Podcast
Questions and Answers
What virtue is associated with the resolution of trust vs. mistrust in infancy?
What virtue is associated with the resolution of trust vs. mistrust in infancy?
- Competence
- Hope (correct)
- Purpose
- Will
In early childhood, the primary psychosocial conflict is between autonomy and shame.
In early childhood, the primary psychosocial conflict is between autonomy and shame.
True (A)
What is the significant relationship that develops during the play age?
What is the significant relationship that develops during the play age?
Family
The conflict during school age is _________ vs. inferiority.
The conflict during school age is _________ vs. inferiority.
Match the age groups with their corresponding psychosocial conflicts:
Match the age groups with their corresponding psychosocial conflicts:
Which of the following terms refers to a self-centered desire based entirely on sexual gratification?
Which of the following terms refers to a self-centered desire based entirely on sexual gratification?
Euphoria is characterized by a complete absence of anxiety and other tensions.
Euphoria is characterized by a complete absence of anxiety and other tensions.
What are the three 'me' personifications acquired during infancy according to Sullivan?
What are the three 'me' personifications acquired during infancy according to Sullivan?
Sullivan referred to his developmental stages as __________.
Sullivan referred to his developmental stages as __________.
Match the levels of cognition with their descriptions:
Match the levels of cognition with their descriptions:
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
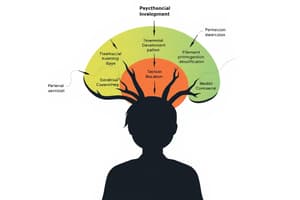
Psychosocial Development of Personality
- Infancy (Birth - 1 year): Conflict is Trust vs. Mistrust; resolution leads to Hope. Maternal care fosters a sense of security and aids motor development.
- Early Childhood (2-3 years): Conflict is Autonomy vs. Shame and Doubt; resolution leads to Will. Children learn to assert independence and navigate toilet training.
- Play Age (4-5 years): Conflict is Initiative vs. Guilt; resolution results in Purpose. Language and imagination flourish as children engage with family.
- School Age (6-11 years): Conflict is Industry vs. Inferiority; resolution produces Competence. Children gain skills through formal and informal education and learn the value of completing tasks.
- Adolescence: Conflict is Identity vs. Role Confusion. Teens navigate personal identity, with anxiety serving as a disruptive force in relationships.
Key Terms from Sullivan's Theory
- Dynamisms: Standard behavior patterns shaped by tensions and social interactions.
- Intimacy, Lust, Malevolence, Self-system: Categories describing interpersonal relationships and self-protection mechanisms.
- Personifications: Subjective perceptions formed during development, influencing self-image and views of others.
Cognitive Levels
- Prototaxic Level: Irreproducible experiences that are non-verbal.
- Parataxic Level: Prelogical, difficult-to-communicate experiences.
- Syntaxic Level: Experiences that can be accurately expressed.
Stages of Development
- Sullivan identified "epochs" based on social environments rather than chronological age, impacting personality and interpersonal relations.
Object Relations Theory (Melanie Klein)
- Paranoid-Schizoid and Depressive Positions: Two developmental stages reflecting infants' perceptions of their caregivers.
- Psychic Life of the Infant: Infants have an inherent drive to mitigate anxiety from conflicting instincts.
Psychic Defense Mechanisms
- Introjection: Process of internalizing external objects’ images for self-identity.
Cattell's Factor Analysis
- Streamlined Allport's personality traits from over 4,200 to 171, using questionnaires to assess personality traits through factor analysis.
Sixteen Personality Factors Identified by Cattell
- Traits like Abstractedness, Emotional stability, and Self-reliance highlight diverse personality dimensions.
Eysenck's Biological Typology
- Proposed a personality model based on three universal traits: Introversion vs. Extraversion, Neuroticism vs. Emotional stability, and Psychoticism.
Tip for Exam Preparation
- Before: Cram early, understand personal study techniques, maintain a healthy lifestyle, and prepare thoroughly.
- During: Stay focused, read carefully, and manage time effectively.
- After: Reflect, relax, and celebrate achievements.
Understanding Anxiety and Human Behavior
- Recognize how anxiety impacts interpersonal relationships as well as the role of past experiences in shaping present behaviors.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.