Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the cell membrane?
What is the primary function of the cell membrane?
To regulate the exchange of matter and energy between the cell and its surroundings.
What model describes the structure of the cell membrane?
What model describes the structure of the cell membrane?
Match the types of transport with their requirements:
Match the types of transport with their requirements:
Passive Transport = No energy required Active Transport = Energy required from ATP Facilitated Diffusion = Requires protein channels Osmosis = Diffusion of water
Active transport occurs without the input of energy.
Active transport occurs without the input of energy.
Signup and view all the answers
What is osmosis?
What is osmosis?
Signup and view all the answers
What term describes a solution with the same concentration as the cell?
What term describes a solution with the same concentration as the cell?
Signup and view all the answers
Facilitated diffusion requires a ______ for the movement of water-soluble substances.
Facilitated diffusion requires a ______ for the movement of water-soluble substances.
Signup and view all the answers
What are the two types of endocytosis?
What are the two types of endocytosis?
Signup and view all the answers
Exocytosis is the process of taking materials into the cell.
Exocytosis is the process of taking materials into the cell.
Signup and view all the answers
Study Notes
-
The Cell Membrane as a Gate Keeper
- Cells are open systems, allowing matter and energy exchange between themselves and the environment.
- The cell membrane regulates this exchange through selective permeability, maintaining internal balance (homeostasis).
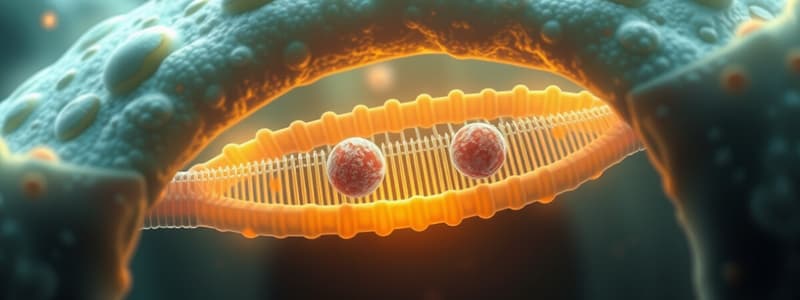
Cell Membrane Structure: The Fluid Mosaic Model
- Composed of a phospholipid bilayer with phosphate groups on each surface, creating a double lipid layer.
- Proteins, some with attached carbohydrates, are interspersed throughout the membrane.
Forms of Cellular Transport
- Passive Transport: Utilizes kinetic energy of molecules without external energy input.
- Active Transport: Requires energy (ATP) for movement against concentration gradients.
Energy and Concentration Gradients
- Concentration gradient defines the difference in molecule concentration inside vs. outside the cell.
- Moving from high to low concentration requires no energy; moving from low to high concentration requires energy (ATP).
Types of Passive Transport
- Diffusion: Spontaneous movement of particles from high concentration to low concentration, continuing until equilibrium is reached.
- Can be accelerated by increasing temperature or agitation.
Diffusion & The Particle Model of Matter
- Particles have large spaces between them and are in constant motion, with the least attraction in gases and most in solids.
Osmosis
- Defined as the diffusion of water through a semi-permeable membrane.
- Water movement depends on the tonicity of solutions:
- Isotonic: Equal concentration (no net water movement).
- Hypotonic: Less solute than cell (water enters cell).
- Hypertonic: More solute than cell (water exits cell).
Facilitated Diffusion
- Occurs for water-soluble substances needing assistance through protein channels or carrier proteins.
- Movement is still from higher to lower concentration.
Types of Active Transport
- Active Transport with Carrier Proteins: Moves molecules from low to high concentration using energy.
-
Endocytosis and Exocytosis: Processes for transferring large molecules that cannot pass through the membrane. Both require ATP.
-
Endocytosis: Intake of substances via vesicle formation.
- Phagocytosis: Engulfment of larger molecules.
- Pinocytosis: Engulfment of liquids and dissolved substances.
-
Endocytosis: Intake of substances via vesicle formation.
Additional Notes
- Various classroom activities include demonstrations, workbook assignments, and simulations to enhance understanding.
- Students may complete flow charts summarizing material transport across membranes.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
This quiz covers key concepts from Science 10 regarding cellular transport and the role of the cell membrane as a selective barrier. Students will explore the fluid mosaic model and the importance of homeostasis in cellular function. Test your understanding of how cells interact with their surroundings through regulated exchanges.