Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the significance of the Northern Plains in India?
What is the significance of the Northern Plains in India?
- It serves as a major agricultural region due to its fertile soil. (correct)
- It contains mountainous terrain and is rich in minerals.
- It is primarily known for its deserts and arid conditions.
- It is a key area for mining activities.
Which part of India is known for its flat-topped hills and mining resources?
Which part of India is known for its flat-topped hills and mining resources?
- Northern Plains
- Himalayas
- Peninsular Plateau (correct)
- Coastal Plains
What are the major river systems of India primarily known for?
What are the major river systems of India primarily known for?
- Creating extensive desert landscapes.
- Their contribution to tropical biodiversity.
- Providing minerals and resources for industry.
- Their role in supporting transportation and cultural significance. (correct)
Which desert located in northwest India is characterized by an arid climate and supports nomadic cultures?
Which desert located in northwest India is characterized by an arid climate and supports nomadic cultures?
The Himalayan mountain range is notable for which of the following features?
The Himalayan mountain range is notable for which of the following features?
Which coastal region in India is influenced by the Arabian Sea?
Which coastal region in India is influenced by the Arabian Sea?
The Andaman and Nicobar Islands are known for their:
The Andaman and Nicobar Islands are known for their:
Which type of soil is known to support a wide variety of agricultural activities in India?
Which type of soil is known to support a wide variety of agricultural activities in India?
Which of the following features is most characteristic of the coastal plains of India?
Which of the following features is most characteristic of the coastal plains of India?
The Deccan Plateau is primarily located in which part of India?
The Deccan Plateau is primarily located in which part of India?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
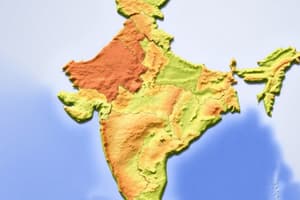
Physical Geography of India: Landforms
-
Himalayas
- Youngest mountain range in the world.
- Stretches across northern India, forming a natural border with Nepal and Bhutan.
- Contains some of the highest peaks, including Kanchenjunga and Nanga Parbat.
- Major rivers, such as the Ganges and Indus, originate here.
-
Northern Plains
- Extensive flat region south of the Himalayas.
- Formed by the alluvial deposits from the Ganges, Brahmaputra, and Indus rivers.
- Divided into three parts: Punjab Plain, Ganges Plain, and Brahmaputra Plain.
- Fertile area, crucial for agriculture.
-
Peninsular Plateau
- Elevated region located in southern India, known for its flat-topped hills (tablelands).
- Divided into two parts: Deccan Plateau (south) and Malwa Plateau (north).
- Rich in minerals and resources, supporting mining activities.
-
Coastal Plains
- Narrow strips of land along the eastern and western coasts.
- Western Coastal Plain: features the Konkan and Malabar coasts, influenced by the Arabian Sea.
- Eastern Coastal Plain: broader and includes the Coromandel Coast, influenced by the Bay of Bengal.
- Important for fisheries and agriculture.
-
Deserts
- Thar Desert: located in the northwest, predominantly in Rajasthan.
- Characterized by arid climate, sandy terrain, and sparse vegetation.
- Supports unique wildlife and nomadic cultures.
-
Island Regions
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands: located in the Bay of Bengal, known for biodiversity and tropical climate.
- Lakshadweep Islands: located in the Arabian Sea, characterized by coral atolls and rich marine life.
-
Major River Systems
- Ganges, Yamuna, Brahmaputra: vital for irrigation, transport, and cultural significance.
- Godavari, Krishna, and Kaveri: major rivers in peninsular India, supporting agricultural activities.
-
Soil Types
- Diverse soil types including alluvial, black (regur), red, and laterite soils, each supporting different types of agriculture.
-
Geological Features
- Significant rock formations include granite, basalt, and sedimentary rocks, influencing the region's geological stability and mineral resources.
Himalayas
- Youngest mountain range globally, primarily spanning northern India.
- Forms a natural border with Nepal and Bhutan, housing some of the highest peaks like Kanchenjunga and Nanga Parbat.
- Source of major rivers such as the Ganges and Indus.
Northern Plains
- Expansive flat region located south of the Himalayas, created by alluvial deposits from the Ganges, Brahmaputra, and Indus rivers.
- Divided into three distinct parts: Punjab Plain, Ganges Plain, and Brahmaputra Plain.
- Highly fertile land, vital for India's agricultural production.
Peninsular Plateau
- Elevated region in southern India, known for its distinctive flat-topped hills or tablelands.
- Comprises two main areas: Deccan Plateau in the south and Malwa Plateau in the north.
- Rich in minerals and resources, significantly contributing to mining industries.
Coastal Plains
- Narrow coastal strips along India’s eastern and western seaboards.
- Western Coastal Plain includes the Konkan and Malabar coasts, influenced by the Arabian Sea.
- Eastern Coastal Plain is broader, featuring the Coromandel Coast, shaped by the Bay of Bengal.
- Crucial for fisheries and agricultural practices.
Deserts
- Thar Desert is located in the northwest region, mainly in Rajasthan.
- Characterized by an arid climate with sandy landscapes and limited vegetation.
- Hosts unique wildlife and nomadic cultures.
Island Regions
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands are situated in the Bay of Bengal, noted for rich biodiversity and a tropical climate.
- Lakshadweep Islands in the Arabian Sea are composed of coral atolls, renowned for abundant marine life.
Major River Systems
- The Ganges, Yamuna, and Brahmaputra rivers are essential for irrigation, transportation, and have significant cultural importance.
- Other critical rivers in peninsular India include Godavari, Krishna, and Kaveri, all supporting agricultural activities.
Soil Types
- India features diverse soil types: alluvial, black (regur), red, and laterite, each supporting various agricultural practices.
Geological Features
- The region's geological stability and mineral wealth are influenced by significant rock formations like granite, basalt, and sedimentary rocks.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.