Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following is NOT a technique used in brain destruction studies to produce focused damage?
Which of the following is NOT a technique used in brain destruction studies to produce focused damage?
- Cold
- Heat
- Tiny electrodes
- Magnetic stimulation (correct)
What is the primary function of neuropsychological tests in the context of brain destruction studies?
What is the primary function of neuropsychological tests in the context of brain destruction studies?
- To determine the genetic basis of brain disorders
- To identify the specific brain area responsible for a particular cognitive function
- To assess the extent of brain damage and its impact on cognitive abilities (correct)
- To stimulate specific brain areas and observe their effects on behavior
What is the main difference between an ablation and a lesion?
What is the main difference between an ablation and a lesion?
- Ablation involves removing a portion of the brain, while a lesion involves creating a focused area of damage (correct)
- Lesions are only used in animal studies, while ablations are used in human studies
- Lesions are used to stimulate brain activity, while ablations are used to destroy brain tissue
- Ablation is a more focused technique than a lesion
Which of the following examples best illustrates a surgical lesion in a human study?
Which of the following examples best illustrates a surgical lesion in a human study?
In what way can neuropsychological tests be considered standardized?
In what way can neuropsychological tests be considered standardized?
Which of the following is NOT a disadvantage of CT scans?
Which of the following is NOT a disadvantage of CT scans?
What is the main difference between an EEG and fMRI?
What is the main difference between an EEG and fMRI?
What is the primary application of neuropsychological testing in clinical/medical evaluations?
What is the primary application of neuropsychological testing in clinical/medical evaluations?
Which of the following is an advantage of using fMRI over other brain imaging techniques?
Which of the following is an advantage of using fMRI over other brain imaging techniques?
How can neuropsychological testing be used to infer the extent of brain damage?
How can neuropsychological testing be used to infer the extent of brain damage?
Which of the following is most closely related to understanding ‘localization of function’ in brain studies?
Which of the following is most closely related to understanding ‘localization of function’ in brain studies?
What is the primary function of neural networks?
What is the primary function of neural networks?
The Wilder Penfield experiment involved stimulating the brain of awake patients during brain surgery. What was the major objective of this experiment?
The Wilder Penfield experiment involved stimulating the brain of awake patients during brain surgery. What was the major objective of this experiment?
What is the primary benefit of using micro-electrodes in brain research?
What is the primary benefit of using micro-electrodes in brain research?
Based on the text, which of the following statements about fMRI is TRUE?
Based on the text, which of the following statements about fMRI is TRUE?
Why is it important to study the brain using different methods?
Why is it important to study the brain using different methods?
Which lobe of the brain is primarily responsible for auditory processing?
Which lobe of the brain is primarily responsible for auditory processing?
What is the primary function of the prefrontal cortex?
What is the primary function of the prefrontal cortex?
What is the role of association areas of the brain?
What is the role of association areas of the brain?
Which of the following is NOT a function of the frontal lobe?
Which of the following is NOT a function of the frontal lobe?
Which of the following is a consequence of damage to the prefrontal cortex?
Which of the following is a consequence of damage to the prefrontal cortex?
What is the primary function of the parietal lobe?
What is the primary function of the parietal lobe?
What is the primary function of Broca's area?
What is the primary function of Broca's area?
Which lobe of the brain is responsible for processing information related to touch, temperature, and pain?
Which lobe of the brain is responsible for processing information related to touch, temperature, and pain?
Which of the following best describes the "default network" in the brain?
Which of the following best describes the "default network" in the brain?
Which brain imaging technique would be most suitable for studying the relationship between the amygdala and hippocampus during emotional processing?
Which brain imaging technique would be most suitable for studying the relationship between the amygdala and hippocampus during emotional processing?
Which of the following statements about primary areas of the brain is true?
Which of the following statements about primary areas of the brain is true?
What is the primary characteristic that distinguishes the human brain from the brains of other animals?
What is the primary characteristic that distinguishes the human brain from the brains of other animals?
Which of the following is NOT a major function of the frontal lobe?
Which of the following is NOT a major function of the frontal lobe?
What is the primary function of neurons?
What is the primary function of neurons?
What is a key characteristic of the cerebral cortex?
What is a key characteristic of the cerebral cortex?
Which of the following is NOT a technique used to study the brain?
Which of the following is NOT a technique used to study the brain?
Which of the following is NOT a function typically associated with the left hemisphere of the brain?
Which of the following is NOT a function typically associated with the left hemisphere of the brain?
Damage to Broca's area, located in the frontal lobe, would most likely result in:
Damage to Broca's area, located in the frontal lobe, would most likely result in:
What is the primary role of the corpus callosum?
What is the primary role of the corpus callosum?
Which of the following statements accurately reflects the difference between the left and right hemispheres?
Which of the following statements accurately reflects the difference between the left and right hemispheres?
Which of the following skills would you expect to be more strongly associated with the right hemisphere?
Which of the following skills would you expect to be more strongly associated with the right hemisphere?
Damage to Wernicke's area, located in the temporal lobe, would primarily affect a person's ability to:
Damage to Wernicke's area, located in the temporal lobe, would primarily affect a person's ability to:
Which of the following statements accurately describes the distinction between Broca's and Wernicke's area?
Which of the following statements accurately describes the distinction between Broca's and Wernicke's area?
The statement that 'both hemispheres have the capacity to perform a given function' suggests that:
The statement that 'both hemispheres have the capacity to perform a given function' suggests that:
What is the main function of the corpus callosum?
What is the main function of the corpus callosum?
What is the primary reason for performing a commissurotomy?
What is the primary reason for performing a commissurotomy?
In split-brain patients, which visual field is processed by the right hemisphere?
In split-brain patients, which visual field is processed by the right hemisphere?
What is the defining characteristic of a split-brain patient?
What is the defining characteristic of a split-brain patient?
In split-brain patients, what happens when an object is presented in the right visual field?
In split-brain patients, what happens when an object is presented in the right visual field?
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of split-brain patients?
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of split-brain patients?
What is the key difference between how the brain processes visual information and how it processes other sensory information?
What is the key difference between how the brain processes visual information and how it processes other sensory information?
How can split-brain patients be used to study hemispheric organization?
How can split-brain patients be used to study hemispheric organization?
What is the primary function of the optic chiasm in the context of visual information processing?
What is the primary function of the optic chiasm in the context of visual information processing?
What is the main reason for the separation of information processing between the left and right hemispheres of the brain in split-brain patients?
What is the main reason for the separation of information processing between the left and right hemispheres of the brain in split-brain patients?
Flashcards
Localization of Function
Localization of Function
Specific areas of the brain support specific cognitive functions.
Ablation
Ablation
Removal of a portion of the brain, typically in animal studies.
Lesion
Lesion
Focused damage to a specific area of the brain, often caused by electrodes.
Neuropsychology
Neuropsychology
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neuropsych tests
Neuropsych tests
Signup and view all the flashcards
Severity of Impairments
Severity of Impairments
Signup and view all the flashcards
Working Memory
Working Memory
Signup and view all the flashcards
Digit Span
Digit Span
Signup and view all the flashcards
Default Network
Default Network
Signup and view all the flashcards
fMRI Method
fMRI Method
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neurons
Neurons
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cerebral Cortex
Cerebral Cortex
Signup and view all the flashcards
Functional Categorization
Functional Categorization
Signup and view all the flashcards
Parietal Lobe
Parietal Lobe
Signup and view all the flashcards
Frontal Lobe Functions
Frontal Lobe Functions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hemispheric Functions
Hemispheric Functions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Occipital Lobe
Occipital Lobe
Signup and view all the flashcards
Temporal Lobe
Temporal Lobe
Signup and view all the flashcards
Broca's Area
Broca's Area
Signup and view all the flashcards
Prefrontal Cortex
Prefrontal Cortex
Signup and view all the flashcards
Primary Somatosensory Cortex
Primary Somatosensory Cortex
Signup and view all the flashcards
Primary Auditory Cortex
Primary Auditory Cortex
Signup and view all the flashcards
Association Cortices
Association Cortices
Signup and view all the flashcards
Implications of Prefrontal Damage
Implications of Prefrontal Damage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stimulation
Stimulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Wilder Penfield
Wilder Penfield
Signup and view all the flashcards
Invasive Stimulation
Invasive Stimulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Non-invasive Methods
Non-invasive Methods
Signup and view all the flashcards
CAT/CT
CAT/CT
Signup and view all the flashcards
Advantages of CAT/CT
Advantages of CAT/CT
Signup and view all the flashcards
Disadvantages of CAT/CT
Disadvantages of CAT/CT
Signup and view all the flashcards
MRI
MRI
Signup and view all the flashcards
Advantages of MRI
Advantages of MRI
Signup and view all the flashcards
Disadvantages of MRI
Disadvantages of MRI
Signup and view all the flashcards
EEG
EEG
Signup and view all the flashcards
Advantages of EEG
Advantages of EEG
Signup and view all the flashcards
Disadvantages of EEG
Disadvantages of EEG
Signup and view all the flashcards
fMRI
fMRI
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neural Networks
Neural Networks
Signup and view all the flashcards
Broca’s Area
Broca’s Area
Signup and view all the flashcards
Wernicke’s Area
Wernicke’s Area
Signup and view all the flashcards
Corpus Callosum
Corpus Callosum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Left Hemisphere Functions
Left Hemisphere Functions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Right Hemisphere Functions
Right Hemisphere Functions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hemispheric Specialization
Hemispheric Specialization
Signup and view all the flashcards
Role of Neurons
Role of Neurons
Signup and view all the flashcards
Contralateral Control
Contralateral Control
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vision Exception
Vision Exception
Signup and view all the flashcards
Commissurotomy
Commissurotomy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Split Brain Patients
Split Brain Patients
Signup and view all the flashcards
Split Brain Phenomenon
Split Brain Phenomenon
Signup and view all the flashcards
Right Visual Field
Right Visual Field
Signup and view all the flashcards
Left Visual Field
Left Visual Field
Signup and view all the flashcards
Task Performance in Split Brain
Task Performance in Split Brain
Signup and view all the flashcards
Michael Gazzaniga
Michael Gazzaniga
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Cognitive Psychology - PSYC 365 - Cognitive Neuroscience
- The course is Cognitive Psychology, PSYC 365, specifically focusing on cognitive neuroscience.
- Objectives include defining and identifying neuron components, describing their role in representation, explaining brain study techniques, outlining cortical structures and functions, and comparing/contrasting hemispheric functions.
What are Neurons?
- Neurons are nerve cells.
- Their function is to create and transmit information.
- Neurons have characteristics including sending and receiving electrical signals.
- Neurons are interconnected in networks.
- On average, each neuron has 10,000 connections.
- The brain is a 3.5 lb structure.
- Neurons are the building blocks of the brain.
Three Components of a Neuron
- Dendrites: Receive messages from other neurons.
- Cell Body (Soma): Combines and processes incoming signals from dendrites. It contains vital cell structures like the nucleus and DNA.
- Axons: Send signals (electrical impulses) to other neurons, muscles, or glands.
Neural Representation
- Neural representation is the way the nervous system represents stimuli, not a direct contact.
- Sight is represented by light, and sound by sound waves.
- Taste and smell are represented by chemicals.
- Processing stimuli from sensory neurons triggers an action potential in neurons.
- Multiple brain regions work together for accurate representation.
Theories of Neural Representation
- Specificity Coding: Each stimulus is represented by a specialized neuron (e.g., "grandmother cell"). Problems include insufficient neurons and lack of evidence from single-cell recordings regarding new objects.
- Population Coding: Each stimulus is represented by a pattern of firing across many neurons. It has supporting evidence. Problems include the need for numerous neurons for all functions.
- Sparse Coding: Each stimulus is represented by a pattern of firing across a small subset of neurons (many not firing). This theory has reliable evidence and is considered most reliable.
Major Techniques for Studying the Brain
- Destruction:
- Animal studies: Ablation (removal), lesions (focused damage) using electrodes or chemicals
- Human studies: Lesions from accidents/diseases (e.g., stroke), or surgical lesions to control seizures
- Neuropsychology: Used with human tests. Assessing simple-to-complex functions, impairments, and severity. Standardized tests help.
- Techniques are used because destruction and stimulation of brain regions help see their effects in behavior.
- Stimulation: Mild electric current used; enhancing or disrupting cognitive functions. Used in invasive (e.g., brain surgery) or some less invasive ways.
Specific Brain Imaging Techniques
-
CAT/CT: Computerized axial tomography, X-Ray imaging; good for localized tumors/lesions but poor spatial resolution and exposure to radiation.
-
MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; shows brain structures, reveals soft tissue abnormalities, great spatial resolution, non-invasive.
-
EEG: Electroencephalography; Records electrical activity of large groups of neurons; excellent temporal resolution (milliseconds), but poor spatial resolution and sensitive to movement.
-
fMRI: Functional magnetic resonance imaging; Measures blood flow changes correlating with oxygen usage; indirect measure of brain activity/cognition, inferring active areas based on oxygen use, similar advantages/disadvantages to MRI.
fMRI: Connectivity
- Brain areas connect and work together to form cognitive processes.
- Connections can be structural or functional.
- Neural networks exist where brain areas consistently communicate, extending sparse/distributed coding.
fMRI: Brain Networks
- Default network: Active brain areas during "rest" or mind wandering. Thinking about the past or future, ourselves and others.
Exercise: Naming a Technique for a Study
- fMRI would be a best method for a study of the amygdala and hippocampus during the processing of emotional information.
Cerebral Cortex
- The cerebral cortex is the top wrinkly layer of the brain, containing ~80% of neurons.
- Its ratio to the size of the brain differentiates humans from other mammals.
- Categorization groups similar functions into cortical areas. Some functions involve multiple areas.
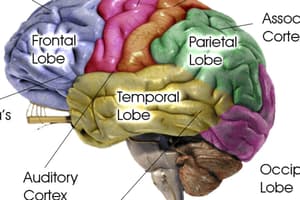
Major Functions of Four Lobes
- Frontal: Many functions (speech, movement, planning, emotion).
- Parietal: Somatosensory (touch, temp) and high level vision.
- Temporal: Auditory and high level visual processing, memory.
- Occipital: Visual (color, form, spatial).
Primary Areas of Four Lobes
- Areas in the cortex where sensory information is first processed. The location is critical to the function.
Association Areas
- These areas exist in all four lobes, and they are involved in many higher mental functions. These areas combine multiple sensory/motor systems to achieve sophisticated outcomes eg language, problem-solving, memory encoding and recall.
Major Functions of Frontal Cortex
- Broca's area: Speech production.
- Motor cortex: Muscle movements.
- Prefrontal cortex: Executive functions (setting goals, planning, emotion regulation, self-awareness). If damaged, problems predict/produce actions, impulse control, and empathy. Also, recall of a sequence or prior learning.
Corpus Callosum & Split-Brain
- The corpus callosum is a nerve bundle for information transfer.
- In split-brain patients, the corpus callosum is severed.
- This can lead to unique performance patterns. Information in a specific visual field is processed more appropriately by the opposite side of the brain.
Commsissurotomy
- Commisurotomy is a technique to disconnect both hemispheres of the brain, in patients with severe epilepsy, allowing examination of the role of each separate brain region.
Split Brain Phenomenon
- In split-brain patients, hemispheres cannot communicate.
- Information from one visual field is only processed by the opposite hemisphere.
Lessons from Split-Brain Phenomenon
- The split-brain effect can be helpful to understand brain functionality and how hemispheres are interconnected.
- The method may not always be consistent, as functional abilities may be limited when specific areas are severed or limited by prior injury or conditions, or by other factors affecting brain functionality.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.