Podcast
Questions and Answers
What percentage of circulating blood volume is held by the liver?
What percentage of circulating blood volume is held by the liver?
- 10%
- 20%
- 15% (correct)
- 25%
What is the primary function of the portal vein in the Hepatic Portal Vein System?
What is the primary function of the portal vein in the Hepatic Portal Vein System?
- Carries oxygenated blood from the heart to the liver
- Carries deoxygenated blood from the liver to the heart
- Carries nutrients from food broken down back to the liver (correct)
- Carries waste products from the liver to the kidneys
What is the byproduct of RBC breakdown or hemolysis that causes Jaundice?
What is the byproduct of RBC breakdown or hemolysis that causes Jaundice?
- Ammonia
- Urea
- Bilirubin (correct)
- Bile
What process is used to metabolize substances like alcohol and Tylenol in the liver?
What process is used to metabolize substances like alcohol and Tylenol in the liver?
What is the function of the liver in regulating blood glucose levels?
What is the function of the liver in regulating blood glucose levels?
What is the primary function of the stomach in the digestive process?
What is the primary function of the stomach in the digestive process?
Which structure is responsible for propelling food from the esophagus into the stomach?
Which structure is responsible for propelling food from the esophagus into the stomach?
What is the name of the reflex that occurs when the body tries to expel stomach contents?
What is the name of the reflex that occurs when the body tries to expel stomach contents?
What is the medical term for difficulty swallowing?
What is the medical term for difficulty swallowing?
Which of the following is NOT a part of the upper GI tract?
Which of the following is NOT a part of the upper GI tract?
What is the treatment regimen for a patient suffering from a food bolus obstruction?
What is the treatment regimen for a patient suffering from a food bolus obstruction?
What is the primary cause of inflammation of tissue at the lower end of the esophagus in reflux esophagitis?
What is the primary cause of inflammation of tissue at the lower end of the esophagus in reflux esophagitis?
Which of the following is a common symptom of hiatal hernia?
Which of the following is a common symptom of hiatal hernia?
What is the term for the backward flow of stomach contents into the esophagus?
What is the term for the backward flow of stomach contents into the esophagus?
What is the primary cause of esophageal varices?
What is the primary cause of esophageal varices?
What is the treatment for esophageal varices?
What is the treatment for esophageal varices?
What is the term for the inflammation of the tonsils?
What is the term for the inflammation of the tonsils?
What is the primary reason for liver failure when both alcohol and Tylenol are present in the body?
What is the primary reason for liver failure when both alcohol and Tylenol are present in the body?
Which of the following pancreatic enzymes is responsible for breaking down carbohydrates?
Which of the following pancreatic enzymes is responsible for breaking down carbohydrates?
What is the primary function of the hormone somatostatin?
What is the primary function of the hormone somatostatin?
What is the purpose of octreotide in the treatment of upper GI bleeds?
What is the purpose of octreotide in the treatment of upper GI bleeds?
What is the primary function of the gallbladder in digestion?
What is the primary function of the gallbladder in digestion?
What triggers dumping syndrome?
What triggers dumping syndrome?
What is the consequence of rapid gastric emptying?
What is the consequence of rapid gastric emptying?
Which of the following is NOT a space within the abdominal cavity?
Which of the following is NOT a space within the abdominal cavity?
What is the most common cause of peritonitis?
What is the most common cause of peritonitis?
What is the laboratory finding that may indicate peritonitis?
What is the laboratory finding that may indicate peritonitis?
What is the complication of untreated peritonitis?
What is the complication of untreated peritonitis?
What is the consequence of sugar moving from the stomach into the small bowel too quickly?
What is the consequence of sugar moving from the stomach into the small bowel too quickly?
Which of the following organs is NOT located in the peritoneal space?
Which of the following organs is NOT located in the peritoneal space?
What is the most common cause of inflammation of the peritoneum?
What is the most common cause of inflammation of the peritoneum?
What is the laboratory finding that may indicate peritonitis?
What is the laboratory finding that may indicate peritonitis?
What is the potential complication of untreated peritonitis?
What is the potential complication of untreated peritonitis?
What is the primary function of the pancreas in the digestive process?
What is the primary function of the pancreas in the digestive process?
What is the effect of octreotide on the body?
What is the effect of octreotide on the body?
What is the composition of bile?
What is the composition of bile?
What is the cause of newborn jaundice?
What is the cause of newborn jaundice?
What is the consequence of the liver not being able to break down both alcohol and Tylenol?
What is the consequence of the liver not being able to break down both alcohol and Tylenol?
What triggers the dumping syndrome?
What triggers the dumping syndrome?
What is the primary cause of inflammation of tissue at the lower end of the esophagus in reflux esophagitis?
What is the primary cause of inflammation of tissue at the lower end of the esophagus in reflux esophagitis?
What is the term for the inflammation of the tonsils?
What is the term for the inflammation of the tonsils?
What is the primary symptom of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)?
What is the primary symptom of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)?
What is the term for the enlargement of veins in the esophagus due to high pressure?
What is the term for the enlargement of veins in the esophagus due to high pressure?
What is the common symptom of hiatal hernia?
What is the common symptom of hiatal hernia?
What is the treatment for esophageal varices?
What is the treatment for esophageal varices?
What is the primary function of the liver in regulating blood glucose levels?
What is the primary function of the liver in regulating blood glucose levels?
What is the purpose of bilirubin production in the liver?
What is the purpose of bilirubin production in the liver?
What is the process used by the liver to metabolize substances like alcohol and Tylenol?
What is the process used by the liver to metabolize substances like alcohol and Tylenol?
What percentage of circulating blood volume is held by the liver?
What percentage of circulating blood volume is held by the liver?
What is the function of the liver in relation to ammonia?
What is the function of the liver in relation to ammonia?
Which part of the gastrointestinal system is responsible for the breakdown of food in an acid-rich environment?
Which part of the gastrointestinal system is responsible for the breakdown of food in an acid-rich environment?
What is the primary function of the gastroesophageal sphincter?
What is the primary function of the gastroesophageal sphincter?
What is the term for the muscular contractions that propel food through the esophagus and into the stomach?
What is the term for the muscular contractions that propel food through the esophagus and into the stomach?
Which of the following structures is NOT part of the upper GI tract?
Which of the following structures is NOT part of the upper GI tract?
What is the primary function of the hormone glucagon in the treatment of food bolus obstruction?
What is the primary function of the hormone glucagon in the treatment of food bolus obstruction?
What is the term for the condition characterized by difficulty swallowing?
What is the term for the condition characterized by difficulty swallowing?
What is the main complication of an inguinal hernia?
What is the main complication of an inguinal hernia?
What is the likely cause of ulcerative colitis?
What is the likely cause of ulcerative colitis?
What is the primary symptom of gastroenteritis?
What is the primary symptom of gastroenteritis?
What is the name of the inflammation of the vermiform appendix?
What is the name of the inflammation of the vermiform appendix?
What is the term for the twisting of the colon?
What is the term for the twisting of the colon?
What is the primary risk associated with ulcerative colitis?
What is the primary risk associated with ulcerative colitis?
What is the characteristic of stools in lower GI bleeding?
What is the characteristic of stools in lower GI bleeding?
What is the primary symptom of hepatitis?
What is the primary symptom of hepatitis?
What is the term for the enlargement of the liver in hepatitis?
What is the term for the enlargement of the liver in hepatitis?
What is the treatment for hemorrhoids?
What is the treatment for hemorrhoids?
What is the characteristic of upper GI bleeding?
What is the characteristic of upper GI bleeding?
What is the emergency condition that may be associated with GI bleeding?
What is the emergency condition that may be associated with GI bleeding?
What is the complication of cirrhosis that results in a decreased platelet production?
What is the complication of cirrhosis that results in a decreased platelet production?
Which of the following conditions is associated with an elevated risk of bleeding and hemorrhaging?
Which of the following conditions is associated with an elevated risk of bleeding and hemorrhaging?
What is the term for the fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity, a complication of cirrhosis?
What is the term for the fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity, a complication of cirrhosis?
What is the effect of an enlarged spleen on platelet production in cirrhosis?
What is the effect of an enlarged spleen on platelet production in cirrhosis?
What is the term for the condition characterized by the backward flow of stomach contents into the esophagus?
What is the term for the condition characterized by the backward flow of stomach contents into the esophagus?
Which of the following cancers is associated with thrombocytopenia?
Which of the following cancers is associated with thrombocytopenia?
Which type of hepatitis is spread through fecal-oral route and does not lead to chronic hepatitis?
Which type of hepatitis is spread through fecal-oral route and does not lead to chronic hepatitis?
What is the result of abnormal scar tissue altering blood flow through the liver in cirrhosis?
What is the result of abnormal scar tissue altering blood flow through the liver in cirrhosis?
Which type of hepatitis requires the presence of Hep B to replicate?
Which type of hepatitis requires the presence of Hep B to replicate?
What is the common cause of inflammation of the liver in cirrhosis?
What is the common cause of inflammation of the liver in cirrhosis?
Which type of hepatitis is more likely to become chronic hepatitis than Hep B?
Which type of hepatitis is more likely to become chronic hepatitis than Hep B?
What is the result of blood backing up in the hepatic portal vein in cirrhosis?
What is the result of blood backing up in the hepatic portal vein in cirrhosis?
What is the primary cause of dysentery?
What is the primary cause of dysentery?
What is the main characteristic of irritable bowel syndrome?
What is the main characteristic of irritable bowel syndrome?
What is the primary complication of untreated diverticulitis?
What is the primary complication of untreated diverticulitis?
What is the main difference between irritable bowel syndrome and inflammatory bowel disease?
What is the main difference between irritable bowel syndrome and inflammatory bowel disease?
What is the primary treatment for diverticulitis?
What is the primary treatment for diverticulitis?
What is the common symptom of diverticulitis?
What is the common symptom of diverticulitis?
What is the primary cause of peptic ulcer formation?
What is the primary cause of peptic ulcer formation?
What is the primary complication of inguinal hernia?
What is the primary complication of inguinal hernia?
What is the characteristic of stools in peptic ulcer disease?
What is the characteristic of stools in peptic ulcer disease?
What is the probable cause of ulcerative colitis?
What is the probable cause of ulcerative colitis?
What is the primary complication of pyloric stenosis in infants?
What is the primary complication of pyloric stenosis in infants?
What is the role of the small intestine in digestion?
What is the role of the small intestine in digestion?
What is the term for the absence of peristalsis in the intestine?
What is the term for the absence of peristalsis in the intestine?
What is the primary risk associated with ulcerative colitis?
What is the primary risk associated with ulcerative colitis?
What is the primary symptom of Crohn's disease?
What is the primary symptom of Crohn's disease?
What is the treatment for peptic ulcer disease?
What is the treatment for peptic ulcer disease?
What is the term for the inflammation of the vermiform appendix?
What is the term for the inflammation of the vermiform appendix?
What is the primary treatment for gastroenteritis?
What is the primary treatment for gastroenteritis?
What is the primary characteristic of dysentery?
What is the primary characteristic of dysentery?
Which of the following is a risk factor for diverticulitis?
Which of the following is a risk factor for diverticulitis?
What is the primary treatment for irritable bowel syndrome?
What is the primary treatment for irritable bowel syndrome?
What is the primary complication of untreated diverticulitis?
What is the primary complication of untreated diverticulitis?
Which of the following can trigger symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome?
Which of the following can trigger symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome?
What is the primary cause of inflammation of the liver in hepatitis?
What is the primary cause of inflammation of the liver in hepatitis?
What is the characteristic of stools in lower GI bleeding?
What is the characteristic of stools in lower GI bleeding?
What is the primary difference between irritable bowel syndrome and dysentery?
What is the primary difference between irritable bowel syndrome and dysentery?
What is the treatment for hemorrhoids?
What is the treatment for hemorrhoids?
What is the emergency condition associated with GI bleeding?
What is the emergency condition associated with GI bleeding?
What is the characteristic of upper GI bleeding?
What is the characteristic of upper GI bleeding?
What is the consequence of liver failure in hepatitis?
What is the consequence of liver failure in hepatitis?
What is the primary mode of transmission of Hepatitis A?
What is the primary mode of transmission of Hepatitis A?
What is the characteristic of the liver tissue in cirrhosis?
What is the characteristic of the liver tissue in cirrhosis?
Which of the following hepatitis types is more likely to become chronic hepatitis?
Which of the following hepatitis types is more likely to become chronic hepatitis?
What is the consequence of blood backing up in the hepatic portal vein in cirrhosis?
What is the consequence of blood backing up in the hepatic portal vein in cirrhosis?
What is the primary complication of cirrhosis?
What is the primary complication of cirrhosis?
What is the unique characteristic of Hepatitis D?
What is the unique characteristic of Hepatitis D?
What is the primary purpose of a PEJ tube?
What is the primary purpose of a PEJ tube?
Which type of colostomy is performed on the right side of the abdomen?
Which type of colostomy is performed on the right side of the abdomen?
What is the primary advantage of a nasogastric tube over a PEJ tube?
What is the primary advantage of a nasogastric tube over a PEJ tube?
What is the term for the opening created in the abdomen during a colostomy procedure?
What is the term for the opening created in the abdomen during a colostomy procedure?
In which part of the intestine is a PEJ tube typically placed?
In which part of the intestine is a PEJ tube typically placed?
What is the primary characteristic of the discharge from a colostomy stoma?
What is the primary characteristic of the discharge from a colostomy stoma?
What is the primary cause of severe abdominal pain that often radiates to the back in pancreatitis?
What is the primary cause of severe abdominal pain that often radiates to the back in pancreatitis?
Which of the following organs is classified as a solid organ and has a rich blood supply?
Which of the following organs is classified as a solid organ and has a rich blood supply?
What is the term for the presence of gallstones in the gallbladder or bile ducts?
What is the term for the presence of gallstones in the gallbladder or bile ducts?
What is the characteristic of the five F’s that are associated with an increased risk of developing cholelithiasis?
What is the characteristic of the five F’s that are associated with an increased risk of developing cholelithiasis?
What is the treatment for pancreatitis?
What is the treatment for pancreatitis?
What is the difference between solid and hollow organs?
What is the difference between solid and hollow organs?
Where is a transverse colostomy typically performed?
Where is a transverse colostomy typically performed?
What is the consistency of stool in a sigmoid colostomy?
What is the consistency of stool in a sigmoid colostomy?
In which type of colostomy is the stool usually liquid to semiformed in consistency?
In which type of colostomy is the stool usually liquid to semiformed in consistency?
Where is a descending colostomy typically performed?
Where is a descending colostomy typically performed?
What is the main reason for the difference in stool consistency between the different types of colostomy?
What is the main reason for the difference in stool consistency between the different types of colostomy?
What type of pain is caused by a disease process located in one area but perceived in another area?
What type of pain is caused by a disease process located in one area but perceived in another area?
What is the term for the bright red blood in feces?
What is the term for the bright red blood in feces?
What is the term for the procedure of placing a long G-tube through the abdominal wall?
What is the term for the procedure of placing a long G-tube through the abdominal wall?
What is the term for the yellowish discoloration of the skin and eyes?
What is the term for the yellowish discoloration of the skin and eyes?
What is the term for the inflammation of the peritoneum, often caused by perforation of the stomach or intestines?
What is the term for the inflammation of the peritoneum, often caused by perforation of the stomach or intestines?
What is the term for the urge to defecate and having a bowel movement?
What is the term for the urge to defecate and having a bowel movement?
Study Notes
Nasogastric (NG) Tube Feeding
- A nasogastric (NG) tube enters through the nose and ends in the stomach
- Not suitable for patients with swallowing problems or needing long-term tube feeding
Percutaneous Endoscopic Jejunostomy (PEJ) Tube
- Feeding tube inserted into the small intestine (jejunum) instead of the stomach
- Used for patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
Colostomy
- Creation of an opening in the abdomen (ostomy) and pulling a portion of the large intestine (colon) through the opening
- Stool passes directly out of the body, bypassing the diseased or damaged section of the colon
- Four main types: ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid
Diseases of the Gallbladder
- Cholecystitis: inflammation of the gallbladder, caused by gallstones
- Seen often in pregnant females
- Pain after eating greasy or fatty meals
- Cholelithiasis: presence of gallstones in the gallbladder or bile ducts
- Five F's: fair complexion, fat, fertile or has had children, forty years of age or older
Diseases of the Pancreas
- Pancreatitis: inflammation of the pancreas
- Can cause autodigestion of the pancreas and surrounding organs
- Severe abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, diaphoresis, and tachycardia
- High blood amylase levels indicative of pancreatitis
- Treatment: NPO, pain management, and fluids
Solid vs. Hollow Organs
- Solid organs: liver, spleen, pancreas, kidneys
- Have a rich blood supply, can hemorrhage when lacerated
- Hollow organs: digestive tract, urinary bladder, female reproductive organs
- Have a thin wall and a lumen, can generally withstand blunt trauma
Feeding Tubes
- PEG (Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy): long G-tube placed by endoscopy
- Term PEG often used to describe all G-tubes
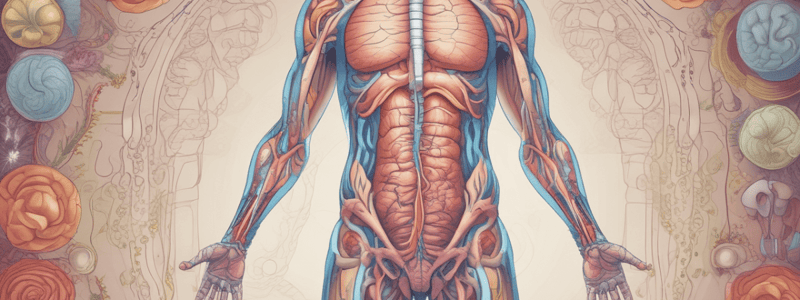
Hepatic Portal Vein System
- Includes stomach, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, and intestines
- Portal vein carries nutrients from food broken down back to the liver
- Liver: holds 15% of circulating blood volume, balances glucose levels, and aids in blood clotting and bile production
Diseases of the Throat and Esophagus
- Pharyngitis: viral or bacterial infection of the throat
- Reflux Esophagitis: inflammation of tissue at the lower end of the esophagus
- Hiatal Hernia: sliding of part of the stomach into the chest cavity
- Esophageal Varices: high pressure in veins of the esophagus, can rupture and cause a life-threatening event
Abdominal Cavity
- Divided into three spaces: peritoneal, retroperitoneal, and pelvic
- Peritonitis: acute or chronic inflammation of the peritoneum
- Causes: abdominal and GI problems, surgery, and trauma
- Symptoms: tender abdomen, pain, nausea, vomiting, fever, and increased WBC and lactate levels### Liver and Pancreas Diseases
- Portal Vein: carries venous blood from the spleen and digestive organs to the liver
- Cirrhosis: chronic, irreversible, degenerative disease of the liver
- Replacement of normal liver cells with non-functioning fibrous scar tissue (hobnail liver)
- Causes: alcoholism, idiopathic, chronic hepatitis, and congestive heart failure
- Complications: blood backs up in the hepatic portal vein, leading to portal hypertension
- Symptoms: pain, blood in stools, anemia, diarrhea, and ascites (fluid in abdominal cavity)
Hepatitis
- Hepatitis A: most benign, spread through fecal-oral route, does not lead to chronic hepatitis
- Hepatitis B: serious form, spread through saliva, urine, feces, and semen, can spread transplacental, vaccine available
- Hepatitis C: blood or sexual contact, more likely to become chronic hepatitis than Hep B
- Hepatitis D: Delta virus, requires presence of Hep B to replicate
- Hepatitis E: similar to Hep A, spread through fecal-oral route, commonly caused by water contamination
Intestinal Diseases
- Inguinal Hernia: out-pouching of the small intestine and peritoneum into the groin area, more common in males
- Intussusception: telescoping of the intestine, can lead to intestinal obstruction
- Volvulus: twisting of the colon, can lead to intestinal obstruction
- Crohn's Disease: chronic inflammatory disease affecting the small intestine and local lymph nodes
- Symptoms: painful, anorexia, flatulence, abdominal pain, colicky pain, diarrhea, and constipation
- Treatment: supportive, low residue diet, medications to control diarrhea, inflammation, and infection
- Ulcerative Colitis: chronic inflammation of the colon, cause unknown, but possibly hereditary or autoimmune
- Symptoms: abdominal pain, blood in stools, anemia, and diarrhea
- Treatment: diet limitations, stress reduction, anti-inflammatory medications
- Dysentery: acute inflammation of the colon or colitis, caused by bacterial, viral, or parasitic invasion
- Symptoms: abdominal pain, cramping, and diarrhea
- Treatment: medications, fluids, prevention through good hand washing, refrigeration of food, and avoidance of contaminated water
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome: functional disorder of motility, leading to abdominal pain, diarrhea, and constipation
- Triggers: spicy foods, caffeine, alcohol, and stress
- Diverticulitis: condition of having little out-pouches in the colon (sigmoid), increases with age and associated with poor dietary habits
- Symptoms: abdominal pain, cramping, and fever
- Treatment: antibiotics, bowel resection if necessary
Other Diseases
- Gastritis: inflammation of the stomach, caused by aspirin, alcohol, coffee, tobacco, or bacterial-laden foods
- Symptoms: abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting
- Treatment: antibiotics, diet modifications
- Peptic Ulcer: area of tissue erosion, leaving a crater-like appearance, found in the stomach and duodenum
- Complications: major bleeding, perforation, and obstruction
- Causes: severe stress, heavy intake of drugs, smoking, and presence of Helicobacter bacteria
- Treatment: medications reducing gastric acidity (Tagamet, Pepcid, Zantac)
- Gastroenteritis: inflammation of the stomach and intestines, caused by bacterial, viral, or parasitic invasion
- Symptoms: abdominal cramping, diarrhea, and vomiting
- Treatment: medications, fluids, prevention through good hand washing, refrigeration of food, and avoidance of contaminated water
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
Test your knowledge of the gastrointestinal system, including its functions, organs, and pathologies. This quiz covers the upper and lower GI tracts, including the stomach, liver, pancreas, and intestines. Learn about the acid-rich environment of the stomach and the breakdown of food in the duodenum.