Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which characteristic is NOT associated with Campylobacter spp.?
Which characteristic is NOT associated with Campylobacter spp.?
- Motile with one polar flagellum
- Fermentative (correct)
- Microaerophilic
- Oxidase positive
What is the primary growth atmosphere required for isolating Campylobacter spp.?
What is the primary growth atmosphere required for isolating Campylobacter spp.?
- Anaerobic conditions
- High oxygen levels
- Standard atmospheric conditions
- 5% O2, 10% CO2, and nitrogen (correct)
Which Campylobacter species is commonly associated with causing enteritis, especially in children?
Which Campylobacter species is commonly associated with causing enteritis, especially in children?
- Campylobacter jejuni (correct)
- Campylobacter mucosalis
- Campylobacter coli
- Campylobacter fetus
Which of the following biochemical reactions is positive for Campylobacter jejuni?
Which of the following biochemical reactions is positive for Campylobacter jejuni?
What is the typical colony morphology of Campylobacter jejuni?
What is the typical colony morphology of Campylobacter jejuni?
Which characteristic is NOT associated with Vibrio spp.?
Which characteristic is NOT associated with Vibrio spp.?
Which Vibrio species is typically associated with causing voluminous ‘rice water’ diarrhea?
Which Vibrio species is typically associated with causing voluminous ‘rice water’ diarrhea?
What is the preferred culture medium for isolating Vibrio spp.?
What is the preferred culture medium for isolating Vibrio spp.?
Which of the following tests is used to identify Vibrio cholerae?
Which of the following tests is used to identify Vibrio cholerae?
Which Vibrio species is characterized by a positive reaction to Nitrate to Nitrite conversion?
Which Vibrio species is characterized by a positive reaction to Nitrate to Nitrite conversion?
What is the optimal salt concentration for growing most Vibrio spp. in the lab?
What is the optimal salt concentration for growing most Vibrio spp. in the lab?
Which test can yield a positive pink color indicating the presence of V. cholerae?
Which test can yield a positive pink color indicating the presence of V. cholerae?
Vibrio spp. typically exhibit which type of lactose fermentation characteristic?
Vibrio spp. typically exhibit which type of lactose fermentation characteristic?
Which species is recognized as the most common human isolate within the Aeromonas genus?
Which species is recognized as the most common human isolate within the Aeromonas genus?
What characteristic is NOT true for Aeromonas spp.?
What characteristic is NOT true for Aeromonas spp.?
Which selective culture medium would you use to grow Aeromonas species for identification?
Which selective culture medium would you use to grow Aeromonas species for identification?
What is the expected result of the oxidase test for Aeromonas spp.?
What is the expected result of the oxidase test for Aeromonas spp.?
Which Vibrio species is known to exhibit variable growth in 6% NaCl?
Which Vibrio species is known to exhibit variable growth in 6% NaCl?
Which of the following is a characteristic of Campylobacter spp.?
Which of the following is a characteristic of Campylobacter spp.?
Which of the following Vibrio species is characterized by producing yellow colonies on TCBS?
Which of the following Vibrio species is characterized by producing yellow colonies on TCBS?
Which of the following agent is Aeromonas spp. resistant to?
Which of the following agent is Aeromonas spp. resistant to?
What distinctive morphological characteristic is associated with Mycobacterium tuberculosis colonies?
What distinctive morphological characteristic is associated with Mycobacterium tuberculosis colonies?
Which biochemical test result is true for Mycobacterium tuberculosis?
Which biochemical test result is true for Mycobacterium tuberculosis?
Which of the following mycobacterial species is known to be associated with Buruli ulcers?
Which of the following mycobacterial species is known to be associated with Buruli ulcers?
What is a common characteristic of the Mycobacterium avium complex?
What is a common characteristic of the Mycobacterium avium complex?
How long does it typically take for Mycobacterium ulcerans to show visible growth during incubation?
How long does it typically take for Mycobacterium ulcerans to show visible growth during incubation?
Which culture medium would best support the growth of Listeria monocytogenes?
Which culture medium would best support the growth of Listeria monocytogenes?
What differentiates Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae from Listeria monocytogenes?
What differentiates Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae from Listeria monocytogenes?
What characteristic distinguishes Mycobacterium from gram-negative organisms?
What characteristic distinguishes Mycobacterium from gram-negative organisms?
What is the primary purpose of incubating Mycobacterium culture media in 5-10% CO2?
What is the primary purpose of incubating Mycobacterium culture media in 5-10% CO2?
What is the result of the Niacin test for Mycobacterium tuberculosis?
What is the result of the Niacin test for Mycobacterium tuberculosis?
Which of the following statements regarding Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae is incorrect?
Which of the following statements regarding Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae is incorrect?
Why is the Nitrate reduction test used for differentiating Mycobacterium species?
Why is the Nitrate reduction test used for differentiating Mycobacterium species?
What characteristic of Mycobacterium colonies can be observed on Middlebrook 7H10 agar?
What characteristic of Mycobacterium colonies can be observed on Middlebrook 7H10 agar?
Which Vibrio species is characterized by a positive result for Arginine Dihydrolase?
Which Vibrio species is characterized by a positive result for Arginine Dihydrolase?
Which species is identified by producing gas from glucose fermentation?
Which species is identified by producing gas from glucose fermentation?
Which Vibrio species shows a negative result for Indole?
Which Vibrio species shows a negative result for Indole?
Which species can be identified by a green coloration on TCBS agar?
Which species can be identified by a green coloration on TCBS agar?
Which Vibrio species does not grow at 0% NaCl concentration?
Which Vibrio species does not grow at 0% NaCl concentration?
Which of the following species is a positive lactose fermenter?
Which of the following species is a positive lactose fermenter?
Which of these Vibrio species can reduce nitrate to nitrite?
Which of these Vibrio species can reduce nitrate to nitrite?
Which Vibrio species is indicated as positive for sucrose fermentation?
Which Vibrio species is indicated as positive for sucrose fermentation?
Which characteristic is unique to Campylobacter jejuni compared to Campylobacter coli?
Which characteristic is unique to Campylobacter jejuni compared to Campylobacter coli?
What is the capacity of Campylobacter spp. to grow in specific environmental conditions?
What is the capacity of Campylobacter spp. to grow in specific environmental conditions?
Which of the following statements about the motility of Campylobacter is accurate?
Which of the following statements about the motility of Campylobacter is accurate?
Which biochemical reaction is associated with Campylobacter jejuni?
Which biochemical reaction is associated with Campylobacter jejuni?
What is the expected appearance of colonies of Campylobacter jejuni on culture media?
What is the expected appearance of colonies of Campylobacter jejuni on culture media?
Which species is least likely to exhibit growth in the presence of 6% NaCl?
Which species is least likely to exhibit growth in the presence of 6% NaCl?
Which organism is characterized by being a non-Inositol fermenter?
Which organism is characterized by being a non-Inositol fermenter?
Which selective culture medium primarily supports the identification of Aeromonas spp.?
Which selective culture medium primarily supports the identification of Aeromonas spp.?
Which of the following species is recognized for producing yellow colonies on TCBS agar?
Which of the following species is recognized for producing yellow colonies on TCBS agar?
Which characteristic is true for V.cholerae?
Which characteristic is true for V.cholerae?
Which Aeromonas species is noted for having unusual susceptibility to ampicillin?
Which Aeromonas species is noted for having unusual susceptibility to ampicillin?
Which biochemical test gives a positive result for Aeromonas spp.?
Which biochemical test gives a positive result for Aeromonas spp.?
Which factor does NOT contribute to isolating Campylobacter spp. in the laboratory?
Which factor does NOT contribute to isolating Campylobacter spp. in the laboratory?
Which Vibrio species exhibits a positive reaction for both Lysine Decarboxylase and Arginine Dihydrolase?
Which Vibrio species exhibits a positive reaction for both Lysine Decarboxylase and Arginine Dihydrolase?
Which of the following species is characterized by a negative result for Ornithine Decarboxylase?
Which of the following species is characterized by a negative result for Ornithine Decarboxylase?
Which Vibrio species shows variability in its reaction to Lysine Decarboxylase testing?
Which Vibrio species shows variability in its reaction to Lysine Decarboxylase testing?
Which species shows a positive growth reaction in 0% NaCl conditions?
Which species shows a positive growth reaction in 0% NaCl conditions?
Which Vibrio species is recognized for showing a positive reaction to Lysine Decarboxylase but does not reduce nitrate?
Which Vibrio species is recognized for showing a positive reaction to Lysine Decarboxylase but does not reduce nitrate?
Which species among the following shows a negative reaction for Arginine Dihydrolase?
Which species among the following shows a negative reaction for Arginine Dihydrolase?
Which Vibrio specie is classified as variable in its Ornithine Decarboxylase testing?
Which Vibrio specie is classified as variable in its Ornithine Decarboxylase testing?
Which of these Vibrio species is NOT known to exhibit a positive reaction for Lysine Decarboxylase?
Which of these Vibrio species is NOT known to exhibit a positive reaction for Lysine Decarboxylase?
What is a unique morphological characteristic of Mycobacterium tuberculosis colonies?
What is a unique morphological characteristic of Mycobacterium tuberculosis colonies?
Which biochemical test shows a positive result in Mycobacterium tuberculosis?
Which biochemical test shows a positive result in Mycobacterium tuberculosis?
What is the incubation period for Mycobacterium ulcerans to show visible growth?
What is the incubation period for Mycobacterium ulcerans to show visible growth?
Which of the following characteristics is NOT associated with the Mycobacterium avium complex?
Which of the following characteristics is NOT associated with the Mycobacterium avium complex?
Which of the following is true about the biochemical characteristics of Mycobacterium tuberculosis?
Which of the following is true about the biochemical characteristics of Mycobacterium tuberculosis?
Which is the optimal culture medium for isolating Vibrio spp. to promote growth?
Which is the optimal culture medium for isolating Vibrio spp. to promote growth?
Which of the following Vibrio species does NOT produce gas from glucose?
Which of the following Vibrio species does NOT produce gas from glucose?
What does a positive Cholera red reaction indicate when testing for Vibrio cholerae?
What does a positive Cholera red reaction indicate when testing for Vibrio cholerae?
Which of the following biochemical tests shows a positive result for all Vibrio species listed?
Which of the following biochemical tests shows a positive result for all Vibrio species listed?
Which Vibrio species exhibits a positive result for Ornithine Decarboxylase?
Which Vibrio species exhibits a positive result for Ornithine Decarboxylase?
What is the characteristic colony appearance of Vibrio species on Sheep Blood Agar (SBA)?
What is the characteristic colony appearance of Vibrio species on Sheep Blood Agar (SBA)?
Which Vibrio species is characterized by producing a green coloration on TCBS agar?
Which Vibrio species is characterized by producing a green coloration on TCBS agar?
In laboratory diagnostics, which test is primarily used for the identification of Vibrio cholerae?
In laboratory diagnostics, which test is primarily used for the identification of Vibrio cholerae?
Which culture medium is commonly used to detect Listeria monocytogenes beta hemolysis?
Which culture medium is commonly used to detect Listeria monocytogenes beta hemolysis?
Which characteristic is unique to Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae in comparison to Listeria monocytogenes?
Which characteristic is unique to Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae in comparison to Listeria monocytogenes?
What feature distinguishes Mycobacterium cultures when using Lowenstein-Jensen (L-J) medium?
What feature distinguishes Mycobacterium cultures when using Lowenstein-Jensen (L-J) medium?
In which test is Mycobacterium tuberculosis identified by a positive Niacin reaction?
In which test is Mycobacterium tuberculosis identified by a positive Niacin reaction?
Which culture method is used for identifying Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae?
Which culture method is used for identifying Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae?
Which of the following is true regarding Mycobacterium species and their culture conditions?
Which of the following is true regarding Mycobacterium species and their culture conditions?
What biochemical reaction differentiates Mycobacterium tuberculosis from Mycobacterium bovis?
What biochemical reaction differentiates Mycobacterium tuberculosis from Mycobacterium bovis?
Which of the following characteristics is NOT true for Mycobacterium species?
Which of the following characteristics is NOT true for Mycobacterium species?
Flashcards
Vibrio spp. characteristic
Vibrio spp. characteristic
Gram-negative, comma-shaped, curved, or straight bacilli; facultative anaerobes; catalase negative, oxidase positive; can reduce nitrate to nitrite (except V.metschnikovii).
Vibrio cholerae identification
Vibrio cholerae identification
Uses the string test (emulsifying in sodium deoxycholate) and cholera red reaction (adding sulfuric acid to 24-hr peptone water culture) to distinguish.
Vibrio spp. optimal growth medium
Vibrio spp. optimal growth medium
Alkaline (pH 8.4) peptone broth and Thiosulfate Citrate Bile Salts (TCBS) agar are optimal for isolation.
Vibrio cholerae diarrhea
Vibrio cholerae diarrhea
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vibrio alginolyticus
Vibrio alginolyticus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vibrio cholerae reactions
Vibrio cholerae reactions
Signup and view all the flashcards
TCBS Agar
TCBS Agar
Signup and view all the flashcards
Selective Differential Media
Selective Differential Media
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vibrio fumissii characteristics
Vibrio fumissii characteristics
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vibrio harveyi characteristics
Vibrio harveyi characteristics
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vibrio metschnikovii traits
Vibrio metschnikovii traits
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vibrio mimicus traits
Vibrio mimicus traits
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vibrio parahaemolyticus traits
Vibrio parahaemolyticus traits
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vibrio vulnificus characteristics
Vibrio vulnificus characteristics
Signup and view all the flashcards
Indole test for Vibrio species
Indole test for Vibrio species
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glucose test for Vibrio species
Glucose test for Vibrio species
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vibrio Growth in NaCl
Vibrio Growth in NaCl
Signup and view all the flashcards
TCBS Agar Color
TCBS Agar Color
Signup and view all the flashcards
Aeromonas spp. Key Characteristics
Aeromonas spp. Key Characteristics
Signup and view all the flashcards
Aeromonas spp. Selective Media
Aeromonas spp. Selective Media
Signup and view all the flashcards
Aeromonas spp. Presumptive Identification
Aeromonas spp. Presumptive Identification
Signup and view all the flashcards
Campylobacter spp.
Campylobacter spp.
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vibrio spp. Key Features
Vibrio spp. Key Features
Signup and view all the flashcards
Aeromonas spp. Resistance
Aeromonas spp. Resistance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Campylobacter Morphology
Campylobacter Morphology
Signup and view all the flashcards
Campylobacter Growth Conditions
Campylobacter Growth Conditions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Campylobacter jejuni
Campylobacter jejuni
Signup and view all the flashcards
Campylobacter Culture
Campylobacter Culture
Signup and view all the flashcards
Campylobacter Biochemical Reactions
Campylobacter Biochemical Reactions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mycobacterium tuberculosis Growth
Mycobacterium tuberculosis Growth
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mycobacterium tuberculosis Biochemical Characteristics
Mycobacterium tuberculosis Biochemical Characteristics
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mycobacterium ulcerans
Mycobacterium ulcerans
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mycobacterium avium Complex
Mycobacterium avium Complex
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the typical incubation temperature for Mycobacterium ulcerans?
What is the typical incubation temperature for Mycobacterium ulcerans?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Listeria monocytogenes Culture
Listeria monocytogenes Culture
Signup and view all the flashcards
Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae Characteristics
Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae Characteristics
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mycobacterium Culture Media
Mycobacterium Culture Media
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mycobacterium Identification
Mycobacterium Identification
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mycobacterium Biochemical Tests
Mycobacterium Biochemical Tests
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mycobacterium Growth Rate
Mycobacterium Growth Rate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Umbrella Shaped Pattern
Umbrella Shaped Pattern
Signup and view all the flashcards
Test Tube Brush Growth
Test Tube Brush Growth
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vibrio spp. growth condition
Vibrio spp. growth condition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vibrio spp. selective media
Vibrio spp. selective media
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vibrio cholerae's signature diarrhea
Vibrio cholerae's signature diarrhea
Signup and view all the flashcards
Campylobacter spp. growth requirements
Campylobacter spp. growth requirements
Signup and view all the flashcards
Campylobacter jejuni's impact
Campylobacter jejuni's impact
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mycobacterium tuberculosis identification
Mycobacterium tuberculosis identification
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lysine Decarboxylase Test
Lysine Decarboxylase Test
Signup and view all the flashcards
Arginine Dihydrolase Test
Arginine Dihydrolase Test
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ornithine Decarboxylase Test
Ornithine Decarboxylase Test
Signup and view all the flashcards
Growth in 0% NaCl
Growth in 0% NaCl
Signup and view all the flashcards
Yellow TCBS Colonies
Yellow TCBS Colonies
Signup and view all the flashcards
Green TCBS Colonies
Green TCBS Colonies
Signup and view all the flashcards
Campylobacter spp. Key Characteristics
Campylobacter spp. Key Characteristics
Signup and view all the flashcards
Campylobacter spp. Growth Needs
Campylobacter spp. Growth Needs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mycobacterium ulcerans Infection
Mycobacterium ulcerans Infection
Signup and view all the flashcards
Listeria monocytogenes growth pattern
Listeria monocytogenes growth pattern
Signup and view all the flashcards
Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae growth pattern
Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae growth pattern
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a key difference between Listeria and Erysipelothrix?
What is a key difference between Listeria and Erysipelothrix?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the Niacin test used for?
What is the Niacin test used for?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does Tween 80 hydrolysis work?
How does Tween 80 hydrolysis work?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a key characteristic used to identify M. tuberculosis?
What is a key characteristic used to identify M. tuberculosis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Non-Enteric Gastrointestinal Pathogens
- Vibrio spp. are oxidase positive, except V. metschnikovii
- Vibrio spp. produce gas from glucose, except V. fumissii, which causes voluminous "rice water" diarrhea.
- Vibrio spp. are best cultured in alkaline peptone broth (pH 8.4)
- Thiosulfate citrate bile salts (TCBS) agar is the best medium for isolating Vibrio.
- Vibrio spp. are gram-negative, comma-shaped, curved, or straight bacilli.
- Vibrio spp. are facultative anaerobes.
- Vibrio spp. are catalase negative and oxidase-positive, reducing nitrate to nitrite except V. metschnikovii.
Vibrio spp. Other Reactions of V. cholerae
- V. cholerae: MR is negative.
- V. cholerae: VP is positive/variable.
- V. cholerae: Citrate is positive.
- V. cholerae: Urease is negative.
- V. cholerae: TSI shows A/A, gas is negative, and H2S is negative.
- String test (emulsify organism in 0.5% sodium deoxycholate on a slide)
- Cholera red reaction (add concentrated sulphuric acid to 24hrs peptone water culture with V. cholerae results in positive pink color)
Vibrio spp. Salt Concentration (0.5%)
- Nutrient agar or sheep blood agar (SBA) are commonly used laboratory media.
- Colonies on SBA or chocolate agar (CHOC) appear smooth, opaque, and iridescent with a greenish hue (medium to large colonies).
- Cefsulodin-Irgasan-Novobiocin (CIN) agar is a selective differential medium for Vibrio spp.
- MAC agar is a selective differential medium.
Differentiation of Pathogenic Vibrio Species
- Table detailing the differentiation based on TCBS, Lact. Ferm., Cholera Red React., String Test, and Kanagawa Pheno for different pathogenic Vibrio species.
Summary for Vibrio spp.
- Summarized traits specific to different Vibrio species: positive oxidase with different sugars, lysines, decarboxylase, salt concentrations, color on TCBS, etc
Indole for Vibrio spp.
- Table of Vibrio spp. categorized by positive and negative Indole.
Glucose for Vibrio spp.
- Table of Vibrio spp. categorized by positive and negative Glucose.
Sucrose for Vibrio spp.
- Table of Vibrio spp. categorized by positive and negative Sucrose.
Lysine Decarboxylase for Vibrio spp.
- Table of Vibrio spp. categorized by positive and negative Lysine Decarboxylase.
Arginine Dihydrolase for Vibrio spp.
- Table of Vibrio spp. categorized by positive and negative Arginine Dihydrolase.
Ornithine Decarboxylase for Vibrio spp.
- Table of Vibrio spp. categorized by positive and negative Ornithine Decarboxylase.
Growth in 0% NaCl for Vibrio spp.
- Table of Vibrio spp. categorized by positive and negative growth in 0% NaCl.
Growth in 6% NaCl for Vibrio spp.
- Table of Vibrio spp. categorized by positive and negative growth in 6% NaCl.
- Colony color and characteristics on TCBS agar.
Aeromonas spp. Key Characteristics
- Gram-negative, straight bacilli
- Facultative anaerobe
- Fermentative
- Indole positive
- Oxidase positive
- Motile
- Resistant to vibriostatic agent O/129 (2,4 diamino-6,7-diisopropylpteridine)
- Non-inositol fermenter
- A. hydrophila is the most common human isolate
Aeromonas spp. Selective Culture Media
- MAC Agar, ferment lactose (A. caviae), unusual universal susceptibility to ampicillin.
- CIN Medium, pink-centered colonies from fermentation of mannitol, uneven clear apron resembling Yersinia enterocolitica.
- Alkaline peptone water.
Aeromonas spp. Presumptive Identification
- Oxidase test (positive)
- Spot indole test on suspicious colonies (especially beta-hemolytic colonies)
- Ability to grow in the presence of NaCl.
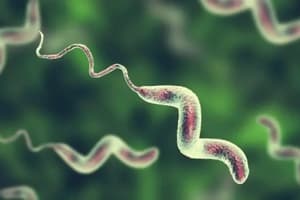
Campylobacter spp. Key Characteristics
- Gram-negative, comma, curved, S-shaped, seagull wing-shaped bacilli
- Microaerophilic (5% O2)
- Capnophilic
- Motile (one polar flagellum)
- Oxidase-positive
- Non-fermentative
- Sodium Hippurate Hydrolysis-positive
- Urease-negative
- Exhibit characteristic motility (hanging drop preparations/phase contrast microscopy).
Campylobacter spp. (Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli)
- Causes enteritis (esp. children)
- Leading cause of acute diarrhea worldwide.
- Sometimes responsible for bacteremia or endocarditis
- Culture: Incubate in 5% O2, 10% CO2, and nitrogen atmosphere for 48 hours.
- Isolation media: "Campy-thio" or "Campy-blood" agar.
- Use antibiotics in the media to make it selective.
Campylobacter spp. Biochemical reactions of C. jejuni
- Non-fermentative
- Oxidase (+), Catalase (+), Nitrate (+), H2S (-)
- Grows in 1% glycine
- Hippurate (+). C. coli is negative.
- C. jejuni and other enteric Campylobacters
- Moist, runny look; spreading, usually non hemolytic, some round and others flat.
- C. fetus subsp. fetus
- Produces smooth, convex, translucent colonies.
- C. mucosalis and C. hyointestinalis
- Can produce a dirty yellow pigment.
Helicobacter pylori
- Curved, flagellated, motile gram-negative rods
- "Triple positive": catalase (+), oxidase (+), urease (+)
- Diagnosis: Biopsy, Urea breath test, Stool antigen
Aerobic Gram-Positive Bacilli
- Corynebacterium
Corynebacterium
- Non-spore-forming, nonbranching, catalase-positive bacilli.
- Also called Kleb Coeffler's bacillus
- Microscopy: Highly pleomorphic gram-positive bacilli.
- Club-shaped swellings and beaded forms are common.
- Metachromatic areas (Babes-Ernst granules) stain intensely.
- Facultative anaerobes.
- Best growth at 37°C, but can multiply from 15°C to 40°C.
- Grows well on nutrient agar, serum/blood-containing media (ex. Coeffler Serum or Pai Agar).
- Cystine-tellurite blood agar (CTBA) - modification of Tinsdale medium, sheep red blood cells, bovine serum, cystine, potassium tellurite. Inhibits non-Coryneform bacteria.
- Characteristics of C. diphtheriae- non motile, nitrate reduction (+), urease (-), catalase (+), glucose & maltose fermented, sucrose not fermented.
Corynebacterium (continued)
- Culture from threat, nasopharynx, skin wounds
- Special culture media: Coeffler's or Tinsdale
- Black colonies on Tinsdale media
- Metachromatic (blue/red) granules on Coeffler's media
- Media to enhance pleomorphism and granule production
- Coeffler serum agar + poached egg colonies, Pai coagulated egg medium
Listeria monocytogenes
- Facultative intracellular Catalase positive
- Tumbling motility (at room temp) but usually nonmotile at 35-37°C
- Hippurate hydrolysis-positive
- Esculin-positive, salicin (+)
- CAMP positive (hemolysis looks like a shovel, not arrowhead)
- Grows from 0.5-45°C
- Cold enrichment may be used
Listeria monocytogenes (Culture)
- Sheep blood agar (detect beta-hemolysis, blue-green colonies)
- McBride Cisteria medium (sheep blood).
- Phenylethylalcohol agar (inhibits gram-negative organisms).
- Hold suspect cultures at 4°C up to 6 months, subculture weekly for 1 month, monthly thereafter.
- Umbrella-shaped pattern.
Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae
- Slender, pleomorphic gram-positive rods that form filaments
- Alpha hemolytic (on blood agar)
- Decolorizes easily in gram stain, may appear gram-negative.
- Catalase, oxidase, indole negative
- Produces H2S, differentiating it from Listeria monocytogenes.
- Test tube brush growth.
Mycobacterium
- Obligate aerobes
- Slender, non-spore-forming, acid-fast, gram-positive rods.
- Do not gram stain well.
- Culture media (incubate in 5-10% CO2):
- -Cowenstein-Jensen (C-J) (green color and opaque) - Contains egg glycerol, promotes growth of more species (less drying), good for niacin test. Difficult to prepare, often used for cultures.
- -Middlebrook 7H10 or 7H11 agar (Clear agar)
- Good for antimicrobial susceptibility testing, fewer contaminants grow.
- Contains glycerol. Enhances growth of human strain of M. tuberculosis.
Mycobacterium (Identification)
- Pigment production, growth rate, biochemical reactions.
- Niacin test (best for M. tuberculosis) - enzymatic hydrolysis of Tween 80 releases oleic acid. The indicator (neutral red) changes color depending on the species.
- Runyon groups I and III positive in 5 days.
- M. tuberculosis positive in 5 days.
Mycobacterium (Nitrate reduction)
- M. tuberculosis is positive
- M. bovis is negative
- M. kansasii is a positive control.
Mycobacterium (Catalase reaction)
- Almost all Mycobacteria are catalase-positive.
- M. tuberculosis and M. bovis are catalase-negative after incubation at 69°C for 30 minutes.
Biochemical tests (NTM identification)
- Includes tests for Tween-80 hydrolysis, Niacin test, Nitrate reduction test, Tellurite reduction test, Urea hydrolysis test and Citrate utilization test for Mycobacteria other than tuberculosis.
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- Rough, wrinkled, dry, elevated, buff-colored ("cauliflower-like") at 35-37°C
- Slow growth: 2-3 weeks or longer
- Innoculate in 2 C-J slants, wrap in aluminum foil.
- Incubate at 35°C until visible growth occurs in unshielded tube, expose covered tube to light for 1 hour, cover again, and reincubate overnight.
- Niacin positive/yellow
- Tween 80 hydrolyzed in 10-20 days (pink color)
- Nitrate positive
- Catalase at 68C: negative
- No growth in MacConkey Medium
- Arylsulfatase negative
Mycobacterium ulcerans
- Associated with skin lesions in tropical and subtropical areas (Buruli ulcers in Africa)
- Requires several weeks (6-9) of incubation at 32°C for growth to become visible.
- Negative for niacin, nitrate reduction, Tween 80.
Mycobacterium leprae
- Hansen's bacillus
- Causes Hansen's disease (leprosy)
- Acid-fast rod in nasal mucosa of affected patients.
- Smears of tissue juice - acid-fast stain for lepra cells (macrophages containing acid-fast bacilli).
- Culture: Grows very slowly, not cultured on artificial media or human tissue. Culture can be performed on footpad of mice.
- Lepromin test - skin test for leprosy using a sterile extract from lepromatous nodules (24-48 hrs = early/Fernandez; 3-4 weeks = late/Mitsuda reaction)
Nocardia
- Thin, branching and beaded modified acid-fast positive rods.
- Key characteristics: obligate aerobe, partially acid-fast, delicate mycelium, catalase (+), urease (+).
- Culture: growth on any media without antibiotics.
- Complete biochemical tests needed for identification.
Anaerobes
- Found throughout human bodies as part of normal microbiota.
- Frequently cause polymicrobial infections.
- Anaerobic culture methods: Enriched agar, selective media:
- KV (kanamycin-vancomycin) blood agar (anaerobic gram (-) rods).
- KVL (kanamycin-vancomycin-laked) blood agar (esp. Bacteroides melaninogenicus).
- Neomycin-vancomycin blood agar (for Fusobacteria, Veilonella).
- Neomycin blood agar (for clostridia and anaerobic gram-positive cocci).
- Naegler agar (with egg yolk, neomycin) (for clostridia).
- Chopped meat glucose broth, supplemented thioglycollate broth. Boil 10 min and cool rapidly to drive off oxygen prior to inoculation.
Commonly Isolated Anaerobes
- Clostridium (anaerobic, gram-positive, spore-forming, motile rods; mostly peritrichous flagella)
- May produce lecithinase and lipase, ferment sugars, digest proteins.
- Table displaying motility, lecithinase, lipase, glucose and lactose results for different Clostridium species. C. perfringens, C. botulinum, C. tetani, and C. difficile.
Clostridium tetani
- Terminal spores ('lollipop').
- Positive for gelatin hydrolysis, glucose fermentation.
- Produces neurotoxin (tetanospasmin) causes tetanus (spastic paralysis).
Clostridium botulinum
- Causes botulism (floppy baby syndrome in infants)
Clostridium perfringens
- Causes gas gangrene (clostridial myonecrosis).
- Alpha toxin destroys muscle tissue, causes hemolysis.
- Phospholipase (lecithinase) degrades phospholipids in cell membranes.
- Double zone of hemolysis around colonies on blood agar.
Clostridium difficile
- Causes pseudomembranous colitis in patients undergoing prolonged antibiotic therapy.
- Cycloserine-cefoxitin-fructose agar (CCFA) used to recover C. difficile from stool cultures.
- Naegler's test - inhibition by anti-perfringens antitoxin of the precipitate around growth on egg yolk agar.
Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (Kirby-Bauer Disk Diffusion Test)
- Principle: Inverse linear relationship between zone diameter inhibited growth and antibiotic MIC.
- Testing parameters:
- Use Mueller Hinton Agar in a 150x15mm plate.
- pH: 7.2-7.4
- Agar depth constant at 4mm (some sources 4-6mm).
- Inoculum density: equivalent to 0.5 McFarland standard (1.5 x 108 CFU/mL) using 0.5 mL of 1.175% BaCl2 and 99.5 mL of 1% H2SO4
- Too heavy inoculum = smaller zones, too light = larger zones
- Incubate plate at 35 ± 2°C for 18 hours.
- <16 hours = ↑ zone, false susceptible
-
18 hours = ↓ zone, false resistant
- Measure zone of inhibition using ruler, caliper, or template (on the opposite of blood agar plate).
- Resistant, intermediate, or susceptible based on zone inhibition in millimeters.
- QC strains of E. coli, S. aureus, P. aeruginosa, Enteroccocus faecalis for 20-30 days for frequent testing. Reduce frequency to weekly if results are acceptable.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Related Documents
Description
Test your knowledge on microbiological characteristics of Campylobacter and Vibrio species. This quiz covers aspects such as growth conditions, biochemical reactions, and disease associations. It is a great resource for students and professionals in microbiology or related fields.