Podcast
Questions and Answers
According to Puranam, Alexy, & Reitzig (2014), which of the following is NOT a common feature of an organization?
According to Puranam, Alexy, & Reitzig (2014), which of the following is NOT a common feature of an organization?
- A single decision-maker (correct)
- System-level goals
- Identifiable boundaries
- A multi-agent system
According to Nadler & Tushman's model, which of the following is NOT considered one of the four interrelated components of an organization?
According to Nadler & Tushman's model, which of the following is NOT considered one of the four interrelated components of an organization?
- People
- Strategy (correct)
- Formal structure
- Work
In organizational change, what does a 'temporal lens' primarily focus on?
In organizational change, what does a 'temporal lens' primarily focus on?
- Analyzing an organization's financial performance over time.
- Comparing how organizations were in the past to how they are now. (correct)
- Comparing an organization's structure to its competitors.
- Evaluating the impact of leadership changes on company culture.
Which organizational change metaphor describes change as reflecting the growth of an organism from birth to maturity, followed by potential decline?
Which organizational change metaphor describes change as reflecting the growth of an organism from birth to maturity, followed by potential decline?
According to Nadler and Tushman, what is essential for an organization to succeed in relation to its environment?
According to Nadler and Tushman, what is essential for an organization to succeed in relation to its environment?
According to McGahan (2004), what is the primary factor that determines an organization's success in relation to industry change?
According to McGahan (2004), what is the primary factor that determines an organization's success in relation to industry change?
According to McGahan (2004), which trajectory denotes industries where activities are generally not threatened, and assets may or may not be threatened?
According to McGahan (2004), which trajectory denotes industries where activities are generally not threatened, and assets may or may not be threatened?
In the context of organizational life cycles, what is a key characteristic of the 'Entrepreneurial Stage', according to Tushman & O'Reilly?
In the context of organizational life cycles, what is a key characteristic of the 'Entrepreneurial Stage', according to Tushman & O'Reilly?
What defines the 'Collectivity Stage' in organizational development according to Tushman & O'Reilly?
What defines the 'Collectivity Stage' in organizational development according to Tushman & O'Reilly?
In organizational change, what does the 'Formalization and Control Stage' emphasize, according to Tushman and O'Reilly?
In organizational change, what does the 'Formalization and Control Stage' emphasize, according to Tushman and O'Reilly?
What factor contributes to 'Failing to Achieve Aspirations' as an internal pressure for organizational change?
What factor contributes to 'Failing to Achieve Aspirations' as an internal pressure for organizational change?
In assessing an organization's future aspirations, what role does 'past performance' play?
In assessing an organization's future aspirations, what role does 'past performance' play?
According to Meeks and Whittington (2023), what was identified as the most important factor for the survival of companies listed on the UK stock exchange in 1948?
According to Meeks and Whittington (2023), what was identified as the most important factor for the survival of companies listed on the UK stock exchange in 1948?
According to Morgan (2006), what is one way organizations can be described which affects how they change?
According to Morgan (2006), what is one way organizations can be described which affects how they change?
In the Life-Cycle Theory, what is a key aspect associated with change in organizations?
In the Life-Cycle Theory, what is a key aspect associated with change in organizations?
What does the Congruence Model (Nadler & Tushman, 1989) state as a requirement for organizational success?
What does the Congruence Model (Nadler & Tushman, 1989) state as a requirement for organizational success?
According to Starbuck & Nystrom (1997), what primarily causes organizational failure relating to crisis or decline?
According to Starbuck & Nystrom (1997), what primarily causes organizational failure relating to crisis or decline?
What does the 'burnout syndrome' in Probst & Raisch's (2005) model of premature organisational failure entail?
What does the 'burnout syndrome' in Probst & Raisch's (2005) model of premature organisational failure entail?
According to Amankwah-Amoah, Khan & Wood (2021), what is key to avoid failure in response to a crisis?
According to Amankwah-Amoah, Khan & Wood (2021), what is key to avoid failure in response to a crisis?
According to Weick and Quinn (1999), what is a characteristic of episodic change?
According to Weick and Quinn (1999), what is a characteristic of episodic change?
In Nadler and Tushman's (1989) model of episodic change, what differentiates strategic change from incremental change?
In Nadler and Tushman's (1989) model of episodic change, what differentiates strategic change from incremental change?
Building an effective organization requires satisfying three key factors, as argued by Alfred P. Sloan. What are these factors?
Building an effective organization requires satisfying three key factors, as argued by Alfred P. Sloan. What are these factors?
According to Oxman and Smith (2003), what is the most important outcome to consider when making structural changes?
According to Oxman and Smith (2003), what is the most important outcome to consider when making structural changes?
What is a typical characteristic of a 'divisional structure' in an organization?
What is a typical characteristic of a 'divisional structure' in an organization?
What is true of individuals as they manage themselves through an M&A integration process?
What is true of individuals as they manage themselves through an M&A integration process?
Flashcards
Organization Definition
Organization Definition
A system with identifiable boundaries, system-level goals, and multi-agent contributions.
Nadler & Tushman's model
Nadler & Tushman's model
Four interrelated components: work, people, informal structure, and formal structure.
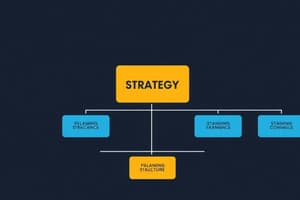
Strategy
Strategy
Configuration of resource deployment decisions in response to environmental factors.
Congruence
Congruence
Signup and view all the flashcards
Organizational Change
Organizational Change
Signup and view all the flashcards
Evolution Metaphor
Evolution Metaphor
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lifecycle Metaphor
Lifecycle Metaphor
Signup and view all the flashcards
Threat to Core Activities
Threat to Core Activities
Signup and view all the flashcards
Threat to Core Assets
Threat to Core Assets
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stages of organization growth
Stages of organization growth
Signup and view all the flashcards
Failing to Achieve Aspirations
Failing to Achieve Aspirations
Signup and view all the flashcards
Life-Cycle Theory
Life-Cycle Theory
Signup and view all the flashcards
Crisis Definition
Crisis Definition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Organizational Failure
Organizational Failure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Organizational Crisis
Organizational Crisis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Optimism Bias
Optimism Bias
Signup and view all the flashcards
Institutional misfit
Institutional misfit
Signup and view all the flashcards
Continuous change
Continuous change
Signup and view all the flashcards
Episodic change
Episodic change
Signup and view all the flashcards
Entrepreneurial structure
Entrepreneurial structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Functional structure
Functional structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Divisional structure
Divisional structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Matrix structure
Matrix structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Synergy in M&A
Synergy in M&A
Signup and view all the flashcards
Evolution vs Revolution
Evolution vs Revolution
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- Company lifespan is shrinking
Organisation Definition
- Different definitions exist, but include these common features:
- A multi-agent system
- Identifiable boundaries
- System-level goals towards which agents contribute
Nadler & Tushman's Definition
- Defines organisations as complex systems connecting inputs (environment, resources, history) with output
System Structure
- The complex system breaks into four interrelated components:
- Work
- People
- Informal structure
- Formal structure
- Strategy, the pattern of decisions over time, allocates resource deployment responding to environmental opportunities & threats
Effective Output
- Requires both strategy and organisation
- Congruence, where inputs, strategy, and components are aligned, ensures effective output
Organisational Change
- Studying how organisations evolve involves comparing their past and present states, affecting the components and elements of strategy
Organisational Growth
Tushman & O'Reilly Model
- Argues that all organisations grow align an S-curve with 3 stages: innovation, differentiation, and maturity reflecting an evolutionary perspective
Organisational Change Metaphors
Evolution
- Change comes from evolutionary forces of variation, selection, and retention, developing complexity over time
Lifecycle
- Change mirrors the growth of an organism, including birth, maturity, and potential decline
Reasons for Organisational Change
External Factors
- Evolution suggests external factors drive change
- For success, inputs (environment) match the elements of the system (strategy & components)
- Organisations must adapt with environmental shifts to maintain congruence which include
- Technological advances
- Government regulations
- Societal values
- Political dynamics
- Demographics
- Globalisation
- Pandemics
Adapting to Industry Change
McGahan's Argument
- Organisations must understand and align with industry changes for success
Four Types of Industry Change Perspectives
- A threat to core activities that have historically generated profit as these activities become irrelevant to suppliers / customers
- A threat to core assets that made the organisation unique, when they fail to generate value
Industry Trajectories
- Industries start with creative or progressive trajectories
- Face pressure from customer demands and new technologies which threatens activities
- This pushes industry towards radical or intermediating trajectories that unfold over decades
Internal Factors
- Internal biological lifecycles are the key to change
Tushman & O'Reilly Stages
Entrepreneurial Stage
- Founders develop ideas, seeking capital, and creating a niche
- Processes are introduced for managing staff
- Decision making and coordination are typically informal
Collectivity Stage
- Founders focus on product development and seeking capital
- A family feeling as vision is pursued
- Commitment is built as they work long hours for low pay
- There is informal coordination but more consistency
Formalization and Control Stage
- Guided by formal processes, there is a strict division of labor
- Efficiency of operation, increased professional managers, departments, and levels in the hierarchy
Elaboration Stage
- Managers balance efficiency and innovation
- Empowered lower-level managers and associates exist alongside formal rules and procedures.
Causes of Organisational Change
Changing Workforce
- New skills and expectations
- Retirement
- New CEO
- Increased cultural diversity
Failing Aspirations
- Perception of a discrepancy between current and desired state
- Affected by past aspirations
- Past performance vs targets
- Social comparison with other organizations
Company Survival
Meeks and Whittington Findings
- Being large, growing rapidly, and operating in the appropriate industry support survival
- The most important factor is being able to adapt to changes
Perspectives on Change
Two Kinds of Change
- Changes that people implement in organisations to hit goals
- Changes that naturally occur in organisations
Strategy vs Organisation
Nadler and Tushman Distinction
- Strategy is the pattern of decisions about resource deployment according to environment
- Organisation is the mechanism for enacting that strategy
Reasons to Change
Morgan's States
- Organisations are living organisms with lifecycles
- Organisations evolve by adapting to survive
Life-Cycles vs Evolution
Life-Cycle Theory
- Change is internal, imminent, and follows a form where key renewal and revival
Evolution
- Congruence model from Nadler & Tushman where success is:
- Strategy being consistent with environment
- Congruence between the organization's components
Adjusting to Discontinuity
- The fittest survive until a major discontinuity in an external environment like technology
- Organisations must successfully adjust strategy to survive and explains change
Focus on Change
- Why change happens
Organisations in Crisis
Crisis Definitions
- Crises involve a threat to important goals, uncertainty, and time pressure
Crisis Severity
- Crises are high impact when they involve more important goals and uncertainty about resolution
Causes of Organisational Crisis
- Org crisis can be due to internal factors (properties of organisations)
- Org crisis can be due to external factors (properties of the environment)
- However, externally-caused crises receive a lot of attention
Cameron et al's focus
- When the resource base shrinks, the organisation is in decline
Broad Approach
- Any occasion when performance is less than ideal.
Patterns of Decline
McMillan and Overall ID
- Decline patterns in organisations
- Classic Lifecycle Model, the organisation will decline over time as birth, growth and maturity are reached
- Precipitous decline when specific issues cause a chain of consequences
- Slow decline when that lead to eventual failure caused by internal and external misalignments
Organisational Failure
Strategic Elements
- Scarcity of resources, unstable goal preferences, and poor strategy options
Failure Triggers
- Organisations fail when they fail to appropriately respond to decline caused by internal & external factors
- Patterns that were previously successful lead to downfall because prevent managers from seeing world as it is
- Unable to understand challenges or see the state of the environment, cannot respond appropriately
Perspectives on Organisational Failure
Levels of Organisational Failure
Level 1 - Simple Failure
- Involves simple failures and managers address these if sufficiently aware
Level 2 - Complex Failure
- failures result from a lack of planning and foresight
- if not addressed it can accumulate and lead to the final failure level
Level 3 - Catastrophic Failure
- failures across all levels require major structural corporate transformation to get solved
Model of Premature Organisational Failure
Two causes of failure
- Burnout syndrome due to uncontrolled change
- Premature aging syndrome due to weak leadership
Lecture Notes
- Organisational decline & crisis occurs where uncertainty reaches extreme levels
- Ignoring sings = Optimism Bias
- Organisation-environment fit is key
Deterministic
- External
Voluntaristic
- Firm specific attributes
- Institutional Misfit
- Strategic Misfit
Episodic Change
- Changed, were changed, or died due to survival
The Tempo Theory of Change
- Changes fall into episodic and continuous
- 1)Episodic Change
- occasional interruption driven externally
- prototypically its a failure to adapt
- 2)Continuous change
- Modifications driven driven internally
- Episodic change tends to be external, infrequent and discontinuous while continuous change is constant, cumulative
Four Types of Episodic Change
Nadler and Tushman's Model
- Two dimensions
- Incremental vs strategic
- Anticipatory or reactive
Alfred P. Sloan's organization building
- Build organisation by strategy, structure and supporting systems
McKinsey 7 S's
- 4 soft and 3 standard
Structural change
- change organizational charts that help in performance
four major organizational structures
- what organisation is trying to do
Entrepreneurial structure
- Organized by one person
- Founders may not have all data for small firms
Functional structure
- Centralized by tasks
Divisional structure
- Decentralized and organized by geography or product
- suited for international markets
Matrix structure
- has dual control on tasks and skills
- Suits innovative products
Pros and Cons of Structural Change
Benefits
- aligned structures can lead to savings, Increased understanding and increased service quality
Disadvantages
- repeated restructuring erodes morale
Formal Hierarchy
- argue that thinking about structuring is wrong since structures can...
- 1 separate actions but is too rigid
- 2 allocate resources but has people self selecting
- 3 cause communication issues, but has instant communication
- 4 modern organizations use more 360 feedback
- 5 modern career management will promote
- 6 has needs for order but may not be valuable.
Mergers and Aquisitions
- M&A's is a general term to consolidated organization due to financial processes
- A merger occurs when to organization make one
- Auquisition is when an organization takes over another
Types of Mergers
- 1 Horizontal mergers two companies compete
- 2 Vertical mergers two customers and supplier
- 3 Generic mergers two businesses serve from same place
- 4 Conglomerate deals two companies have no business in common
M&A's benefits
- growth is fast
- management cannot do it alone properly
- Synergy builds distribution
- grow revenue
- diversification produces portfolio's
- Integration is most effective form of economic gain and service
- defensive process and reaction
- deals is a CEOs process
Major Disadvantages
- turnover causes stress an burn out caused by cultures causing issues
GReiner (1988)
- theories of change due to revolution
- weick in Quinn theory focus on change based on trauma
Romanellin and Tushman
- revolutionary changes can change even environments and CEO succession
Klarher and Raisch
- examine change a solution for change and stability
Taxonomy
- identified a rhythm of strategic change
- regular
- temporal
- Puctuated
- no change
- Meeks and Whittington most companies undergo mergers
- high levels combined can cause employee stress.
ELE WEEK 4 Continuous improvement
Tsoukas and Chia (2002) -Traditional continuous change, need to see the normal state
- Change is a normal process and should adopt to be in organization -Focus on micro processes -
- more attuned people can be able to be adaptive to change that is radical
continious change
- eliminate all change
- Improviziation, a workers action -
- limits exist, only change will occur that lead to superior performance
factors of improv
Organizational 1:An experiment 2: data 3:Memory Group 1: expertise 2 team work Fisher and Barret
- Improvisatiton
- Associated with feeings Obstacles
small action radial
meyerson
- disruptive
- verbal
- opportunitim
- alliance
Ele 5. Change management
lewin forcefield analysis
- unfreezing ,change,freeze
Nadler and Tushman frame
- 1 initializing
- vision
- energy
- then change content -magic leader, ACHieve Change,
Vandeven
Change takes one type
Dialectal
In organization regulated cycle/ recurring models evolutionary process
Burnes
- argues Lwein matters Kotter states change is not simply but his model
- hues models.
Sirkin
hard facts are important
- dici golden biddle
- Act with compassion-personal
- Foster
- sustaining continuity
Change management methods
models on action
LeCTure 6
- organization aldecline is worse than it shud be
- McMillan says factors are outside
- catz & Kahn says leadership failed
- Turnaround - organization attempts to act against decline
two types of actions that can deciline
- strategic
- operational
Turn around spirals model
The innovation leads to decline etc
- Anssell and Boin are practical
- weill said crisis needs 4 capabilities
- stutcliffe said 7 things
-Amsell - you need people
- Lectre 7 zombiew are abletopay back over period of time , change maodels have key 10 things
- Mcmillian said deslice is abetween 2 thing
Probst
- said 4 factors can contribute
- cameron
ELE 7 Notes The study guide you re making has several issues you should go change
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.