Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the kidneys?
What is the primary function of the kidneys?
- Storage of urine
- Production of hormones
- Transport of urine to the bladder
- Removal of waste products from the blood (correct)
Which component of the renal system is responsible for transporting urine from the kidneys to the bladder?
Which component of the renal system is responsible for transporting urine from the kidneys to the bladder?
- Ureters (correct)
- Nephron
- Urethra
- Bladder
What role does the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) play in the renal system?
What role does the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) play in the renal system?
- Facilitates electrolyte absorption
- Controls blood pressure (correct)
- Promotes urine storage
- Regulates blood pH
What is the typical capacity of the bladder?
What is the typical capacity of the bladder?
Which of the following conditions is characterized by a sudden decline in kidney function?
Which of the following conditions is characterized by a sudden decline in kidney function?
Which functional unit of the kidney is primarily involved in filtration?
Which functional unit of the kidney is primarily involved in filtration?
What is a common symptom of a urinary tract infection (UTI)?
What is a common symptom of a urinary tract infection (UTI)?
What hormone produced by the kidneys stimulates red blood cell production?
What hormone produced by the kidneys stimulates red blood cell production?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
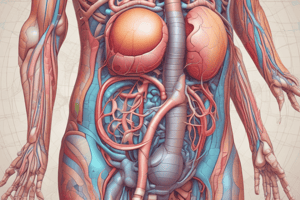
Overview of the Renal System
- The renal system, or urinary system, is responsible for the regulation of water, electrolytes, and the elimination of waste products.
- Comprises the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra.
Major Components
-
Kidneys
- Bean-shaped organs located on either side of the spine.
- Function: Filtration of blood, regulation of blood pressure, electrolyte balance, acid-base balance, and production of urine.
- Nephrons: Functional units of the kidney; each kidney contains about 1 million nephrons.
- Key processes: Filtration, reabsorption, secretion, and excretion.
-
Ureters
- Muscular tubes that transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
- Peristaltic contractions facilitate urine flow.
-
Bladder
- Hollow muscular organ that stores urine until excretion.
- Capable of expanding and contracting; typical capacity is about 400-600 mL.
-
Urethra
- Tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body.
- Length varies: shorter in females (about 4 cm) than in males (about 20 cm).
Functions of the Renal System
-
Filtration of Blood
- Removes waste products (e.g., urea, creatinine) and excess substances (e.g., water, salts).
-
Regulation of Blood Pressure
- Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) helps control blood pressure through fluid balance and vasoconstriction.
-
Acid-Base Balance
- Maintains pH through excretion of hydrogen ions and reabsorption of bicarbonate.
-
Electrolyte Management
- Regulates levels of sodium, potassium, calcium, and phosphate.
-
Hormone Production
- Produces erythropoietin (stimulates red blood cell production) and calcitriol (active form of vitamin D).
Common Disorders
-
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
- Gradual loss of kidney function; stages based on glomerular filtration rate (GFR).
-
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)
- Sudden decline in kidney function, often reversible; can be caused by dehydration, medications, or infections.
-
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
- Infections affecting any part of the urinary system; common symptoms include burning sensation during urination and frequent urge to urinate.
-
Kidney Stones
- Hard mineral deposits that form in the kidneys; can cause severe pain and obstruction.
Diagnostic Tests
-
Urinalysis
- Examines the physical, chemical, and microscopic properties of urine.
-
Blood Tests
- Assess levels of creatinine, urea, and electrolytes; evaluate kidney function.
-
Imaging
- Ultrasound, CT scans, or X-rays to visualize kidney structure and detect abnormalities.
Treatment Options
-
Medications
- Diuretics, antihypertensives, and medications to manage underlying conditions.
-
Dialysis
- Hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis for patients with severe kidney failure.
-
Kidney Transplant
- Surgical replacement of a diseased kidney with a healthy one from a donor.
Recommendations for Kidney Health
- Stay hydrated.
- Maintain a balanced diet low in sodium and high in fruits and vegetables.
- Regular exercise and weight management.
- Monitor blood pressure and blood sugar levels.
- Avoid excessive use of over-the-counter medications that can harm the kidneys.
Overview of the Renal System
- The renal or urinary system regulates water, electrolytes, and eliminates waste products.
- Key components include the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra.
Major Components
-
Kidneys
- Bean-shaped organs located beside the spine.
- Functions include blood filtration, blood pressure regulation, electrolyte and acid-base balance, and urine production.
- Comprised of about 1 million nephrons per kidney, which are the functional units.
- Key processes involve filtration, reabsorption, secretion, and excretion.
-
Ureters
- Muscular tubes that transport urine from kidneys to the bladder.
- Urine movement is facilitated by peristaltic contractions.
-
Bladder
- Hollow muscular organ for urine storage until excretion.
- Expands and contracts, with a typical capacity of 400-600 mL.
-
Urethra
- Tube that carries urine from the bladder to the external body.
- Length differs: about 4 cm in females and about 20 cm in males.
Functions of the Renal System
-
Filtration of Blood
- Eliminates waste (e.g., urea, creatinine) and excess substances (e.g., water, salts).
-
Regulation of Blood Pressure
- Managed by the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) through fluid balance and vasoconstriction.
-
Acid-Base Balance
- Maintained by excreting hydrogen ions and reabsorbing bicarbonate to regulate pH.
-
Electrolyte Management
- Controls sodium, potassium, calcium, and phosphate levels in the body.
-
Hormone Production
- Produces erythropoietin (stimulates red blood cell production) and calcitriol (active vitamin D form).
Common Disorders
-
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
- Gradual loss of kidney function with stages defined by glomerular filtration rate (GFR).
-
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)
- Sudden decline in kidney functionality; can be reversible and caused by dehydration, medications, or infections.
-
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
- Infections affecting the urinary system; symptoms include burning sensation while urinating and frequent urges.
-
Kidney Stones
- Hard mineral deposits in the kidneys causing severe pain and potential obstruction.
Diagnostic Tests
-
Urinalysis
- Examines physical, chemical, and microscopic urine properties.
-
Blood Tests
- Evaluates creatinine, urea, and electrolyte levels to assess kidney function.
-
Imaging
- Uses ultrasound, CT scans, or X-rays to visualize kidney structure and identify abnormalities.
Treatment Options
-
Medications
- Diuretics, antihypertensives, and drugs for managing underlying conditions.
-
Dialysis
- Includes hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis for severe kidney failure patients.
-
Kidney Transplant
- Surgical replacement of a diseased kidney with a donor kidney.
Recommendations for Kidney Health
- Stay adequately hydrated.
- Maintain a balanced diet with low sodium and high fruits and vegetables.
- Engage in regular exercise and manage weight effectively.
- Monitor blood pressure and blood sugar levels regularly.
- Minimize the use of over-the-counter medications that can damage the kidneys.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.