columnar Epithelium - Location
- Primarily found in the lining of the digestive tract, providing a surface for absorption and secretion.
- Absence of goblet cells in the stomach lining, which instead has microvilli for absorption purposes.
Goblet Cells
- Specialized cells located in the lining of the majority of the digestive tract.
- Not present in the stomach lining where absorption occurs primarily through microvilli.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
Explore the structure, function, and location of simple columnar epithelium in this quiz. Learn about the role of microvilli and goblet cells in absorption and mucin secretion, particularly in the digestive tract. Understand how this specialized epithelium contributes to nutrient absorption and protective mucus formation.