Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following is NOT a way of studying the brain?
Which of the following is NOT a way of studying the brain?
- Electroencephalogram (EEG)
- Cytoarchitecture
- Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)
- Phrenology (correct)
What is the main function of the sodium-potassium pump in a neuron?
What is the main function of the sodium-potassium pump in a neuron?
- To create a concentration gradient for sodium and potassium ions across the cell membrane. (correct)
- To generate action potentials by rapidly transporting potassium ions out of the cell.
- To create a membrane potential that is more negative than the resting potential.
- To maintain the neuron's resting potential by pumping sodium ions into the cell and potassium ions out.
What is the main difference between an action potential and a graded potential?
What is the main difference between an action potential and a graded potential?
- Graded potentials are all-or-nothing events, while action potentials are not.
- Graded potentials are faster than action potentials.
- Action potentials are faster than graded potentials.
- Action potentials are all-or-nothing events, while graded potentials are not. (correct)
What is the role of the myelin sheath in the transmission of action potentials?
What is the role of the myelin sheath in the transmission of action potentials?
Which of the following is NOT a feature of an excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP)?
Which of the following is NOT a feature of an excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP)?
Which of the following is a characteristic of the refractory period in a neuron?
Which of the following is a characteristic of the refractory period in a neuron?
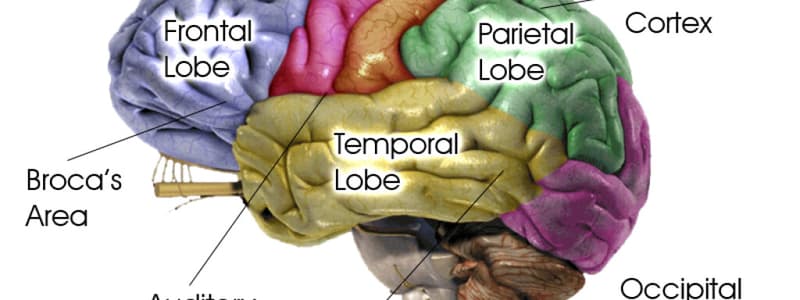
What is the main function of the parietal lobe?
What is the main function of the parietal lobe?
Which of the following is NOT a type of somatosensation?
Which of the following is NOT a type of somatosensation?
What is the role of the basilar membrane in the inner ear?
What is the role of the basilar membrane in the inner ear?
Which of the following is a genetic condition that results in a masculine phenotype in XX individuals?
Which of the following is a genetic condition that results in a masculine phenotype in XX individuals?
Which brain region is involved in the processing of sexual behavior?
Which brain region is involved in the processing of sexual behavior?
What is the neurotransmitter associated with pair bonding and social attachment?
What is the neurotransmitter associated with pair bonding and social attachment?
Which of the following cognitive abilities is typically associated with males?
Which of the following cognitive abilities is typically associated with males?
According to Savic and Lindstromin's (2008) research, which of the following statements is true regarding the amygdala in gay men?
According to Savic and Lindstromin's (2008) research, which of the following statements is true regarding the amygdala in gay men?
Which of the following brain regions is known to be larger in homosexual men than in heterosexual men?
Which of the following brain regions is known to be larger in homosexual men than in heterosexual men?
What is the proposed explanation for the differences in brain structures between heterosexual and homosexual individuals?
What is the proposed explanation for the differences in brain structures between heterosexual and homosexual individuals?
Flashcards
Dualism
Dualism
The belief that mind and body are separate entities that influence behavior.
Cytoarchitecture
Cytoarchitecture
Study of the cellular structure and organization of the brain.
Neuropsychology
Neuropsychology
The study of how brain lesions affect behavior and cognitive functions.
Action potential
Action potential
Signup and view all the flashcards
Resting potential
Resting potential
Signup and view all the flashcards
Myelinated axons
Myelinated axons
Signup and view all the flashcards
EPSP
EPSP
Signup and view all the flashcards
Refractory period
Refractory period
Signup and view all the flashcards
Occipital lobe
Occipital lobe
Signup and view all the flashcards
Somatosensation
Somatosensation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Synesthesia
Synesthesia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Basilar membrane
Basilar membrane
Signup and view all the flashcards
SCN
SCN
Signup and view all the flashcards
Doppler effect
Doppler effect
Signup and view all the flashcards
Parkinson’s disease
Parkinson’s disease
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Theories of the Brain
- Aristotle believed the heart was the center of thought, crucial for life, sensitive to touch, and emotionally affected.
- Modern understanding posits that invertebrates have sensations but lack brains, implying the brain isn't essential for life and is not touch or emotionally sensitive.
- Descartes' dualism proposed that the mind and body are separate, with the brain acting like a machine.
- Gall proposed the size of brain areas correlates with their influence.
- The brain is studied using methods like cytoarchitecture (cell connectivity), neuropsychology (brain lesion studies), and imaging techniques (MRI, fMRI, EEG, ERP), and stimulating techniques (TMS).
Ways of Studying the Brain
- Neuropsychology: focuses on brain lesions and their effects on behavior.
- Imaging techniques:
- MRI provides good spatial resolution and poor temporal resolution, suitable for anatomical studies.
- fMRI measures brain activity by changes in blood flow; it has good spatial resolution and poor temporal resolution.
- EEG uses electrodes to measure electrical brain activity, offering good temporal resolution but poor spatial resolution.
- ERP measures brief electrical changes related to sensory or cognitive processing, offering both good temporal and spatial resolution.
- Stimulating techniques:
- TMS delivers magnetic pulses to stimulate specific brain areas, providing good spatial and temporal resolution.
Action Potential
- Action potentials are rapid, all-or-nothing electrical signals generated at the axon hillock and propagated along the axon.
- Myelinated axons conduct action potentials faster than unmyelinated axons.
- EPSPs (Excitatory Postsynaptic Potentials) are graded potentials.
- IPSPs (Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potentials) are graded potentials.
- Sodium-potassium pumps maintain a resting potential.
Somatosensation
- Haptic (touch):
- Meissner's corpuscles detect light touch. Rapid adaptation
- Pacinian corpuscles detect vibration. Rapid adaptation
- Ruffini corpuscles detect sustained pressure. Rapid adaptation
- Nociception (pain and temperature): Slow adaptation
- Proprioception (body awareness): Rapid adaptation
Sound
- Sound is detected by sensory receptors in the inner ear.
- Loudness is determined by amplitude (number of air molecule vibrations).
- Frequency relates to pitch.
- The Doppler effect demonstrates changes in perceived pitch with changes in distance or frequency, like police sirens.
Other Brain Areas, Functions & Diseases
- Brodmann areas classify brain regions; they have different functions
- Limbic system includes the amygdala, hippocampus, hypothalamus, responsible for emotions and memory
- Sleep stages include REM and nREM, with different brain activity and functions.
- Genetic mutations like Turner's syndrome (XO) and CAH can cause disruptions in sexual development and behavior.
- Damage to the brain affects sensory, motor and cognitive functions.
- Oxytocin, a hormone, is linked to pair bonding.
- Differences in brain structure have been observed between gay and straight men and women.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.