Podcast
Questions and Answers
What does the partial pressure of a gas refer to?
What does the partial pressure of a gas refer to?
- The total pressure exerted by all gases in a mixture
- The pressure exerted by gases in the lungs only
- The pressure a single gas exerts in a mixture of gases (correct)
- The average pressure of all gases in the atmosphere
How does temperature affect the pressure exerted by gas molecules?
How does temperature affect the pressure exerted by gas molecules?
- Higher temperature increases gas pressure (correct)
- Higher temperature decreases gas pressure
- Gas pressure is only affected by gas concentration
- Temperature has no effect on gas pressure
What is the average atmospheric pressure at sea level?
What is the average atmospheric pressure at sea level?
- 1013 mmHg
- 760 mmHg (correct)
- 500 mmHg
- 700 mmHg
What percentage of oxygen is present in the atmosphere?
What percentage of oxygen is present in the atmosphere?
Which law explains the behavior of gas mixtures and their partial pressures?
Which law explains the behavior of gas mixtures and their partial pressures?
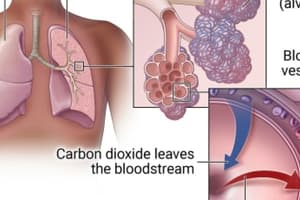
Which of the following describes bulk flow in gas exchange?
Which of the following describes bulk flow in gas exchange?
In the context of gas exchange, what effect does high partial pressure of oxygen have?
In the context of gas exchange, what effect does high partial pressure of oxygen have?
Which of the following mechanisms primarily governs gas exchange between blood and tissues?
Which of the following mechanisms primarily governs gas exchange between blood and tissues?
What is the partial pressure of inspired oxygen (PIO2) at sea level in dry air?
What is the partial pressure of inspired oxygen (PIO2) at sea level in dry air?
How does the partial pressure of O2 change when moving to higher elevations?
How does the partial pressure of O2 change when moving to higher elevations?
What is the effect of increasing the fractional concentration of O2 in inspired air to 80% on PIO2 at sea level?
What is the effect of increasing the fractional concentration of O2 in inspired air to 80% on PIO2 at sea level?
What does Henry's Law describe about gas concentration in a liquid?
What does Henry's Law describe about gas concentration in a liquid?
Which factor is NOT considered when calculating the partial pressure of inspired oxygen (PIO2)?
Which factor is NOT considered when calculating the partial pressure of inspired oxygen (PIO2)?
What is the partial pressure of O2 at the top of Mt. Humphrey’s where atmospheric pressure is 520 mm Hg?
What is the partial pressure of O2 at the top of Mt. Humphrey’s where atmospheric pressure is 520 mm Hg?
Which of the following statements about dissolved gases is true?
Which of the following statements about dissolved gases is true?
What happens to the partial pressure of O2 when air is humidified?
What happens to the partial pressure of O2 when air is humidified?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Partial Pressure
- Partial pressure of a gas (Pgas) is the pressure a single gas exerts in a mixture of gases.
- The most abundant gas in our atmosphere is nitrogen.
- The average atmospheric pressure at sea level is ≈ 760 mmHg.
- The partial pressure of oxygen in air is 21%.
Calculating Partial Pressure
- Dalton's Law: the total pressure of a mixture of gases is the sum of the individual pressures.
- Px = Patm x Fx
- Px = partial pressure of a gas (mm Hg)
- F = fractional concentration of gas
- Px = (Patm – PH2O) x Fx
- Px = partial pressure of a gas
- PH2O = partial pressure of water vapor in the mixture
Partial Pressure of Oxygen
- PO2 at sea level in dry inspired air is 160 mmHg.
- PIO2 (partial pressure of inspired oxygen) is ≈ 150 mm Hg
- PIO2 is lower at higher elevations because atmospheric pressure is lower.
- PIO2 is higher when receiving supplemental oxygen because the fractional concentration of oxygen (FIO2) increases.
Henry's Law
- Defines the relationship between the concentration of a gas in a liquid and its partial pressure.
- Concentration of a GAS (in liquid) = Px x solubility
- The concentration of a gas in a solution is only due to the dissolved gas, not bound or chemically modified.
- This means that the partial pressure of a gas in the liquid phase is equivalent to its partial pressure in the gas phase.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.