Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the peripheral nervous system?
What is the primary function of the peripheral nervous system?
Which spinal nerves form the brachial plexus?
Which spinal nerves form the brachial plexus?
What structures arise directly from the roots of the brachial plexus?
What structures arise directly from the roots of the brachial plexus?
How many cords are formed in the brachial plexus?
How many cords are formed in the brachial plexus?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following nerves exclusively innervates the diaphragm?
Which of the following nerves exclusively innervates the diaphragm?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the correct mnemonic to remember the branches of the brachial plexus?
What is the correct mnemonic to remember the branches of the brachial plexus?
Signup and view all the answers
Which group of spinal nerves is categorized under the lumbosacral plexus?
Which group of spinal nerves is categorized under the lumbosacral plexus?
Signup and view all the answers
Which component of the brachial plexus does NOT exist?
Which component of the brachial plexus does NOT exist?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary role of anterior rami in spinal nerves?
What is the primary role of anterior rami in spinal nerves?
Signup and view all the answers
Which branch of the brachial plexus is responsible for innervating the muscles of the upper limb?
Which branch of the brachial plexus is responsible for innervating the muscles of the upper limb?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary function of the nerves arising from the anterior divisions of the brachial plexus?
What is the primary function of the nerves arising from the anterior divisions of the brachial plexus?
Signup and view all the answers
Which nerve is responsible for innervating the Pectoralis Major from the lateral cord?
Which nerve is responsible for innervating the Pectoralis Major from the lateral cord?
Signup and view all the answers
Which muscle is NOT innervated by the Radial nerve?
Which muscle is NOT innervated by the Radial nerve?
Signup and view all the answers
What are the three cords of the brachial plexus named after?
What are the three cords of the brachial plexus named after?
Signup and view all the answers
Which trunk of the brachial plexus contributes to the Innervation of the Supraspinatus and Infraspinatus?
Which trunk of the brachial plexus contributes to the Innervation of the Supraspinatus and Infraspinatus?
Signup and view all the answers
Which nerve innervates the Teres Major muscle?
Which nerve innervates the Teres Major muscle?
Signup and view all the answers
What happens to the trunks of the brachial plexus just distal to the clavicle?
What happens to the trunks of the brachial plexus just distal to the clavicle?
Signup and view all the answers
Which nerve arises from the posterior cord and innervates the Latissimus Dorsi?
Which nerve arises from the posterior cord and innervates the Latissimus Dorsi?
Signup and view all the answers
Which two nerves arise from the medial cord and their main targets?
Which two nerves arise from the medial cord and their main targets?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the origin of the C8 and T1 roots in the brachial plexus?
What is the origin of the C8 and T1 roots in the brachial plexus?
Signup and view all the answers
Study Notes
Peripheral Nervous System Overview
- Composed of nervous tissue outside the vertebral canal and brainstem.
- Connects the body to the central nervous system (CNS).
- Includes cranial nerves and spinal nerves.
Spinal Nerve Components
- Spinal nerves include 8 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral, and 1 coccygeal nerve.
Plexus Formation
- Anterior rami of spinal nerves other than thoracic join to form plexuses.
- Three major plexuses:
- Cervical Plexus (C1-C4): Primarily innervates neck muscles.
- Brachial Plexus (C5-T1): Supplies muscles of the upper limb.
- Lumbosacral Plexus (L1-S5): Supplies muscles of the lower limb.
- Thoracic nerves remain as intercostal nerves.
Cervical Plexus Details
- Formed from C1-C4 spinal nerves.
- Key branches include:
- C2: Sternocleidomastoid.
- C3 & C4: Trapezius.
- C3-C5: Levator Scapulae.
- C4: Anterior Scalene.
- C3-C4: Middle Scalene.
- C3-C5: Phrenic nerve for diaphragm innervation.
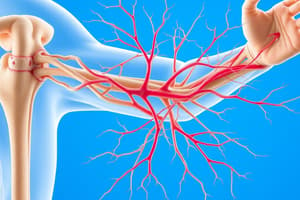
Brachial Plexus Structure
- Formed by the anterior rami of C5-T1 spinal nerves.
- Composed of:
- 5 Roots.
- 3 Trunks: Superior (C5-6), Middle (C7), Inferior (C8-T1).
- 6 Divisions: Anterior and posterior.
- 3 Cords: Lateral, posterior, medial.
- 5 Terminal branches: Musculocutaneous, axillary, radial, median, ulnar.
- Mnemonic for branches: "Read The Darn Cadaver Book."
Brachial Plexus Pathway
- Located between the anterior and middle scalene muscles alongside the subclavian artery and vein.
- Roots: C5-6, C7, C8-T1.
- Nerves emerging from roots:
- Dorsal scapular nerve (C5): Innervates rhomboids and levator scapulae.
- Long thoracic nerve (C5, C6, C7): Innervates serratus anterior.
Trunks and Their Nerves
- Trunks formed from roots:
- Superior (C5-C6): Suprascapular nerve (innervates supraspinatus, infraspinatus), subclavius nerve (innervates subclavius).
- Middle (C7): No specific branches detailed.
- Inferior (C8-T1): No specific branches detailed.
Divisions and Their Functions
- Trunks divide into anterior and posterior divisions just distal to the clavicle.
- Anterior divisions supply flexor (anterior compartment) muscles.
- Posterior division supplies extensor (posterior compartment) muscles.
- No specific nerves emerge from divisions.
Cords and Associated Nerves
- Named based on their position relative to the axillary artery.
- Lateral cord:
- Lateral pectoral nerve (innervates pectoralis major).
- Medial cord:
- Medial pectoral nerve (innervates pectoralis major and minor).
- Posterior cord:
- Upper subscapular nerve (innervates subscapularis).
- Thoracodorsal nerve (innervates latissimus dorsi).
- Lower subscapular nerve (innervates subscapularis and teres major).
Terminal Branches
- Musculocutaneous, axillary, median, radial, ulnar nerves emerge from the cords.
Nerve Innervations
- Axillary nerve: Innervates deltoid, teres minor, long head of triceps.
- Musculocutaneous nerve: Innervates biceps brachii, brachialis, coracobrachialis.
- Radial nerve: Innervates triceps, anconeus, brachioradialis.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
This quiz covers the peripheral nervous system, specifically focusing on the brachial plexus. It examines the structure and function of cranial and spinal nerves, including their role in connecting the body to the central nervous system. Perfect for students in OT 505, the quiz will help reinforce key concepts related to nerve formation and organization.