Podcast
Questions and Answers
What type of collagen do odontoblasts primarily synthesize?
What type of collagen do odontoblasts primarily synthesize?
- Type III collagen
- Type V collagen
- Type II collagen
- Type I collagen (correct)
What is phosphophoryn, and where is it primarily found?
What is phosphophoryn, and where is it primarily found?
- A highly phosphorylated phosphoprotein unique to dentin (correct)
- A proteoglycan found in the extracellular matrix
- A lysosomal enzyme found in odontoblasts
- A type of collagen found in bone
Which enzyme secreted by odontoblasts is thought to be linked to mineralization?
Which enzyme secreted by odontoblasts is thought to be linked to mineralization?
- Collagenase
- Phospholipase
- Alkaline phosphatase (correct)
- Acid phosphatase
Which structural feature is unique to odontoblasts compared to osteoblasts and cementoblasts?
Which structural feature is unique to odontoblasts compared to osteoblasts and cementoblasts?
What structural feature is characteristic of the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) in odontoblasts?
What structural feature is characteristic of the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) in odontoblasts?
What do odontoblasts, osteoblasts, and cementoblasts have in common during matrix formation?
What do odontoblasts, osteoblasts, and cementoblasts have in common during matrix formation?
What significant change occurs to odontoblasts after the completion of root development?
What significant change occurs to odontoblasts after the completion of root development?
Which of the following components have been proposed to be involved in odontoblasts' immune regulation?
Which of the following components have been proposed to be involved in odontoblasts' immune regulation?
How do odontoblast processes interconnect and communicate within the mineralized matrix?
How do odontoblast processes interconnect and communicate within the mineralized matrix?
What is the primary role of acid phosphatase in odontoblasts?
What is the primary role of acid phosphatase in odontoblasts?
What cellular component of odontoblasts is notably large and can contain multiple nucleoli (up to four)?
What cellular component of odontoblasts is notably large and can contain multiple nucleoli (up to four)?
Which is NOT an electrophysiological characteristic noted in odontoblasts in relation to nerves?
Which is NOT an electrophysiological characteristic noted in odontoblasts in relation to nerves?
What is the main difference in anatomical relationship between odontoblasts and osteoblasts?
What is the main difference in anatomical relationship between odontoblasts and osteoblasts?
What characteristic do odontoblasts, osteoblasts, and cementoblasts share regarding their RNA content?
What characteristic do odontoblasts, osteoblasts, and cementoblasts share regarding their RNA content?
Which of the following cell types plays a role similar to that of odontoblasts but is located in a different mineralized tissue?
Which of the following cell types plays a role similar to that of odontoblasts but is located in a different mineralized tissue?
What is the primary role of alkaline phosphatase in odontoblasts?
What is the primary role of alkaline phosphatase in odontoblasts?
Which component of the odontoblast layer is responsible for recognizing bacterial components?
Which component of the odontoblast layer is responsible for recognizing bacterial components?
Which type of collagen is minimally synthesized alongside type I collagen by odontoblasts?
Which type of collagen is minimally synthesized alongside type I collagen by odontoblasts?
What significant change occurs in the structure of odontoblasts following dentin production shifts from primary to secondary?
What significant change occurs in the structure of odontoblasts following dentin production shifts from primary to secondary?
Which ion channels have been observed in odontoblasts indicating their excitability?
Which ion channels have been observed in odontoblasts indicating their excitability?
⭐️Which type of enzyme is acid phosphatase classified as in the context of odontoblast function?
⭐️Which type of enzyme is acid phosphatase classified as in the context of odontoblast function?
In what manner is the Golgi complex of odontoblasts characterized?
In what manner is the Golgi complex of odontoblasts characterized?
What primarily distinguishes the processes of active odontoblasts from those of inactive odontoblasts?
What primarily distinguishes the processes of active odontoblasts from those of inactive odontoblasts?
How do odontoblasts contribute to the composition of the extracellular matrix (ECM)?
How do odontoblasts contribute to the composition of the extracellular matrix (ECM)?
Which structural feature is most associated with rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) in odontoblasts?
Which structural feature is most associated with rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) in odontoblasts?
Which best describes the morphological characteristic of fully developed odontoblasts?
Which best describes the morphological characteristic of fully developed odontoblasts?
What is the main difference in the anatomical relationship of odontoblasts compared to osteoblasts?
What is the main difference in the anatomical relationship of odontoblasts compared to osteoblasts?
⭐️Which cellular feature is abundant in odontoblasts and contributes to their protein-secreting function?
⭐️Which cellular feature is abundant in odontoblasts and contributes to their protein-secreting function?
How do odontoblasts, osteoblasts, and cementoblasts differ in their intercellular connections?
How do odontoblasts, osteoblasts, and cementoblasts differ in their intercellular connections?
Which characteristic is common to odontoblasts, osteoblasts, and cementoblasts in relation to their cellular composition?
Which characteristic is common to odontoblasts, osteoblasts, and cementoblasts in relation to their cellular composition?
⭐️What specialized function do odontoblast processes serve within the dentin matrix?
⭐️What specialized function do odontoblast processes serve within the dentin matrix?
What is a common structural feature of odontoblasts that supports their role in matrix production?
What is a common structural feature of odontoblasts that supports their role in matrix production?
Which component distinguishes the dentin matrix produced by odontoblasts from those produced by osteoblasts?
Which component distinguishes the dentin matrix produced by odontoblasts from those produced by osteoblasts?
What is a key feature of the nucleus found in active odontoblasts?
What is a key feature of the nucleus found in active odontoblasts?
Which shared feature indicates the physiological role that odontoblasts, osteoblasts, and cementoblasts fulfill within their respective tissues?
Which shared feature indicates the physiological role that odontoblasts, osteoblasts, and cementoblasts fulfill within their respective tissues?
What is the function of Phosphophoryn?
What is the function of Phosphophoryn?
What does the Odontoblast secrete?
What does the Odontoblast secrete?
Where are ribosomes primarily found in odontoblast cells?
Where are ribosomes primarily found in odontoblast cells?
What is the role of ribosomes attached to the Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum in odontoblasts?
What is the role of ribosomes attached to the Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum in odontoblasts?
What function do free ribosomes in the cytoplasm of odontoblasts serve?
What function do free ribosomes in the cytoplasm of odontoblasts serve?
How do ribosomes support the overall health of dental tissue?
How do ribosomes support the overall health of dental tissue?
Why is the arrangement of ribosomes important for odontoblasts?
Why is the arrangement of ribosomes important for odontoblasts?
Where is the Ribosome located in the odontoblast?
Where is the Ribosome located in the odontoblast?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
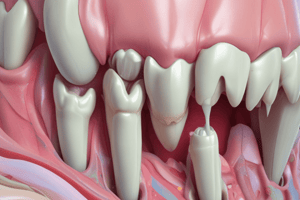
Odontoblast: The Dentin-Producing Cell
- Key Role: Odontoblasts are responsible for dentinogenesis, both during tooth development and aging.
- Dentin Formation: Odontoblasts form dentin and the dentinal tubules.
- Dentin: A Living Tissue: Odontoblasts reside within the dentinal tubules, making dentin a responsive tissue.
- Similarities to Other Cells: Odontoblasts share characteristics with osteoblasts (bone) and cementoblasts (cementum).
- Shared Features: These cells produce a matrix composed of collagen, proteins, and proteoglycans that undergo mineralization.
- Ultrastructural Similarities: All three cell types exhibit a well-developed rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER), Golgi complex, secretory granules, and numerous mitochondria.
- Protein-Secreting Characteristics: Their abundance of RNA and prominent nucleoli in the nucleus indicate their specialized role in protein synthesis.
- Morphological Differences: While osteoblasts and cementoblasts are polygonal or cuboidal, odontoblasts are tall and columnar.
- Cellular Embedding: Osteoblasts and cementoblasts become embedded in the matrix as osteocytes and cementocytes, respectively.
- Dentinal Tubule Formation: Odontoblasts leave behind a cellular process to form the dentinal tubule, with the cell body residing outside the mineralized tissue.
- Intercellular Communication: Lateral branches between odontoblast processes connect through canaliculi, facilitating communication and fluid/metabolite exchange.
- Active Odontoblast Structure: Active odontoblasts possess a large nucleus with multiple nucleoli, a central Golgi complex, numerous mitochondria, and a prominent RER.
- Protein Synthesis: Active odontoblasts mainly synthesize type I collagen, with small amounts of type V collagen, proteoglycans, dentin sialoprotein, and phosphophoryn.
- Phosphophoryn: Unique to Dentin: Phosphophoryn, a highly phosphorylated protein involved in mineralization, is exclusive to dentin.
- Enzymes: Odontoblasts produce acid phosphatase, potentially involved in resorbed material digestion, and alkaline phosphatase, linked to mineralization.
- Resting Odontoblast Characteristics: Resting or inactive odontoblasts have fewer organelles and may shorten, occurring after root development and eruption.
- Odontoblast and Nerve Interaction: Odontoblasts exhibit excitability, possess receptors for neuropeptides, contain thermosensitive TRP ion channels, and express voltage-gated sodium channels, suggesting direct interaction with dental nerves.
- Immune Role: Odontoblasts possess innate immune components and may recognize and respond to bacterial components, contributing to immune and pulp-dentine barrier functions.
Odontoblast: Master of Dentin
-
Key Role: Creates and maintains dentin, the hard tissue underlying enamel, throughout tooth development and life.
-
Structure: Tall, columnar cell with a large nucleus and a prominent Golgi apparatus.
-
Location: Resides in the dentin pulp complex, with its cell body outside the mineralized dentin.
-
Key Characteristics:
- Highly ordered rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER): Important for protein synthesis
- Prominent Golgi complex: Involved in packaging and secretion
- Secretory granules: Store and release molecules like dentin matrix proteins
- Numerous mitochondria: Provide energy for cell functions
-
Secretory Products:
- Primarily type I collagen: Provides structural framework for dentin
- Dentin sialoprotein (DSP): Important for dentin mineralization
- Phosphophoryn: A phosphorylated phosphoprotein that plays a key role in extracellular mineralization, unique to dentin.
- Acid phosphatase: A lysosomal enzyme potentially involved in breaking down resorbed dentin matrix.
- Alkaline phosphatase: Important for mineral deposition, its exact role in dentinogenesis is not fully understood.
-
Dentinal Tubules: The odontoblast leaves behind a cellular process which forms the dentinal tubule, a pathway through the dentin that connects the cell body to the dentin surface.
-
Intercellular Communication: Lateral branches of odontoblast processes connect via canaliculi, allowing fluid and metabolites to circulate within the dentin.
-
Functional States:
- Active odontoblast: Highly active in protein synthesis and dentin formation.
- Resting/Inactive odontoblast: Decreased organelle activity, may become shorter in length.
-
Potential Role in Immune Regulation: The presence of innate immune components in the odontoblast layer suggests a role in recognizing and responding to bacterial components, potentially acting as a barrier against infection.
-
Sensitivity and Communication:
- Excitability: Odontoblasts respond to stimuli, like temperature changes.
- Neuropeptide receptors: Odontoblasts express receptors for neuropeptides, allowing communication with nerves.
- Thermosensitive TRP ion channels: Detect temperature changes, contributing to pain perception.
- Voltage-gated sodium channels: Important for nerve impulse transmission.
-
Similarities with Osteoblasts and Cementoblasts: All three cell types create mineralized matrices and share similar ultrastructural features, but each produces a different type of tissue.
Ribosome Location in Odontoblasts
- Ribosomes are critical for protein synthesis
- In odontoblast cells, ribosomes are primarily located on the Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER) and in the cytoplasm.
- Ribosomes attached to the RER synthesize proteins involved in dentin formation.
- Free ribosomes in the cytoplasm likely synthesize proteins for use within the odontoblast itself.
- The high number of ribosomes attached to the RER reflect odontoblast's high secretory capacity.
- Odontoblasts secrete collagen and other proteins that form the dentin matrix.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.