Podcast
Questions and Answers
What type of bacteria is Campylobacter?
What type of bacteria is Campylobacter?
- Gram-positive
- Anaerobic
- Gram-negative (correct)
- Aerobic
Which of the following food items is NOT mentioned as a potential source of Campylobacter?
Which of the following food items is NOT mentioned as a potential source of Campylobacter?
- Raw fish (correct)
- Undercooked poultry
- Raw beef
- Unwashed vegetables
What is the most common bacterial cause of human gastroenteritis worldwide?
What is the most common bacterial cause of human gastroenteritis worldwide?
- E. coli
- Salmonella
- Campylobacter (correct)
- Listeria
Which species of Campylobacter is the most common cause of human disease?
Which species of Campylobacter is the most common cause of human disease?
What temperature range do Campylobacter bacteria grow best in?
What temperature range do Campylobacter bacteria grow best in?
Which species of Campylobacter is a known cause of recurrent diarrhea in children?
Which species of Campylobacter is a known cause of recurrent diarrhea in children?
What does the name 'Campylobacter' mean?
What does the name 'Campylobacter' mean?
Which type of individuals are at risk of fatal Campylobacter infections?
Which type of individuals are at risk of fatal Campylobacter infections?
What is the motility characteristic of Campylobacter bacteria?
What is the motility characteristic of Campylobacter bacteria?
What type of bacteria is Campylobacter based on its scientific classification?
What type of bacteria is Campylobacter based on its scientific classification?
Which factor mediates the bacterial invasion of the intestinal epithelium and inflammation in Campylobacter infection?
Which factor mediates the bacterial invasion of the intestinal epithelium and inflammation in Campylobacter infection?
What is the most common trigger of Guillain–Barré syndrome?
What is the most common trigger of Guillain–Barré syndrome?
Which environment does Campylobacter grow best in?
Which environment does Campylobacter grow best in?
What is the incubation period for Campylobacter infection after infection?
What is the incubation period for Campylobacter infection after infection?
Which type of medication may increase the risk of contracting Campylobacter disease?
Which type of medication may increase the risk of contracting Campylobacter disease?
What are the common routes of transmission for Campylobacter?
What are the common routes of transmission for Campylobacter?
Which factor makes Campylobacter sensitive to the stomach's normal production of hydrochloric acid?
Which factor makes Campylobacter sensitive to the stomach's normal production of hydrochloric acid?
What are the symptoms associated with Campylobacter infection?
What are the symptoms associated with Campylobacter infection?
What is the primary purpose of Campylobacter Blood Agar (CVA)?
What is the primary purpose of Campylobacter Blood Agar (CVA)?
Which antibiotic is NOT typically found in Campylobacter Blood Agar (CVA)?
Which antibiotic is NOT typically found in Campylobacter Blood Agar (CVA)?
What is the optimal temperature range for the growth of Campylobacter bacteria?
What is the optimal temperature range for the growth of Campylobacter bacteria?
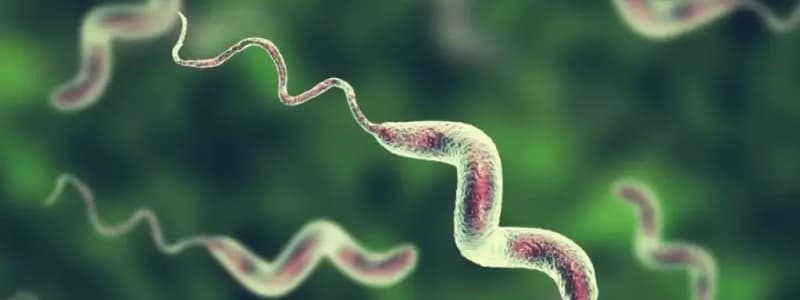
Which characteristic shape is observed in Campylobacter bacteria when viewed under a microscope?
Which characteristic shape is observed in Campylobacter bacteria when viewed under a microscope?
What are the two key characteristics of Campylobacter bacteria demonstrated by biochemical tests?
What are the two key characteristics of Campylobacter bacteria demonstrated by biochemical tests?
What type of environment is required for the incubation of Campylobacter cultures?
What type of environment is required for the incubation of Campylobacter cultures?
What is the typical duration of symptomatic Campylobacter infection?
What is the typical duration of symptomatic Campylobacter infection?
Which type of treatment is usually sufficient for non-complex cases of Campylobacter infection?
Which type of treatment is usually sufficient for non-complex cases of Campylobacter infection?
What type of testing is carried out to select appropriate antibiotics for Campylobacter infection?
What type of testing is carried out to select appropriate antibiotics for Campylobacter infection?
What is a distinguishing feature seen in the Gram stain from culture media of Campylobacter?
What is a distinguishing feature seen in the Gram stain from culture media of Campylobacter?
What type of temperature range is required for incubation of Campylobacter cultures?
What type of temperature range is required for incubation of Campylobacter cultures?
What is the purpose of sensitivity testing in Campylobacter infections?
What is the purpose of sensitivity testing in Campylobacter infections?
In non-complex cases, what is the impact of antibiotic treatment on the typical duration of Campylobacter infection?
In non-complex cases, what is the impact of antibiotic treatment on the typical duration of Campylobacter infection?
What are the drugs of choice for treating Campylobacter infections in high-risk patients?
What are the drugs of choice for treating Campylobacter infections in high-risk patients?
What measures are recommended for preventing Campylobacter infections?
What measures are recommended for preventing Campylobacter infections?
What is the typical impact of antibiotic treatment on the duration of Campylobacter infection in non-complex cases?
What is the typical impact of antibiotic treatment on the duration of Campylobacter infection in non-complex cases?
Which antibiotics are recommended as drugs of choice for treating Campylobacter infections in high-risk patients?
Which antibiotics are recommended as drugs of choice for treating Campylobacter infections in high-risk patients?
What is the primary purpose of sensitivity testing in Campylobacter infections?
What is the primary purpose of sensitivity testing in Campylobacter infections?
What measures are recommended for preventing Campylobacter infections?
What measures are recommended for preventing Campylobacter infections?
Which type of antibiotics are considered the drugs of choice for treating Campylobacter infections?
Which type of antibiotics are considered the drugs of choice for treating Campylobacter infections?
In case of systemic infection, which type of bactericidal antibiotics are used for treating Campylobacter infections?
In case of systemic infection, which type of bactericidal antibiotics are used for treating Campylobacter infections?
Which of the following antibiotic combinations are NOT typically considered effective for treating Campylobacter infections?
Which of the following antibiotic combinations are NOT typically considered effective for treating Campylobacter infections?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Campylobacter Overview
- Campylobacter is a genus of bacteria known for causing gastrointestinal infections in humans.
- It is a Gram-negative, spiral-shaped, and motile bacterium.
Common Pathogens and Sources
- Campylobacter jejuni is the most common species responsible for human disease.
- Common sources include undercooked poultry, unpasteurized milk, and contaminated water. Some food items are not typically associated with Campylobacter.
Growth and Environment
- Optimal growth temperature for Campylobacter is between 37°C and 42°C, with preference for microaerobic conditions.
- Campylobacter is sensitive to acidic environments, such as the stomach's hydrochloric acid.
Symptoms and Transmission
- Symptoms include diarrhea, abdominal pain, fever, and nausea.
- Common transmission routes are through contaminated food or water.
Risk Factors
- Young children, the elderly, and immunocompromised individuals are particularly at risk for severe illness or complications.
- Certain medications, such as antacids or proton pump inhibitors, may increase the susceptibility to infection.
Incubation and Duration
- The incubation period for Campylobacter infection ranges from 2 to 5 days.
- Typical duration of symptomatic infection is about 1 week; antibiotic treatment is generally effective for non-complex cases, potentially reducing symptoms.
Diagnostic and Treatment
- Campylobacter Blood Agar (CVA) is used for culturing these bacteria.
- Antibiotic susceptibility testing is essential to guide treatment choices.
- Drugs of choice for high-risk patients include macrolides (e.g., azithromycin) and fluoroquinolones.
Complications
- Campylobacter is the most common trigger for Guillain–Barré syndrome, a rare neurological disorder.
- In cases of systemic infection, bactericidal antibiotics are administered.
Prevention Measures
- Preventative measures include proper food handling, cooking meat thoroughly, and avoiding unpasteurized dairy products.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.