Podcast
Questions and Answers
What are the two main types of sacral torsions?
What are the two main types of sacral torsions?
Forward and backward.
List three classifications of sacroiliac dysfunctions.
List three classifications of sacroiliac dysfunctions.
Forward/backward sacral torsions, flexed/extended sacrum, anterior/posterior sacrum.
Which structures are palpated and compared bilaterally in the case of sacral torsion?
Which structures are palpated and compared bilaterally in the case of sacral torsion?
Sacral sulci and inferior lateral angles (ILA).
Identify the acronym SSSIPP and its relevance in sacroiliac pathology assessment.
Identify the acronym SSSIPP and its relevance in sacroiliac pathology assessment.
Signup and view all the answers
What terminology refers to the direction the anterior portion of the sacrum is looking towards during oblique axis rotations?
What terminology refers to the direction the anterior portion of the sacrum is looking towards during oblique axis rotations?
Signup and view all the answers
What is classified as a dysfunction of the movement between the sacrum and ilium?
What is classified as a dysfunction of the movement between the sacrum and ilium?
Signup and view all the answers
In sacral torsion, what is the main axis around which the torque occurs?
In sacral torsion, what is the main axis around which the torque occurs?
Signup and view all the answers
What are the physiological types of dysfunctions that can occur in sacroiliac pathology?
What are the physiological types of dysfunctions that can occur in sacroiliac pathology?
Signup and view all the answers
Which two structures are primarily assessed during the palpation for sacral torsion?
Which two structures are primarily assessed during the palpation for sacral torsion?
Signup and view all the answers
In oblique axis rotations, what does 'L on R' signify regarding the sacrum's orientation?
In oblique axis rotations, what does 'L on R' signify regarding the sacrum's orientation?
Signup and view all the answers
Explain the significance of the sacral base in assessing sacroiliac pathologies.
Explain the significance of the sacral base in assessing sacroiliac pathologies.
Signup and view all the answers
Differentiate between forward and backward sacral torsions in terms of their orientation.
Differentiate between forward and backward sacral torsions in terms of their orientation.
Signup and view all the answers
List and describe the role of the sacrotuberous ligament in sacroiliac assessment.
List and describe the role of the sacrotuberous ligament in sacroiliac assessment.
Signup and view all the answers
What is the importance of comparing the sacral sulci during palpation for sacral torsion?
What is the importance of comparing the sacral sulci during palpation for sacral torsion?
Signup and view all the answers
Discuss the clinical relevance of palpating the hamstrings in the context of sacroiliac pathologies.
Discuss the clinical relevance of palpating the hamstrings in the context of sacroiliac pathologies.
Signup and view all the answers
What are the implications of a fixated sacrum in terms of sacroiliac dysfunction?
What are the implications of a fixated sacrum in terms of sacroiliac dysfunction?
Signup and view all the answers
Describe the significance of palpating the inferior lateral angles (ILA) in sacral torsion assessment.
Describe the significance of palpating the inferior lateral angles (ILA) in sacral torsion assessment.
Signup and view all the answers
What role do the gluteal muscles play in relation to sacroiliac dysfunction?
What role do the gluteal muscles play in relation to sacroiliac dysfunction?
Signup and view all the answers
Explain the concept of the oblique axis in relation to sacral movements.
Explain the concept of the oblique axis in relation to sacral movements.
Signup and view all the answers
How do pathological/non-physiological sacral dysfunctions differ from physiological dysfunctions?
How do pathological/non-physiological sacral dysfunctions differ from physiological dysfunctions?
Signup and view all the answers
What implications do forward and backward sacral torsions have for treatment strategies in a clinical setting?
What implications do forward and backward sacral torsions have for treatment strategies in a clinical setting?
Signup and view all the answers
How would palpating the sacral base contribute to diagnosing sacroiliac pathologies?
How would palpating the sacral base contribute to diagnosing sacroiliac pathologies?
Signup and view all the answers
Explain the role of the inferior lateral angles (ILA) in the assessment of sacral torsion.
Explain the role of the inferior lateral angles (ILA) in the assessment of sacral torsion.
Signup and view all the answers
What challenges may arise from a fixated sacrum during a restriction assessment?
What challenges may arise from a fixated sacrum during a restriction assessment?
Signup and view all the answers
Discuss how the quadratus lumborum's involvement is essential in evaluating sacroiliac joints.
Discuss how the quadratus lumborum's involvement is essential in evaluating sacroiliac joints.
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following options represents the main types of sacral dysfunctions?
Which of the following options represents the main types of sacral dysfunctions?
Signup and view all the answers
A sacral somatic dysfunction includes only pathological dysfunctions.
A sacral somatic dysfunction includes only pathological dysfunctions.
Signup and view all the answers
Name one of the structures palpated for sacroiliac pathology that starts with the letter 'S'.
Name one of the structures palpated for sacroiliac pathology that starts with the letter 'S'.
Signup and view all the answers
The two types of sacral torsions are _______ and _______.
The two types of sacral torsions are _______ and _______.
Signup and view all the answers
Match the following oblique axis rotations with their descriptions:
Match the following oblique axis rotations with their descriptions:
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following are included in the six most relevant structures to palpate for a sacroiliac pathology? (Select all that apply)
Which of the following are included in the six most relevant structures to palpate for a sacroiliac pathology? (Select all that apply)
Signup and view all the answers
A sacral somatic dysfunction can only be classified as pathological.
A sacral somatic dysfunction can only be classified as pathological.
Signup and view all the answers
What is the main difference between forward and backward sacral torsions?
What is the main difference between forward and backward sacral torsions?
Signup and view all the answers
The two types of dysfunctions in sacroiliac pathology are __________ and __________.
The two types of dysfunctions in sacroiliac pathology are __________ and __________.
Signup and view all the answers
Match the following structures with their roles in assessing sacroiliac pathology:
Match the following structures with their roles in assessing sacroiliac pathology:
Signup and view all the answers
What describes the fixation of the sacrum during motion?
What describes the fixation of the sacrum during motion?
Signup and view all the answers
The inferior lateral angles (ILA) are significant structures to palpate for sacral torsion assessment.
The inferior lateral angles (ILA) are significant structures to palpate for sacral torsion assessment.
Signup and view all the answers
What are the two primary types of dysfunction in sacroiliac pathology?
What are the two primary types of dysfunction in sacroiliac pathology?
Signup and view all the answers
The two types of sacral torsions are __________ and __________.
The two types of sacral torsions are __________ and __________.
Signup and view all the answers
Match the following sacral torsion structures with their functions in assessment:
Match the following sacral torsion structures with their functions in assessment:
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following structures is NOT included in the six most relevant structures for palpating sacroiliac pathology?
Which of the following structures is NOT included in the six most relevant structures for palpating sacroiliac pathology?
Signup and view all the answers
Forward sacral torsion is characterized by the sacrum facing towards the left oblique axis.
Forward sacral torsion is characterized by the sacrum facing towards the left oblique axis.
Signup and view all the answers
Name one of the five somewhat relevant structures to palpate in sacroiliac pathology assessment.
Name one of the five somewhat relevant structures to palpate in sacroiliac pathology assessment.
Signup and view all the answers
The two types of dysfunctions in sacroiliac pathology are _______ and _______.
The two types of dysfunctions in sacroiliac pathology are _______ and _______.
Signup and view all the answers
Match the following types of oblique axis rotations with their descriptions:
Match the following types of oblique axis rotations with their descriptions:
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following is a physiological dysfunction in sacroiliac pathology?
Which of the following is a physiological dysfunction in sacroiliac pathology?
Signup and view all the answers
Forward and backward sacral torsions refer to the orientation of the sacrum in relation to the ilium.
Forward and backward sacral torsions refer to the orientation of the sacrum in relation to the ilium.
Signup and view all the answers
Name two structures that are most relevant to palpate for sacroiliac pathology.
Name two structures that are most relevant to palpate for sacroiliac pathology.
Signup and view all the answers
Match the following terminology with their corresponding descriptions in sacroiliac assessment:
Match the following terminology with their corresponding descriptions in sacroiliac assessment:
Signup and view all the answers
Study Notes
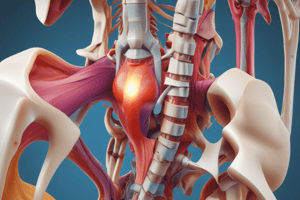
Sacroiliac Pathologies
- Sacroiliac pathology refers to a dysfunction in the movement of the sacrum on the ilium, classified as a sacral somatic dysfunction.
- The sacrum can become fixated during its movement.
- Dysfunctions can be physiological (normal) or pathological (abnormal).
- Further classifications include forward/backward sacral torsions, and flexion/extension of the sacrum, and anterior/posterior positioning.
Palpation Structures (SSSIPP & HHILS)
- Key structures for palpation in sacroiliac pathology include:
- Sacral base
- Sacral sulci
- Sacrotuberous ligaments
- Inferior lateral angles (ILA)
- Posterior superior iliac spine (PSIS)
- Piriformis muscle
- Other somewhat relevant structures include:
- Hamstrings
- Hip flexors
- Ilia
- Lumbosacral joint
- Sacroiliac joints
Sacral Torsion
- Sacral torsion is a dysfunction around an oblique axis with torque between the sacrum and innominates.
- Two types of sacral torsions are forward and backward.
- For sacral torsion, bilateral comparisons are made of:
- Sacral sulci
- Inferior lateral angles (ILA).
Palpation for Sacral Torsion
- 7 primary palpatory structures include:
- Gluteal muscles
- Quadratus lumborum
- Abdominal muscles
- Sacrotuberous ligaments
- Inguinal ligaments
- Greater trochanters
- Hamstrings
Oblique Axis Rotations
- Four types of oblique axis rotations exist:
- Left on Left (L on L)
- Right on Left (R on L)
- Right on Right (R on R)
- Left on Right (L on R)
- Note the direction the anterior sacral portion faces.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
Explore the intricacies of sacroiliac pathologies, including sacral somatic dysfunction and the structures involved in palpation. This quiz covers both physiological and pathological dysfunctions, sacral torsion, and key anatomical landmarks. Test your understanding of sacroiliac joint mechanics and palpation methods used in assessment.