Podcast
Questions and Answers
MRI is inferior to CT for evaluating white matter disease.
MRI is inferior to CT for evaluating white matter disease.
False (B)
Functional brain imaging techniques like fMRI and PET are widely used in clinical settings.
Functional brain imaging techniques like fMRI and PET are widely used in clinical settings.
False (B)
Neuropsychological testing is more widely used now than it was previously.
Neuropsychological testing is more widely used now than it was previously.
False (B)
Electroencephalogram (EEG) studies have a significant role in the diagnosis of delirium.
Electroencephalogram (EEG) studies have a significant role in the diagnosis of delirium.
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) examination is essential only in cases of dementia.
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) examination is essential only in cases of dementia.
Genetic testing plays a crucial role in diagnosing a wide range of disorders.
Genetic testing plays a crucial role in diagnosing a wide range of disorders.
Brain biopsy is commonly performed for assessing Alzheimer's disease.
Brain biopsy is commonly performed for assessing Alzheimer's disease.
Longitudinal scans with CT or MRI can help map progressive changes in a patient’s condition.
Longitudinal scans with CT or MRI can help map progressive changes in a patient’s condition.
Clouding of consciousness defines amnesia.
Clouding of consciousness defines amnesia.
A specific deficit in episodic memory is a hallmark of amnestic syndrome.
A specific deficit in episodic memory is a hallmark of amnestic syndrome.
Physical examination plays a minimal role in the assessment of neuropsychiatric patients.
Physical examination plays a minimal role in the assessment of neuropsychiatric patients.
An acute onset of cognitive impairment suggests a possible diagnosis of dementia.
An acute onset of cognitive impairment suggests a possible diagnosis of dementia.
The presence of impaired cognition can help a patient provide a full and accurate history.
The presence of impaired cognition can help a patient provide a full and accurate history.
Investigations for neuropsychiatric evaluation are generally minimal and straightforward.
Investigations for neuropsychiatric evaluation are generally minimal and straightforward.
Familial history is often irrelevant in assessing cognitive impairment.
Familial history is often irrelevant in assessing cognitive impairment.
Pseudodementia can present as a result of depression in the elderly.
Pseudodementia can present as a result of depression in the elderly.
The Argyll-Robertson pupil is associated with vitamin B12 deficiency.
The Argyll-Robertson pupil is associated with vitamin B12 deficiency.
An informant can provide valuable information when assessing a neuropsychiatric patient.
An informant can provide valuable information when assessing a neuropsychiatric patient.
Flashcards
Structural Brain Imaging
Structural Brain Imaging
Imaging techniques like CT and MRI used to identify structural abnormalities in the brain, such as tumors, strokes, or brain atrophy.
Functional Brain Imaging
Functional Brain Imaging
A type of brain imaging that measures brain activity by detecting changes in blood flow.
Neuropsychological Testing
Neuropsychological Testing
Neuropsychological tests are administered to assess cognitive function and measure its severity and progression, especially when brain imaging reveals abnormalities.
EEG
EEG
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lumbar Puncture
Lumbar Puncture
Signup and view all the flashcards
Genetic Testing
Genetic Testing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Brain Biopsy
Brain Biopsy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Delirium
Delirium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Amnesia
Amnesia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dementia
Dementia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Amnestic Syndrome
Amnestic Syndrome
Signup and view all the flashcards
Functional Impairment
Functional Impairment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Medical History
Medical History
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mental State Examination
Mental State Examination
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neurological Examination
Neurological Examination
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cognitive Testing
Cognitive Testing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blood Tests
Blood Tests
Signup and view all the flashcards
Specialty Consultation
Specialty Consultation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
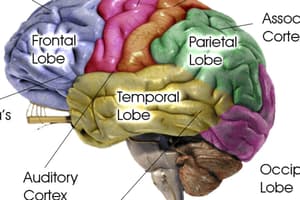
Brain Imaging
- Structural brain imaging is performed using CT or MRI to identify focal and diffuse pathologies; longitudinal scans help track clinical progression.
- MRI outperforms CT for evaluating white matter disease and volumetric measurements.
- Functional brain imaging techniques like fMRI, MRS, SPECT, or PET are often utilized in research but are less common in clinical settings.
Neuropsychological Testing
- Although less frequent due to advanced brain imaging, neuropsychological tests remain valuable in assessing cognitive impairments and measuring their severity and progression.
Additional Methods
- EEG studies can be pivotal for diagnosing conditions like delirium, prion disease, non-convulsive status epilepticus, and stupor.
- CSF examination via lumbar puncture is crucial if inflammation or infection is suspected; it is also gaining traction in dementia evaluation.
- Genetic testing is integral for diagnosing specific familial disorders linked to known genes, such as Huntington's chorea.
- Brain biopsy, especially of the right frontal lobe, is a last-resort diagnostic method for unexplained cognitive impairments or suspected prion disease, balancing risks against potential diagnostic benefits.
Assessment of the Neuropsychiatric Patient
- Initial assessment of cognitive function covers amnesia, delirium, and dementia, with clouding of consciousness being a key indicator of delirium.
- If consciousness is intact, consider amnesia, dementia, or functional impairment as primary diagnostic categories.
- Amnestic syndrome is characterized by episodic memory deficits and may present in individuals with alcohol dependence.
- Functional causes, particularly depression in the elderly (which can mimic dementia), should be systematically assessed as they may masquerade as memory impairments.
History and Mental State Examination
- A comprehensive history is essential in neuropsychiatric assessment, especially when cognitive impairment limits patient self-reporting.
- Key historical elements include onset, duration, and progression of cognitive issues; acute onset often suggests delirium or underlying conditions like subdural hematoma.
- Past medical and family histories are crucial for identifying pre-existing conditions or genetic links that could contribute to cognitive dysfunction.
Physical Examination
- A thorough physical examination is necessary, focusing on the nervous system and identifying peripheral signs indicative of systemic disease or alcohol misuse.
- Specific physical signs, such as the Argyll-Robertson pupil or optic disc pallor, may provide critical diagnostic clues.
Investigations
- Investigative approach depends on findings from history, mental state, and physical examinations; a core set of cognitive and blood tests is typically included in dementia evaluations.
- In atypical or challenging cases, especially in younger patients, more extensive investigations may require consultation with neurologists, physicians, or neurosurgeons.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.