Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following factors would directly decrease the efficiency of oxygen diffusion from the alveoli into the capillary blood?
Which of the following factors would directly decrease the efficiency of oxygen diffusion from the alveoli into the capillary blood?
- Increased hemoglobin concentration in the blood.
- Decreased alveolar surface area. (correct)
- Increased perfusion of systemic capillaries.
- Decreased barometric pressure.
A patient has a ventilation-perfusion (V/Q) ratio of 1.2. Which condition does this indicate?
A patient has a ventilation-perfusion (V/Q) ratio of 1.2. Which condition does this indicate?
- The ventilation is higher than perfusion in the lungs. (correct)
- The ventilation is lower than perfusion in the lungs.
- The perfusion is significantly higher than ventilation.
- There is a balanced match between ventilation and perfusion.
Which of the following compensatory mechanisms would the body likely employ to maintain adequate oxygen delivery to tissues in a patient with anemia (reduced hemoglobin)?
Which of the following compensatory mechanisms would the body likely employ to maintain adequate oxygen delivery to tissues in a patient with anemia (reduced hemoglobin)?
- Reducing the rate of cellular metabolism.
- Increasing the affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen.
- Decreasing cardiac output to reduce oxygen demand.
- Shifting the oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve to the right. (correct)
In an elderly patient, what physiological change contributes most significantly to a reduced ventilatory reserve?
In an elderly patient, what physiological change contributes most significantly to a reduced ventilatory reserve?
How does carbon dioxide transport in the blood primarily facilitate its removal from tissues?
How does carbon dioxide transport in the blood primarily facilitate its removal from tissues?
What is the primary physiological cause of pulmonary artery constriction?
What is the primary physiological cause of pulmonary artery constriction?
Which of the following is NOT a primary function of the pulmonary system?
Which of the following is NOT a primary function of the pulmonary system?
Minute volume is calculated by which of the following formulas?
Minute volume is calculated by which of the following formulas?
What role do Type II alveolar cells play in the pulmonary system?
What role do Type II alveolar cells play in the pulmonary system?
Which of the following lung receptors is primarily responsible for detecting inhaled irritants and triggering a cough reflex?
Which of the following lung receptors is primarily responsible for detecting inhaled irritants and triggering a cough reflex?
Which of the following muscles is NOT typically involved in normal, passive expiration?
Which of the following muscles is NOT typically involved in normal, passive expiration?
Which of the following accurately describes the relationship between the pulmonary and systemic circulations?
Which of the following accurately describes the relationship between the pulmonary and systemic circulations?
What is the primary function of surfactant in the alveoli?
What is the primary function of surfactant in the alveoli?
At what location does the pulmonary artery divide and enter the lung?
At what location does the pulmonary artery divide and enter the lung?
What is the primary role of the larynx within the pulmonary system?
What is the primary role of the larynx within the pulmonary system?
A patient with emphysema typically exhibits hyperinflated lungs. Which of the following is most likely TRUE regarding this patient's lung mechanics?
A patient with emphysema typically exhibits hyperinflated lungs. Which of the following is most likely TRUE regarding this patient's lung mechanics?
How does the body regulate pulmonary circulation in response to local humoral conditions?
How does the body regulate pulmonary circulation in response to local humoral conditions?
Which of the following scenarios would cause the work of breathing to increase the most?
Which of the following scenarios would cause the work of breathing to increase the most?
Which of the following best describes the alveolocapillary membrane?
Which of the following best describes the alveolocapillary membrane?
After gas exchange, where do the pulmonary veins carry oxygenated blood?
After gas exchange, where do the pulmonary veins carry oxygenated blood?
Which of the following lists ONLY structures that are part of the lower airways?
Which of the following lists ONLY structures that are part of the lower airways?
Which of the following scenarios would most directly impair the diffusion of oxygen from the alveoli into the capillary blood?
Which of the following scenarios would most directly impair the diffusion of oxygen from the alveoli into the capillary blood?
In a patient experiencing the Bohr effect, which of the following conditions would promote the release of oxygen from hemoglobin?
In a patient experiencing the Bohr effect, which of the following conditions would promote the release of oxygen from hemoglobin?
What is the primary mechanism by which carbon dioxide is transported in the blood?
What is the primary mechanism by which carbon dioxide is transported in the blood?
How would a significant decrease in chest wall compliance most directly affect the pulmonary system?
How would a significant decrease in chest wall compliance most directly affect the pulmonary system?
The Haldane effect describes how:
The Haldane effect describes how:
What is the primary physiological response that leads to pulmonary artery constriction?
What is the primary physiological response that leads to pulmonary artery constriction?
Which cellular component of the alveoli is primarily responsible for reducing surface tension, thereby preventing alveolar collapse?
Which cellular component of the alveoli is primarily responsible for reducing surface tension, thereby preventing alveolar collapse?
Which of the following receptors is responsible for detecting changes in blood pH and $PCO_2$?
Which of the following receptors is responsible for detecting changes in blood pH and $PCO_2$?
Which group of muscles is primarily involved in active expiration, such as during forceful exhalation?
Which group of muscles is primarily involved in active expiration, such as during forceful exhalation?
What distinguishes the pulmonary circulation from the systemic circulation?
What distinguishes the pulmonary circulation from the systemic circulation?
What is the structural consequence if Type II alveolar cells are damaged?
What is the structural consequence if Type II alveolar cells are damaged?
How does surfactant reduce the work of breathing?
How does surfactant reduce the work of breathing?
What is the relationship between lung compliance and elastic recoil?
What is the relationship between lung compliance and elastic recoil?
Which of the following describes the route that blood takes through the pulmonary circulation?
Which of the following describes the route that blood takes through the pulmonary circulation?
In a healthy individual at rest, which of the following contributes the MOST to the work of breathing?
In a healthy individual at rest, which of the following contributes the MOST to the work of breathing?
A decrease in the caliber (diameter) of pulmonary artery lumina is caused by which process?
A decrease in the caliber (diameter) of pulmonary artery lumina is caused by which process?
Which of the following is the primary function of macrophages located in the alveoli?
Which of the following is the primary function of macrophages located in the alveoli?
If a patient's minute ventilation is 6 L/min and their respiratory rate is 12 breaths/min, what is the tidal volume?
If a patient's minute ventilation is 6 L/min and their respiratory rate is 12 breaths/min, what is the tidal volume?
Which of the following scenarios will most likely result in a DECREASE in lung compliance?
Which of the following scenarios will most likely result in a DECREASE in lung compliance?
Where does the pulmonary artery divide and enter the lungs?
Where does the pulmonary artery divide and enter the lungs?
Which structure connects the upper and lower airways?
Which structure connects the upper and lower airways?
Flashcards
Upper Airways
Upper Airways
The upper part of the respiratory tract, including the nasopharynx and oropharynx.
Larynx
Larynx
Connects the upper and lower airways, facilitating air passage.
Lower Airways
Lower Airways
Includes the trachea, bronchi, and terminal bronchioles.
Gas-Exchange Airways
Gas-Exchange Airways
Signup and view all the flashcards
Type I Alveolar Cells
Type I Alveolar Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Type II Alveolar Cells
Type II Alveolar Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Macrophages (in alveoli)
Macrophages (in alveoli)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Alveolocapillary Membrane
Alveolocapillary Membrane
Signup and view all the flashcards
Main cause of pulmonary artery constriction?
Main cause of pulmonary artery constriction?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chest Wall
Chest Wall
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pleura
Pleura
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pulmonary System Functions
Pulmonary System Functions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ventilation
Ventilation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Respiratory brain centers
Respiratory brain centers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Main muscles of inspiration
Main muscles of inspiration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Function of Surfactant
Function of Surfactant
Signup and view all the flashcards
Alveolar Diffusion
Alveolar Diffusion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Partial Pressure
Partial Pressure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ventilation-Perfusion Ratio
Ventilation-Perfusion Ratio
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oxyhemoglobin Dissociation Curve
Oxyhemoglobin Dissociation Curve
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gas Transport
Gas Transport
Signup and view all the flashcards
Larynx Function
Larynx Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Alveolar Macrophages Function
Alveolar Macrophages Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pulmonary Veins
Pulmonary Veins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pulmonary Circulation Control
Pulmonary Circulation Control
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acidemia Effect on Pulmonary Arteries
Acidemia Effect on Pulmonary Arteries
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pleural Space
Pleural Space
Signup and view all the flashcards
Minute Volume
Minute Volume
Signup and view all the flashcards
Irritant Receptors (Lungs)
Irritant Receptors (Lungs)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stretch Receptors (Lungs)
Stretch Receptors (Lungs)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Central Chemoreceptors
Central Chemoreceptors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Peripheral Chemoreceptors
Peripheral Chemoreceptors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Accessory muscles of inspiration.
Accessory muscles of inspiration.
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Structures of the Pulmonary System
- Pulmonary system handles respiration by directing air through conducting airways.
- Gas exchange occurs in specialized parts of the system.
Conducting Airways
- Features upper airways consisting of the nasopharynx, and the oropharynx.
- The larynx connects upper and lower airways.
- Lower airways are composed of the trachea, bronchi, and terminal bronchioles.
Gas-Exchange Airways
- Gas exchange takes place in the respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts, and alveoli.
- Epithelial cells are critical parts of alveoli.
- Type I alveolar cells maintain alveolar structure.
- Type II alveolar cells produce surfactant.
- Macrophages provide immune protection.
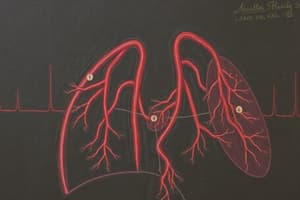
Pulmonary and Bronchial Circulation
- Lower pressure characterizes pulmonary circulation, than systemic circulation.
- Pulmonary vessels are filled with blood, about one-third at any given time.
- Pulmonary artery divides and enters the lung at the hilus.
- Each bronchus and bronchiole has an accompanying artery or arteriole.
- The alveolocapillary membrane features shared alveolar and capillary walls, where gas exchange is made available.
- Pulmonary veins work by draining capillaries.
- Pulmonary veins are dispersed randomly throughout the lung, and enters the left atrium at the hila.
Control of the Pulmonary Circulation
- Contraction of smooth muscle in the arterial walls reduces the calibre of pulmonary artery lumina.
- Contraction (vasoconstriction) and relaxation (vasodilation) are managed by local humoral conditions.
- Low alveolar PO2 is the primary cause of pulmonary artery constriction.
- Acidemia causes pulmonary artery constriction.
Chest Wall and Pleura
- The chest wall includes skin, ribs, and intercostal muscles.
- The chest wall defines the thoracic cavity.
- The pleura, a serous membrane, with parietal and visceral layers.
- The pleural layers are separated by the pleural space (cavity).
- Pleural fluid is contained in the pleural space.
Functions of the Pulmonary System
- The function of the respiratory system is to ventilate the alveoli.
- Gases are diffused into and out of the blood.
- Oxygen is circulated through the lungs so the body receives oxygen.
- Ventilation is the mechanical movement of gas or air into and out of the lungs.
- Minute volume is ventilatory rate multiplied by the volume of air per breath.
- Alveolar ventilation is an aspect of ventillation.
- Ventilation is under neurochemical control.
- The respiratory centre includes dorsal and ventral respiratory groups, with pneumotaxic as well as apneustic centres.
- Lung receptors include irritant, stretch, and J receptors.
- Chemoreceptors in the lung include central and peripheral chemoreceptors.
- Major muscles of ventillation: diaphragm and external intercostals for inspiration, expiration by abdominal muscles, and internal intercostal muscles.
- Surfactant affects alveolar surface tension and ventilation.
- Elastic recoil and compliance defines the elastic properties of the lung and chest wall.
- Work of breathing and airway resistance plays a role in breathing.
Gas Transport
- Gas transport consists of four steps: ventilating the lungs, diffusing oxygen from the alveoli to capillary blood, perfusing systemic capillaries with oxygenated blood, and diffusing oxygen from systemic capillaries into cells.
- Diffusion of CO2 follows the reverse path.
- Barometric pressure and the partial pressures of gas and water vapour come into play
- Gravity and alveolar pressure affects distribution of ventilation and perfusion.
- A ventilation-perfusion ratio of 0.8 is considered normal.
- Oxygen transport via alveolocapillary membrane.
- Arterial oxygenation depends on hemoglobin binding and oxygen saturation.
- Arterial oxygenation relies on oxyhemoglobin association and dissociation.
- Oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve and the Bohr effect become important.
- Carbon dioxide transports when it is dissolved in plasma
- Bicarbonate, and carbamino compounds are all factors.
- The Haldane effect also influences CO2 transport.
Aging and the Pulmonary System
- Chest wall compliance and elastic recoil of the lungs decreases with age.
- Results in reduced ventilatory reserve.
- Lower surface area for exchanging gas and capillary perfusion limits exercise capacity.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Related Documents
Description
An overview of the pulmonary system, including conducting and gas-exchange airways. It also covers pulmonary circulation, which operates at a lower pressure than systemic circulation. Epithelial cells within alveoliType I and Type II alveolar cells are also discussed.