Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary purpose of SDS-PAGE in biochemistry?
What is the primary purpose of SDS-PAGE in biochemistry?
- To visualize specific antibody-antigen interactions
- To separate proteins based on molecular weight (correct)
- To purify bacterial cultures
- To amplify DNA sequences
What type of gel is primarily used in SDS-PAGE?
What type of gel is primarily used in SDS-PAGE?
- Polyethylene glycol gel
- Cellulose acetate gel
- Agarose gel
- Discontinuous polyacrylamide gel (correct)
How does SDS affect proteins in SDS-PAGE?
How does SDS affect proteins in SDS-PAGE?
- It denatures proteins and makes them uniformly negatively charged (correct)
- It causes proteins to aggregate
- It enhances their natural charge
- It stabilizes disulfide bonds
Which of the following molecular weights would migrate the fastest in SDS-PAGE?
Which of the following molecular weights would migrate the fastest in SDS-PAGE?
Which of the following is NOT a component of Laemmli Sample Buffer?
Which of the following is NOT a component of Laemmli Sample Buffer?
What role do reducing agents like β-mercaptoethanol play in SDS-PAGE?
What role do reducing agents like β-mercaptoethanol play in SDS-PAGE?
Which electrode do proteins migrate towards in SDS-PAGE?
Which electrode do proteins migrate towards in SDS-PAGE?
What is the purpose of the protein ladder in SDS-PAGE?
What is the purpose of the protein ladder in SDS-PAGE?
Why is it important to heat protein samples immediately after adding Laemmli buffer?
Why is it important to heat protein samples immediately after adding Laemmli buffer?
What is the total sample volume after adding 15μl of a 5% unknown sample and 5μl of Laemmli buffer?
What is the total sample volume after adding 15μl of a 5% unknown sample and 5μl of Laemmli buffer?
What role does SDS play in the denaturation of proteins during the protocol?
What role does SDS play in the denaturation of proteins during the protocol?
What should be done before removing gels from the electrophoretic apparatus?
What should be done before removing gels from the electrophoretic apparatus?
How long should the gels run at 180 volts during electrophoresis?
How long should the gels run at 180 volts during electrophoresis?
What is the purpose of using Coomassie Blue staining solution?
What is the purpose of using Coomassie Blue staining solution?
What is a significant danger when using 2-mercaptoethanol in the Laemmli buffer?
What is a significant danger when using 2-mercaptoethanol in the Laemmli buffer?
What must be changed in the destaining solution every 5 minutes during the incubation?
What must be changed in the destaining solution every 5 minutes during the incubation?
Flashcards
SDS-PAGE
SDS-PAGE
A laboratory technique separating proteins based on their molecular weight.
Electrophoresis
Electrophoresis
Separating molecules in an electric field, often using a gel as a support.
Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate (SDS)
Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate (SDS)
A detergent that denatures and binds to proteins, making them negatively charged.
Discontinuous Polyacrylamide Gel
Discontinuous Polyacrylamide Gel
Signup and view all the flashcards
Running Buffer
Running Buffer
Signup and view all the flashcards
Laemmli Sample Buffer
Laemmli Sample Buffer
Signup and view all the flashcards
Protein Ladder
Protein Ladder
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gel Staining
Gel Staining
Signup and view all the flashcards
Protein denaturation
Protein denaturation
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is SDS?
What is SDS?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does Laemmli sample buffer contain?
What does Laemmli sample buffer contain?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Overheating gels
Overheating gels
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Coomassie Blue?
What is Coomassie Blue?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Destain?
What is Destain?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Electrophoresis?
What is Electrophoresis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a Protein Ladder?
What is a Protein Ladder?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
MD100 Medical Biochemistry I - Lab Exercise 3: Introduction to SDS PAGE
- Course: Medical Biochemistry I
- Lab Exercise: Introduction to SDS PAGE - Protein identification and characterization
- Semester: Fall 2024
- University: European University Cyprus
- School: School of Medicine
Objectives
- Introduction: SDS-PAGE laboratory technique and theoretical background
- Part A: Sample preparation – dilutions
- Part B: Sample loading – Gel running
- Part C: Gel staining and destaining
- Part D: Protein gel analysis – protein identification
Introduction to SDS-PAGE
- Technique used: Separating proteins based on molecular weight
- Electrophoresis: Separation of macro-molecules in an electric field
- SDS-PAGE: Uses a discontinuous polyacrylamide gel as a support
- SDS: Denatures proteins, creating uniformly negative charge; allowing separation based on size
- Reducing agents: (e.g., β-mercaptoethanol) cleave disulfide bonds and disrupt protein structure
The Principle of SDS-PAGE
- Charged molecules: Migrate to electrode with opposite charge
- Proteins with SDS: Become uniformly negatively charged, migrating toward the positive electrode
- SDS and reducing agents: Unfold proteins to a linear structure, charge proportional to chain length
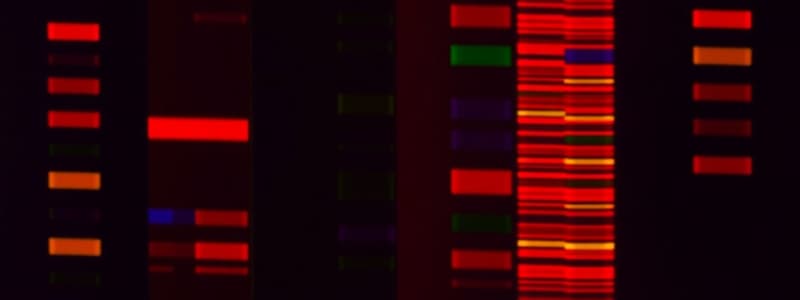
Protein Ladder
- Molecular weight markers: Used to approximate the molecular weight of unknown proteins
- kDa values: Various molecular weight proteins for comparison
Protein Identification
- Albumin (66.5 kDa): Protein isolated from bovine serum
- Casein (24 kDa): Protein isolated from bovine milk
Materials/Equipment
- Gel: Prepared or precast polyacrylamide gels
- Vertical Gel Electrophoresis Chamber
- Protein Samples: Protein solutions
- Running Buffer: (Tris/Glycine/SDS)
- Staining Buffer: For staining the gel
- Destaining Buffer: For removing excess stain
- Protein Ladder: Pre-stained molecular weight standards
- Micropipettes & tips: for accurate measurements
- Laemmli Sample Buffer: Specifically designed buffer to prepare proteins.
Sample Preparation
- 10% Unknown Samples dilutions: 5%, 2.5%, & 1%
- Laemmli Buffer preparation: Tris-HCI (pH 6.8), SDS, glycerol, 2-mercaptoethanol, Bromophenol Blue
- Heat treatment: To denature proteins after adding Laemmli buffer to prevent protease degradation
Protocol
- Dilutions: Prepare 1 ml of 5%, 2.5%, & 1% dilutions using 10% solution
- Sample addition: Add 15 μL of each dilution to separate tubes
- Buffer addition: Add 5 μL of 4x Laemmli Sample Buffer to each sample
- Protein denaturation: Boil samples at 70°C for 2 minutes
- Running buffer: Add running buffer to gel chambers
- Protein ladder loading: Load 10 μL of protein ladder into the first well of the gel.
- Sample loading: Load 10 μL samples onto the gel
- Gel run (voltage): Run at 180 V for ~30 minutes
- Gel staining with Coomassie blue: Stain with Coomassie Blue in a dish
- Destaining: Remove Coomassie Blue and rinse thoroughly with deionized water
- Destain incubation: Incubate the gel in fresh destaining solution for 15 minutes, changing every 5 minutes.
- Overnight destain: Destain gel in deionized water overnight on a rocking table
- Photography: Take gel photograph
Protein Gel Analysis
- Single band: Indicates single protein/subunit
- Multiple bands: Indicates multiple proteins/subunits
- Band darkness: Represents protein concentration
- Comparing to ladder: Estimate molecular weight
Question 1
- Correct answer: C. Smaller proteins migrate more rapidly through the gel
Question 2
- Correct answer: A. Staining them with the dye
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.