Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is a key aspect of hair grooming in a healthcare setting?
What is a key aspect of hair grooming in a healthcare setting?
Avoiding open hair styles
Why is it important to keep nails clean and short in a healthcare setting?
Why is it important to keep nails clean and short in a healthcare setting?
To prevent long nails from busting gloves and causing accidents during venipuncture
What is the primary purpose of hand washing in a healthcare setting?
What is the primary purpose of hand washing in a healthcare setting?
To prevent the spread of infection
What is the definition of infection?
What is the definition of infection?
What is the term for microorganisms that are capable of causing disease?
What is the term for microorganisms that are capable of causing disease?
What is the first step to take in case of a needlestick injury?
What is the first step to take in case of a needlestick injury?
What is the primary purpose of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) for a Phlebotomist?
What is the primary purpose of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) for a Phlebotomist?
When should a Phlebotomist wear gloves?
When should a Phlebotomist wear gloves?
How should a Phlebotomist remove gloves after use?
How should a Phlebotomist remove gloves after use?
What is the purpose of a lab coat in Phlebotomy?
What is the purpose of a lab coat in Phlebotomy?
Why should a Phlebotomist wear goggles and a mask?
Why should a Phlebotomist wear goggles and a mask?
Why is it important to wear whole shoes in Phlebotomy?
Why is it important to wear whole shoes in Phlebotomy?
Why should a Phlebotomist avoid wearing certain accessories?
Why should a Phlebotomist avoid wearing certain accessories?
What should a Phlebotomist do after removing gloves?
What should a Phlebotomist do after removing gloves?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Phlebotomy Safety Standards and Procedures
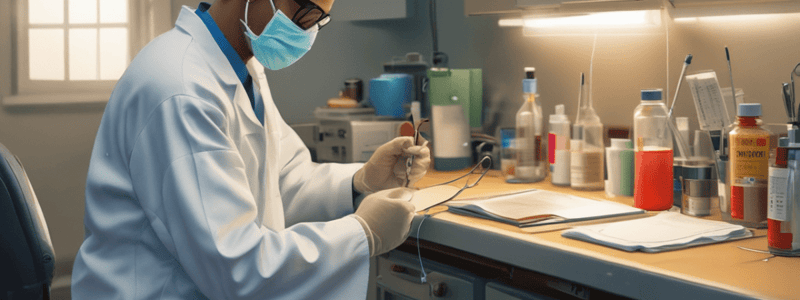
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) protects phlebotomists from contact with blood or other infectious materials.
PPE for Phlebotomist
- Gloves:
- Must be worn at all times when handling blood or other body fluids
- Must be worn when handling contaminated items
- Must be worn when touching non-intact skin or mucous membranes
- Change gloves between each patient
- Don't reuse gloves
- Removal of Gloves:
- Remove gloves in a safe aseptic manner
- Pinch one glove below the wrist and pull it off inside out
- Peel away from the body
- Hold inside out gloves with the other hand
- Slip a finger under the second glove and pull off by touching only the inner surface
- Dispose of gloves in a biohazard bin
- Wash hands
- Lab Coats:
- Protect against accidental spills
- Long sleeves recommended for further protection
- Clean lab coats look professional
- Prevent cross-contamination
- Don't wear lab coats when not on duty
- Goggles and Masks:
- Masks protect against droplets from coughing or sneezing
- Goggles protect the eyes from splashes or sprays of body fluids
- Shoes:
- Wear whole shoes to protect feet from spills
- Wear comfortable and supportive shoes
- Accessories:
- Avoid wearing hanging earrings
- Avoid bangles and bracelets on hands
- Avoid neck chains
- Avoid bulging rings
- Hair:
- Hair should be well-groomed
- Avoid open hair styles
- Nails:
- Nails should be well-groomed
- Clean and neat
- Long nails can bust gloves and cause accidents during venipuncture
Hand Washing
- Wash hands to prevent the spread of infection
- Wash hands before and after each patient
- Hand washing technique:
- Stand back from sink
- Wet hands and apply soap
- Scrub all surfaces, including between fingers and around knuckles
- Rinse hands in downward motion from wrist to fingertips
- Use a clean paper towel to turn off tap
- Dry hands with another paper towel
Infection
- Infection occurs when a microorganism invades the body, multiplies, and causes injury or disease
- Microbes include bacteria, fungi, protozoa, and viruses
- Microbes that cause disease are called pathogens
- Some pathogenic microbes cause communicable infections
Chain of Infection and Bloodborne Pathogens
- Bloodborne pathogens are microorganisms carried in the blood that can cause disease in people
- Examples of bloodborne pathogens include HIV, Hepatitis B, and Hepatitis C
Needlestick
- Steps to take in case of a needlestick:
- Report to supervisor immediately
- Virology testing performed for baseline values
- Antiviral drugs/medications given for safety
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.