Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the purpose of behaviors like nest building and migration in organisms?
What is the purpose of behaviors like nest building and migration in organisms?
- To adapt to changing environments (correct)
- To directly respond to individual stimuli
- To maintain homeostasis
- To control thought processes
Which of the following terms refers to the responsiveness of living cells to environmental stimuli?
Which of the following terms refers to the responsiveness of living cells to environmental stimuli?
- Homeostasis
- Conditioning
- Habituation
- Irritability (correct)
What does the Central Nervous System (CNS) primarily control?
What does the Central Nervous System (CNS) primarily control?
- Autonomous regulation of gastrointestinal functions
- Regulating restorative functions
- Thought, emotion, and hormone regulation (correct)
- Conscious movements
Which part of a neuron receives signals from other neurons?
Which part of a neuron receives signals from other neurons?
In neuron communication, what are synapses responsible for?
In neuron communication, what are synapses responsible for?
How does learning enable individuals to adapt to changing environments?
How does learning enable individuals to adapt to changing environments?
What is the main function of the nervous system?
What is the main function of the nervous system?
Why did the nervous system evolve according to the text?
Why did the nervous system evolve according to the text?
How does the nervous system of higher vertebrates differ from lower invertebrates?
How does the nervous system of higher vertebrates differ from lower invertebrates?
Which form of response involves changes in the environment serving as stimuli?
Which form of response involves changes in the environment serving as stimuli?
What is the function of cytoplasm in lower organisms like algae and protozoans, as mentioned in the text?
What is the function of cytoplasm in lower organisms like algae and protozoans, as mentioned in the text?
What distinguishes centralized systems from diffuse systems in terms of nervous system organization?
What distinguishes centralized systems from diffuse systems in terms of nervous system organization?
Study Notes
Nervous System: Organized Group of Cells Specializing in Electrochemical Stimuli Transmission
The nervous system is a vital component of all living organisms, specialized for the conduction of electrochemical stimuli from sensory receptors. It enables animals to detect changes in their internal and external environments, analyze these changes, and respond appropriately to ensure survival. The nervous system evolved as a response to the need for speedy reactions to environmental changes, surpassing chemical communication between cells' ability to react quickly enough. There are two main types of nervous systems: diffuse and centralized. In lower invertebrates with diffuse systems, neurons are distributed throughout the organism without a distinct brain or spinal cord, while higher vertebrates possess centralized systems that have well-developed brains and spinal cords for coordinating information and directing responses.
Form and Function of Nervous Systems
Stimulus-Response Coordination
The simplest form of response is the direct stimulus-response reaction, where changes in the environment serve as the stimuli, and organisms respond accordingly. Lower organisms like algae and protozoans exhibit nervous system-like behavior through the responsiveness of their cytoplasm, serving functions similar to a true nervous system.
Initiating Functions
Organisms with a nervous system can perform various beneficial behaviors, such as exploratory or appetitive behaviors, nest building, and migration. Although these activities are advantageous for species survival, they are often triggered by collective needs rather than direct responses to individual stimuli.
Learned Behavior
Learning enables individuals to develop complex behaviors beyond homeostatic and initiating functions. This includes conditioning, habituation, sensitization, and classical and instrumental learning, allowing animals to adapt to changing environments.
Intracellular Systems
All living cells possess some level of responsiveness to environmental stimuli, expressed as electrical, chemical, or mechanical changes known as irritability. These responses can lead to various outcomes such as secretion, muscle contraction, plant stem bending, and whiplike "hairs" (cilia) movement by ciliated cells.
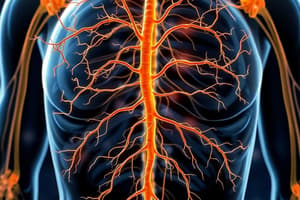
Structure and Function of the Nervous System
Central Nervous System (CNS) and Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
The CNS comprises the brain and spinal cord, responsible for controlling thought, movement, emotion, breathing, heart rate, hormones, and body temperature. On the other hand, the PNS includes all nerves outside the CNS, divided into the voluntary somatic nervous system (controlling conscious movements), involuntary parasympathetic nervous system (regulating restorative functions), sympathetic nervous system (preparing the body for activity), and enteric nervous system (autonomously regulating gastrointestinal functions).
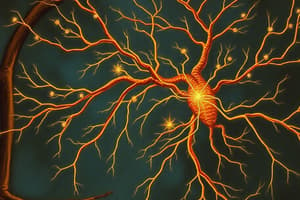
Neuron Communication
Neurons, also called nerve cells, transmit information through electrical signals generated by ion channels in the cell membrane. They receive signals at dendrites, process them in the cell body, and send signals via axons to other neurons, muscles, or glands. Synapses, junctions between neurons or between a neuron and an effector cell, facilitate transmission across short distances within the nervous system.
In summary, the nervous system plays a crucial role in enabling animals to detect and respond to both internal and external changes, ensuring the necessary adaptations for survival. With its complex organization of neurons and efficient means of transmitting electrochemical signals, it allows for rapid decision-making and execution of actions essential for life on Earth.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
Explore the organization and function of the nervous system, a vital component specialized in transmitting electrochemical stimuli for detecting and responding to environmental changes. Learn about the structure of the central and peripheral nervous systems, neuron communication, and how different organisms exhibit nervous system-like behaviors.