Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which intrinsic muscle is responsible for abducting the big toe?
Which intrinsic muscle is responsible for abducting the big toe?
- Abductor hallucis (correct)
- Flexor digitorum brevis
- Adductor hallucis
- Extensor digitorum brevis
What function does the tibialis anterior muscle serve?
What function does the tibialis anterior muscle serve?
- Dorsiflexes and inverts the foot (correct)
- Dorsiflexes and everts the foot
- Plantarflexes and inverts the foot
- Plantarflexes and everts the foot
Which layer of the plantar intrinsic muscles includes the lumbricals?
Which layer of the plantar intrinsic muscles includes the lumbricals?
- Fourth layer (Deep)
- Third layer
- First layer (Superficial)
- Second layer (correct)
Which muscle assists in flexing the proximal phalanx of the little toe?
Which muscle assists in flexing the proximal phalanx of the little toe?
The plantar interossei muscles primarily perform which action?
The plantar interossei muscles primarily perform which action?
Study Notes
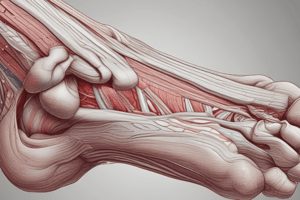
Overview of the Muscles of the Foot
- The foot contains 20 intrinsic muscles and numerous extrinsic muscles, playing key roles in movement and stability.
Intrinsic Muscles
-
Dorsal Muscles
- Extensor digitorum brevis
- Assists in extending the toes.
- Extensor hallucis brevis
- Assists in extending the big toe.
- Extensor digitorum brevis
-
Plantar Muscles (Divided into four layers)
-
First Layer (Superficial)
- Abductor hallucis: Abducts the big toe.
- Flexor digitorum brevis: Flexes the middle phalanges of toes 2-5.
- Abductor digiti minimi: Abducts and flexes the little toe.
-
Second Layer
- Quadratus plantae: Assists in flexing toes 2-5.
- Lumbricals: Flex the metatarsophalangeal joints and extend the interphalangeal joints.
-
Third Layer
- Flexor hallucis brevis: Flexes the proximal phalanx of the big toe.
- Adductor hallucis: Adducts the big toe.
- Flexor digiti minimi brevis: Flexes the proximal phalanx of the little toe.
-
Fourth Layer (Deep)
- Dorsal interossei: Abducts toes 2-4; assists in flexing.
- Plantar interossei: Adducts toes 3-5; assists in flexing.
-
Extrinsic Muscles
- Muscles originating in the leg that affect foot movement:
- Tibialis anterior: Dorsiflexes and inverts the foot.
- Extensor hallucis longus: Extends the big toe; assists in dorsiflexion.
- Extensor digitorum longus: Extends toes 2-5; dorsiflexes.
- Fibularis (peroneus) longus and brevis: Evert the foot and assist in plantarflexion.
- Tibialis posterior: Plantarflexes and inverts the foot, supports the arch.
Functions and Importance
- Provide stability and balance during standing and walking.
- Assist in the actions of walking, running, and jumping by controlling toe movements.
- Maintain the arches of the foot, aiding shock absorption and weight distribution.
Overview of the Muscles of the Foot
- The foot contains 20 intrinsic muscles located within the foot itself, plus numerous extrinsic muscles that originate in the leg but influence foot movement.
- These muscles play a crucial role in movement, stability, and overall foot function.
Intrinsic Foot Muscles
- Dorsal Muscles (located on the top of the foot)
- Extensor digitorum brevis: Assists in extending the toes (pointing them upwards).
- Extensor hallucis brevis: Assists in extending the big toe.
- Plantar Muscles (located on the sole of the foot)
- Four Layers: Muscles are arranged in four layers, with each layer contributing to specific foot motions.
- First Layer (Superficial):
- Abductor hallucis: Moves the big toe away from the midline of the foot.
- Flexor digitorum brevis: Bends the middle section of toes 2-5 downwards.
- Abductor digiti minimi: Moves the little toe away from the midline and bends it downwards.
- Second Layer:
- Quadratus plantae: Assists in bending toes 2-5 downwards.
- Lumbricals: Bend the toes at the base and straighten them at the other joints.
- Third Layer:
- Flexor hallucis brevis: Bends the big toe at its base.
- Adductor hallucis: Moves the big toe towards the middle of the foot.
- Flexor digiti minimi brevis: Bends the little toe at its base.
- Fourth Layer (Deep):
- Dorsal interossei: Move toes 2-4 away from the midline of the foot and assist in bending them.
- Plantar interossei: Move toes 3-5 towards the midline of the foot and assist in bending them.
Extrinsic Foot Muscles
- Muscles located in the leg that influence foot movement:
- Tibialis anterior: Lifts the foot upwards and turns it inwards.
- Extensor hallucis longus: Straightens the big toe and assists in lifting the foot upwards.
- Extensor digitorum longus: Straightens toes 2-5 and lifts the foot upwards.
- Fibularis (peroneus) longus and brevis: Turn the foot outwards and assist in pointing the foot downwards.
- Tibialis posterior: Points the foot downwards and turns it inwards, also supports the arch of the foot.
Functions and Importance
- Stability and Balance: Muscles provide stability during standing and walking, preventing falls and maintaining balance.
- Movement Control: Muscles control toe movements, essential for walking, running, and jumping.
- Arch Support: Muscles maintain the arches of the foot, cushioning impact and distributing weight evenly.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
Explore the key intrinsic and extrinsic muscles of the foot, which comprise 20 intrinsic muscles and several extrinsic muscles crucial for movement and stability. This quiz will help you understand the specific roles of each muscle group, including the dorsal and plantar muscles.