Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary symptom of otosclerosis?
What is the primary symptom of otosclerosis?
- Balance disorders
- Progressive hearing loss (correct)
- Ear infections
- Tinnitus
In which part of the ear does otosclerosis primarily occur?
In which part of the ear does otosclerosis primarily occur?
- Middle ear, around the oval window (correct)
- Outer ear canal
- Inner ear structures
- Eustachian tube
What is the suspected relationship between measles infection and otosclerosis?
What is the suspected relationship between measles infection and otosclerosis?
- Causes a complete loss of hearing
- Triggers acute ear infections
- May relate to the cause of bony overgrowth (correct)
- Has no known connection
What is the genetic inheritance pattern associated with familial otosclerosis?
What is the genetic inheritance pattern associated with familial otosclerosis?
What is primarily secreted by the stria vascularis into the scala media?
What is primarily secreted by the stria vascularis into the scala media?
What role do mitral cells play in the olfactory sensory pathway?
What role do mitral cells play in the olfactory sensory pathway?
During the hearing process, what directly causes the stapes to create a drop in pressure in the scala vestibuli?
During the hearing process, what directly causes the stapes to create a drop in pressure in the scala vestibuli?
What is the result of K+ flooding into the outer hair cells during the hearing process?
What is the result of K+ flooding into the outer hair cells during the hearing process?
What is the function of prestin in the outer hair cells during the process of hearing?
What is the function of prestin in the outer hair cells during the process of hearing?
What occurs in the inner hair cells after they bend towards their longer stereovilli?
What occurs in the inner hair cells after they bend towards their longer stereovilli?
What is the primary role of the auricle in the auditory system?
What is the primary role of the auricle in the auditory system?
Which component of the ear contains ceruminous glands?
Which component of the ear contains ceruminous glands?
Which structure is directly responsible for dampening the sounds transmitted from the tympanic membrane?
Which structure is directly responsible for dampening the sounds transmitted from the tympanic membrane?
Which epithelium type lines the tympanic cavity?
Which epithelium type lines the tympanic cavity?
What does the oval window connect?
What does the oval window connect?
What structure is primarily responsible for equalizing pressure in the middle ear?
What structure is primarily responsible for equalizing pressure in the middle ear?
What type of connective tissue is found in the tympanic membrane?
What type of connective tissue is found in the tympanic membrane?
Which structure conducts sound vibrations from the external ear to the inner ear?
Which structure conducts sound vibrations from the external ear to the inner ear?
What is the primary function of supporting cells within the olfactory epithelium?
What is the primary function of supporting cells within the olfactory epithelium?
Which pathway do the axons of olfactory sensory neurons take to reach the olfactory bulbs?
Which pathway do the axons of olfactory sensory neurons take to reach the olfactory bulbs?
What role do odorant-binding proteins play in the olfactory system?
What role do odorant-binding proteins play in the olfactory system?
What is the lifespan of olfactory sensory neurons?
What is the lifespan of olfactory sensory neurons?
What type of receptors are all olfactory receptors classified as?
What type of receptors are all olfactory receptors classified as?
Which component is involved in the signal transduction cascade initiated by odorant receptors?
Which component is involved in the signal transduction cascade initiated by odorant receptors?
How many functional olfactory genes do individual olfactory sensory neurons express?
How many functional olfactory genes do individual olfactory sensory neurons express?
What anatomical structure forms as a result of the synapse between olfactory sensory neurons and mitral or tufted cells?
What anatomical structure forms as a result of the synapse between olfactory sensory neurons and mitral or tufted cells?
What role do the ossicular chain and its lever system play in hearing?
What role do the ossicular chain and its lever system play in hearing?
What is the primary role of saliva in relation to taste perception?
What is the primary role of saliva in relation to taste perception?
Which structure separates the scala vestibuli from the scala media?
Which structure separates the scala vestibuli from the scala media?
Which taste modality does NOT involve the activation of G protein-coupled receptors?
Which taste modality does NOT involve the activation of G protein-coupled receptors?
What is the primary function of the organ of Corti?
What is the primary function of the organ of Corti?
What mechanism is primarily involved in salt taste perception?
What mechanism is primarily involved in salt taste perception?
How does the cochlea maintain different fluid compositions between endolymph and perilymph?
How does the cochlea maintain different fluid compositions between endolymph and perilymph?
How long does a taste cell typically live before it is replaced?
How long does a taste cell typically live before it is replaced?
What is the significance of the tympanic membrane having a larger surface area compared to the oval window?
What is the significance of the tympanic membrane having a larger surface area compared to the oval window?
Why does the cochlea contain a high concentration of potassium (K+) in endolymph?
Why does the cochlea contain a high concentration of potassium (K+) in endolymph?
Which of the following statements regarding taste bud innervation is accurate?
Which of the following statements regarding taste bud innervation is accurate?
Which membrane separates the scala tympani from the scala media?
Which membrane separates the scala tympani from the scala media?
Which receptors are involved in the perception of sweet taste?
Which receptors are involved in the perception of sweet taste?
What effect do the stapedius and tensor tympani muscles have on auditory function?
What effect do the stapedius and tensor tympani muscles have on auditory function?
What substance is commonly associated with blocking potassium-selective channels in bitter taste perception?
What substance is commonly associated with blocking potassium-selective channels in bitter taste perception?
What primarily causes sound waves to bounce off the oval window without being transmitted to the cochlea?
What primarily causes sound waves to bounce off the oval window without being transmitted to the cochlea?
Which of the following cells in the taste bud serves as a precursor to new taste receptor cells?
Which of the following cells in the taste bud serves as a precursor to new taste receptor cells?
How do the structures of the semicircular canals contribute to the detection of movement?
How do the structures of the semicircular canals contribute to the detection of movement?
What role does the basilar membrane play in the cochlea's function?
What role does the basilar membrane play in the cochlea's function?
What component within the auditory system primarily facilitates sound conduction to the inner ear?
What component within the auditory system primarily facilitates sound conduction to the inner ear?
Which of the following statements accurately describes the relationship between the extracellular matrix (ECM) and the ossicles in sound transmission?
Which of the following statements accurately describes the relationship between the extracellular matrix (ECM) and the ossicles in sound transmission?
What is the primary physiological process involved in sound transmission from the external ear to the inner ear?
What is the primary physiological process involved in sound transmission from the external ear to the inner ear?
What is the primary function of the semicircular canals in the vestibular system?
What is the primary function of the semicircular canals in the vestibular system?
How do the paired semicircular canals function relative to head movements?
How do the paired semicircular canals function relative to head movements?
What structural feature within the ampulla is crucial for detecting angular motion?
What structural feature within the ampulla is crucial for detecting angular motion?
What phenomenon occurs when the head rotates in relation to the endolymph fluid in the semicircular canals?
What phenomenon occurs when the head rotates in relation to the endolymph fluid in the semicircular canals?
Which of the following correctly describes the role of hair cells in the vestibular system?
Which of the following correctly describes the role of hair cells in the vestibular system?
What is the role of bicarbonate secretion in saliva related to taste perception?
What is the role of bicarbonate secretion in saliva related to taste perception?
Which of the following statements about the lifespan of taste cells is correct?
Which of the following statements about the lifespan of taste cells is correct?
Which channels in taste perception allow the entry of sodium (Na+) ions for salt sensitivity?
Which channels in taste perception allow the entry of sodium (Na+) ions for salt sensitivity?
Which receptor combinations are involved in the perception of umami taste?
Which receptor combinations are involved in the perception of umami taste?
How does sour taste transduction occur at the cellular level?
How does sour taste transduction occur at the cellular level?
Which element primarily differentiates the perception of bitter tastants from other tastes?
Which element primarily differentiates the perception of bitter tastants from other tastes?
What cellular components contribute to the structure of a taste bud?
What cellular components contribute to the structure of a taste bud?
Which axon types are connected to taste receptor cells for taste perception transmission?
Which axon types are connected to taste receptor cells for taste perception transmission?
How does the basilar membrane contribute to distinguishing different frequencies of sound?
How does the basilar membrane contribute to distinguishing different frequencies of sound?
What physiological change occurs as a result of increased movement of the basilar membrane?
What physiological change occurs as a result of increased movement of the basilar membrane?
What sound frequency range can younger individuals typically hear?
What sound frequency range can younger individuals typically hear?
Which component of the ear is primarily responsible for detecting dynamic equilibrium?
Which component of the ear is primarily responsible for detecting dynamic equilibrium?
What role do the movements of the oval window and round window play in hearing?
What role do the movements of the oval window and round window play in hearing?
What is specifically detected by hair cells in the organ of Corti?
What is specifically detected by hair cells in the organ of Corti?
What type of neural activity is primarily triggered by the release of glutamate from hair cells in response to sound?
What type of neural activity is primarily triggered by the release of glutamate from hair cells in response to sound?
How do sound waves propagate as described in the content?
How do sound waves propagate as described in the content?
What is the primary consequence of otosclerosis in patients?
What is the primary consequence of otosclerosis in patients?
Which characteristic is true about olfactory sensory neurons?
Which characteristic is true about olfactory sensory neurons?
What primarily initiates the pathological process of otosclerosis?
What primarily initiates the pathological process of otosclerosis?
What is the typical age of onset for more severe cases of otosclerosis?
What is the typical age of onset for more severe cases of otosclerosis?
How do mitral cells contribute to the olfactory sensory pathway?
How do mitral cells contribute to the olfactory sensory pathway?
What is the primary role of olfactory sensory neurons in the olfactory epithelium?
What is the primary role of olfactory sensory neurons in the olfactory epithelium?
What enhances the diffusion of odorants to and from the odorant receptors in the olfactory epithelium?
What enhances the diffusion of odorants to and from the odorant receptors in the olfactory epithelium?
How do odorant receptors mediate their signal transduction?
How do odorant receptors mediate their signal transduction?
What occurs to the olfactory sensory neurons after they have reached the end of their lifespan?
What occurs to the olfactory sensory neurons after they have reached the end of their lifespan?
What structure do the axons of olfactory sensory neurons traverse to reach the olfactory bulbs?
What structure do the axons of olfactory sensory neurons traverse to reach the olfactory bulbs?
What type of cells synapse with olfactory sensory neurons in the olfactory bulb?
What type of cells synapse with olfactory sensory neurons in the olfactory bulb?
What type of signaling cascade typically follows the activation of olfactory receptors?
What type of signaling cascade typically follows the activation of olfactory receptors?
What is the role of supporting cells in the olfactory epithelium?
What is the role of supporting cells in the olfactory epithelium?
Flashcards
Auricle Function
Auricle Function
Focuses sound waves onto the tympanic membrane, emphasizes specific sound frequencies, and changes the nature of sounds from different directions.
Auditory Meatus
Auditory Meatus
The opening of the external auditory canal, containing ceruminous glands to trap foreign substances and protect the canal linings.
Tympanic Membrane
Tympanic Membrane
The border between the outer and middle ear, made of connective tissue covered by epidermis and epithelium.
Tympanic Cavity
Tympanic Cavity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Eustachian Tube
Eustachian Tube
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ossicles
Ossicles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oval Window
Oval Window
Signup and view all the flashcards
Middle Ear Muscles
Middle Ear Muscles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stria vascularis function
Stria vascularis function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sound wave in ear
Sound wave in ear
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hair cell transduction
Hair cell transduction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Outer hair cell contraction
Outer hair cell contraction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Inner hair cell activation
Inner hair cell activation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ossicular Chain Function
Ossicular Chain Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acoustic Impedance Mismatch
Acoustic Impedance Mismatch
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cochlea
Cochlea
Signup and view all the flashcards
Scala Vestibuli
Scala Vestibuli
Signup and view all the flashcards
Scala Tympani
Scala Tympani
Signup and view all the flashcards
Scala Media
Scala Media
Signup and view all the flashcards
Organ of Corti
Organ of Corti
Signup and view all the flashcards
Endolymph
Endolymph
Signup and view all the flashcards
Perilymph
Perilymph
Signup and view all the flashcards
Taste buds location
Taste buds location
Signup and view all the flashcards
Taste bud structure
Taste bud structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Taste receptor cells
Taste receptor cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Salt taste transduction
Salt taste transduction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sour taste transduction
Sour taste transduction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sweet taste receptors
Sweet taste receptors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bitter taste compounds
Bitter taste compounds
Signup and view all the flashcards
Umami taste receptors
Umami taste receptors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Otosclerosis
Otosclerosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Otosclerosis Cause
Otosclerosis Cause
Signup and view all the flashcards
Otosclerosis Progression
Otosclerosis Progression
Signup and view all the flashcards
Otosclerosis Symptoms
Otosclerosis Symptoms
Signup and view all the flashcards
Otosclerosis Epidemiology
Otosclerosis Epidemiology
Signup and view all the flashcards
Olfactory Epithelium
Olfactory Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Olfactory Sensory Neurons
Olfactory Sensory Neurons
Signup and view all the flashcards
Olfactory Receptors
Olfactory Receptors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Olfactory Pathway
Olfactory Pathway
Signup and view all the flashcards
Olfactory Glomeruli
Olfactory Glomeruli
Signup and view all the flashcards
Odorant Receptors Diversity
Odorant Receptors Diversity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Supporting Cells in Olfactory Epithelium
Supporting Cells in Olfactory Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cribriform Plate
Cribriform Plate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ossicles Function
Ossicles Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sound Transmission in the Ear
Sound Transmission in the Ear
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cochlea Structure
Cochlea Structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vestibular System Function
Vestibular System Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
What initiates glutamate release?
What initiates glutamate release?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Where are afferent cell bodies located?
Where are afferent cell bodies located?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does the brain differentiate pitch?
How does the brain differentiate pitch?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does the brain interpret loudness?
How does the brain interpret loudness?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are sound waves?
What are sound waves?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How is sound converted to a signal in the inner ear?
How is sound converted to a signal in the inner ear?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does static equilibrium detect?
What does static equilibrium detect?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does dynamic equilibrium detect?
What does dynamic equilibrium detect?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Semicircular Canals
Semicircular Canals
Signup and view all the flashcards
Otolithic Organs (Utricle & Saccule)
Otolithic Organs (Utricle & Saccule)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Crista Ampullaris
Crista Ampullaris
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cupula
Cupula
Signup and view all the flashcards
Odorant Receptors
Odorant Receptors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Supporting Cells
Supporting Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the Signal Transduction Cascade?
What is the Signal Transduction Cascade?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does the brain differentiate smells?
How does the brain differentiate smells?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
BMS 200 - Physiology of Hearing, Taste, and Olfaction
- This course covers the physiology of hearing, taste, and olfaction.
- The learning objectives for today's sessions include: describing the physiology of taste receptors and taste perception, olfaction, and the anatomy and physiology of the middle and external ears.
- Also, describe the relationship between extracellular matrix components and other middle ear structures.
- Describe the anatomical structures of the organs of hearing and equilibrium, including the external, middle, and inner ear, as well as the vestibular system. Additionally, describe the functions of each component of the auditory system, including the role of the pinna, external auditory canal, tympanic membrane, ossicles, cochlea, and vestibular apparatus.
- Discuss the physiological processes involved in sound transmission, from the capture of sound waves by the external ear to the transduction and amplification of auditory signals.
- Describe the mechanisms of the cochlea, including the organization of hair cells, the basilar membrane, and the cochlear duct function in sound reception.
- Relate the structure of the semicircular canals and otolith organs to detecting rotational and linear acceleration.
Outcomes for Today
- Describe the functions of each component of the auditory system (pinna, external auditory canal, tympanic membrane, ossicles, cochlea, vestibular apparatus).
- Discuss physiological sound transmission processes from external ear sound wave capture to inner ear transduction/amplification.
- Describe sophisticated cochlear mechanisms including hair cell organization, basilar membrane function, and cochlear duct role in sound perception.
- Relate semicircular canal/otolith organ structures to functions of detecting rotational/linear acceleration.
The Ear - General Structure
- The ear is divided into three main sections: outer, middle, and inner ear
- The diagram shows the external auditory meatus, helix, auricle, earlobe, auditory ossicles, tympanic membrane, cochlea, temporal bone, semicircular canals, facial nerve, vestibular nerve, and cochlear nerve.
- The outer ear comprises the helix, auricle, and external auditory meatus.
- The middle ear includes the auditory ossicles (malleus, incus, stapes), tympanic membrane, and auditory tube.
- The inner ear contains the cochlea and semicircular canals, which are components of the vestibular system.
Outer Ear - Structures
- The auricle, also known as the pinna, is the external part of the ear.
- Its structure, including the helix, lobule, and tragus, focuses sound waves onto the tympanic membrane.
- Certain structures in the auricle emphasize specific sound frequencies. The structure of the auricle modifies sound directions.
- The auditory meatus or auditory canal leads to the eardrum. Ceruminous glands secrete cerumen (earwax) in the external auditory canal.
Middle Ear - Structures
- The tympanic membrane separates the outer and middle ear, acting as a border. The tympanic membrane is a fibroelastic connective tissue membrane with an outer layer of epidermis and inner simple cuboidal epithelium.
- The tympanic cavity, lined with simple cuboidal epithelium, is part of the middle ear.
- The auditory ossicles (malleus, incus, and stapes) transmit sound vibrations to the inner ear via the tympanic membrane.
- The Eustachian tube connects the middle ear to the pharynx.
- This tube equalizes pressure between the atmosphere and middle ear.
Middle Ear - Structures (Ossicles)
- Malleus (hammer): connects to the tympanic membrane to transmit vibrations.
- Incus (anvil) forms a joint with the malleus and stapes.
- Stapes (stirrup): joins with the incus and oval window in the inner ear.
- These transmit sound energy from the ear drum to the oval window of the inner ear.
Middle Ear - Key Structures
- The tympanic cavity is within the temporal bone, lining the middle ear.
- The diagram illustrates the malleus, incus, stapes, oval window, round window, and Eustachian tube within the middle ear structure.
Inner Ear - Structures for Sound (Cochlea)
- The cochlea is a spiral-shaped structure in the inner ear.
- It has approximately 1,000,000 moving parts (stereocilia/stereovilli) within the cochlear duct, which is critical for hearing.
- Within the cochlea, the basilar membrane plays a crucial role in sound perception.
- The cochlear duct contains the organ of Corti, which has inner and outer hair cells.
Inner Ear - Structures for Sound (Cochlea - Cont.)
- The scala media houses inner and outer hair cells.
- Endolymph has a unique chemical composition contrasting with perilymph.
- The basilar membrane houses the inner and outer hair cells, contacting the tectorial membrane.
- Reissner's membrane is crucial in separating endolymph and perilymph.
Inner Ear - Structures for Sound
- Discuss the organ of Corti and its role in transducing vibrations into action potentials.
- The organ of Corti is the hearing receptor component of the inner ear. The hair cells in the organ of Corti are responsible for transducing vibrations from the basilar membrane into electrical signals.
- Vibrations in the basilar membrane cause the movement of inner and outer hair cells contacting the tectorial membrane. This generates electrical signals that lead to a nerve impulse.
Inner Ear - Structures for Sound (Cochlea Cont.)
- The scala media contains endolymph with characteristics distinct from perilymph in composition due to stria vascularis's active transport of electrolytes.
- The basilar membrane houses the inner and outer hair cells for sound transduction.
Why is there so much K+ in endolymph?
- Stria vascularis actively transports electrolytes to create a high concentration of K+ in the endolymph.
- This high K+ concentration is crucial for sensory reception in the inner ear.
The Process of Hearing - Step-by-Step
- Sound waves entering the external auditory canal cause the tympanic membrane to vibrate.
- The ossicles (malleus, incus, stapes) amplify these vibrations.
- The stapes' movement causes pressure changes in the scala vestibuli, moving the fluid and then the basilar membrane.
- The hair cells in the basilar membrane cause depolarization.
The Process of Hearing - Step-by-Step (Cont.)
- Basilar membrane bending creates shear forces on the hair cells, resulting in depolarization.
- Depolarization causes contraction and movement of stereocilia within outer hair cells.
- K+ movement during depolarization opens transduction channels.
- Inner hair cells bend toward their longer stereovilli, causing transduction channels to open and depolarization.
The Process of Hearing – Details
- Differences in sound frequency are determined by the location of basilar membrane vibration.
- High-frequency sounds cause maximal vibration nearer the oval window.
- Low-frequency sounds cause maximal vibration nearer the helicotrema.
- Pitch detection depends on the basilar membrane's vibration point.
- Loudness is encoded by the intensity of basilar membrane vibration, leading to greater glutamate release.
Equilibrium and the Vestibular Apparatus
- Two types of equilibrium are detected by the inner ear: static and dynamic.
- Static equilibrium detects head position relative to gravity. Is the head tilted?
- Dynamic equilibrium detects angular and linear accelerations like in an elevator or car. Is the head turning or speeding up or slowing down?
The Vestibular System
- Each ear has three semicircular canals arranged at right angles (horizontal, vertical, and posterior).
- Each side of the canal has a partner (e.g., the left horizontal canal). When one canal is stimulated, the corresponding one on the other side is inhibited.
- This push-pull action allows the vestibular system to determine the direction of rotation or acceleration.
Semicircular Canal Function
- The anterior, posterior, and lateral semicircular canals detect head movement in different planes: front to back, side to side, and rotational movement.
Utricle and Saccule
- Otilithic organs (utricle and saccule) are in the bony chamber of the vestibule between the cochlea and the semicircular canals.
- These sense linear acceleration and deceleration.
- The utricle is more horizontally oriented, and the saccule is more vertically oriented.
Utricle and Saccule (Macula)
- These saclike structures contain sensory tissue, called maculae, that detects head position and linear acceleration.
- Maculae consist of hair cells, supporting cells, and the otolithic membrane, which has calcium carbonate crystals (otoliths).
- The otoliths resist movement, making movement easier in certain directions to detect movement.
Smell and Taste
- Chemoreceptors in the nose (odorants) and mouth (tastants) detect chemical molecules.
- Taste buds are approximately 5,000 found in papillae along the tongue's surface.
- Papillae types include fungiform, circumvallate, and foliate.
- Taste buds have receptor cells for various tastes.
Taste Buds
- Fungiform papillae contain several taste buds.
- Circumvallate papillae are large and contain many taste buds.
- Foliate papillae have multiple taste buds on their sides.
- Filiform papillae lack taste buds but help with texture.
- Taste buds have 50-100 taste receptor cells forming a part of the tongue and its surrounding area. The sensory cells have taste pores and have microvilli.
Taste
- Saliva in the oral cavity dissolves tastants for easier detection.
- Taste buds receive nerve impulses from tastants dissolved in saliva.
- Salivary bicarbonate aids in chemical digestion.
- Taste cells have a lifespan of around 10 days.
- Humans have five basic taste sensations.
Taste Perception
- Salt perception involves sodium channels (ENaC) leading to depolarization.
- Sour perception results from increased proton concentration.
- Sweet, bitter, umami perceptions depend on G protein-coupled receptors.
Olfactory Epithelium
- The olfactory epithelium, located in the upper part of the nasal cavity, contains olfactory sensory neurons that detect odors dissolved in mucus.
- Contains supporting cells for mucus secretion to provide a suitable environment for the detection of odors.
- Each olfactory sensory neuron expresses a single functional olfactory gene and responds to a variety of odorant receptors.
Olfactory Pathway
- In the olfactory bulb, the olfactory sensory axons synapse with mitral and tufted cells, creating distinctive olfactory glomeruli.
- These glomeruli enable a unique two-dimensional map that determines the characteristics of each odor.
- The central nervous system decodes the receptor cell activity patterns to analyze and interpret odors.
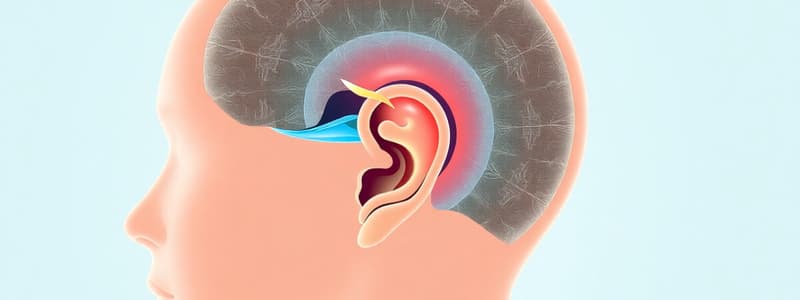
Otosclerosis
- Abnormal bone deposition in the middle ear, typically around the oval window.
- Hearing loss is a common symptom.
- Cause is often familial (autosomal dominant) but may be associated with an immune response or infection.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.