Podcast
Questions and Answers
Under aerobic conditions, what is the primary product of pyruvate conversion?
Under aerobic conditions, what is the primary product of pyruvate conversion?
- Glycogen
- Ethanol
- Acetyl-CoA (correct)
- Lactate
Which of the following is an end product of alcoholic fermentation?
Which of the following is an end product of alcoholic fermentation?
- Lactate
- Ethanol (correct)
- Carbon dioxide
- Pyruvate
What type of fermentation occurs when pyruvate is converted to lactate?
What type of fermentation occurs when pyruvate is converted to lactate?
- Acidic fermentation (correct)
- Lactic acid fermentation
- Aerobic fermentation
- Alcoholic fermentation
Which of the following statements about pyruvate metabolism is correct?
Which of the following statements about pyruvate metabolism is correct?
What role do glucose transporters (GLUTs) play in carbohydrate metabolism?
What role do glucose transporters (GLUTs) play in carbohydrate metabolism?
What is the main purpose of the catabolic reactions described in the content?
What is the main purpose of the catabolic reactions described in the content?
Which reaction in the Krebs cycle produces ATP through substrate-level phosphorylation?
Which reaction in the Krebs cycle produces ATP through substrate-level phosphorylation?
How much ATP is produced from the complete oxidation of two acetyl CoA during two cycles of the Krebs cycle?
How much ATP is produced from the complete oxidation of two acetyl CoA during two cycles of the Krebs cycle?
What is the total ATP yield from glucose oxidation, considering both glycolysis and the Krebs cycle?
What is the total ATP yield from glucose oxidation, considering both glycolysis and the Krebs cycle?
Which shuttle is responsible for transferring electrons from cytosolic NADH to complex II in the electron transport chain?
Which shuttle is responsible for transferring electrons from cytosolic NADH to complex II in the electron transport chain?
What is the primary function of the malate-aspartate shuttle?
What is the primary function of the malate-aspartate shuttle?
What type of energy conversion occurs in the Krebs cycle?
What type of energy conversion occurs in the Krebs cycle?
Which component's oxidation leads to the generation of NADH in the Krebs cycle?
Which component's oxidation leads to the generation of NADH in the Krebs cycle?
What is the primary role of the Krebs cycle in cellular respiration?
What is the primary role of the Krebs cycle in cellular respiration?
Which of the following correctly describes the type of phosphorylation that occurs during the Krebs cycle?
Which of the following correctly describes the type of phosphorylation that occurs during the Krebs cycle?
What is the product formed from carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins that enters the Krebs cycle?
What is the product formed from carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins that enters the Krebs cycle?
How many ATP molecules are produced directly from one molecule of glucose during glycolysis and the Krebs cycle combined?
How many ATP molecules are produced directly from one molecule of glucose during glycolysis and the Krebs cycle combined?
What distinguishes the amphibolic nature of the Krebs cycle?
What distinguishes the amphibolic nature of the Krebs cycle?
Which molecule serves as an important high-energy substrate in substrate-level phosphorylation during the Krebs cycle?
Which molecule serves as an important high-energy substrate in substrate-level phosphorylation during the Krebs cycle?
Why is the location of enzymes in the mitochondria significant for ATP production in the Krebs cycle?
Why is the location of enzymes in the mitochondria significant for ATP production in the Krebs cycle?
What is the significance of NADH and FADH2 generated during the Krebs cycle?
What is the significance of NADH and FADH2 generated during the Krebs cycle?
Which enzyme is responsible for converting glucose into glucose-6-phosphate during glycolysis?
Which enzyme is responsible for converting glucose into glucose-6-phosphate during glycolysis?
Which of the following enzymes is absent from muscle and adipose tissue?
Which of the following enzymes is absent from muscle and adipose tissue?
What is the primary role of the Cori cycle?
What is the primary role of the Cori cycle?
Which of the following best describes glycogen?
Which of the following best describes glycogen?
Which enzyme is primarily responsible for the synthesis of glycogen from glucose?
Which enzyme is primarily responsible for the synthesis of glycogen from glucose?
What process describes the breakdown of glycogen back into glucose?
What process describes the breakdown of glycogen back into glucose?
Which metabolic pathway is involved in synthesizing glucose from non-carbohydrate precursors?
Which metabolic pathway is involved in synthesizing glucose from non-carbohydrate precursors?
What is a consequence of the Cori cycle during intense exercise?
What is a consequence of the Cori cycle during intense exercise?
What process occurs when glucose is synthesized in the liver and kidneys from non-carbohydrate precursors?
What process occurs when glucose is synthesized in the liver and kidneys from non-carbohydrate precursors?
Which metabolic process is primarily responsible for lowering blood glucose levels?
Which metabolic process is primarily responsible for lowering blood glucose levels?
When blood glucose concentration exceeds the kidney threshold, what occurs?
When blood glucose concentration exceeds the kidney threshold, what occurs?
Which of the following processes is stimulated during fasting to increase blood glucose levels?
Which of the following processes is stimulated during fasting to increase blood glucose levels?
What happens to lipids stored in adipose tissues in humans?
What happens to lipids stored in adipose tissues in humans?
In the fed state, which process is NOT stimulated to increase glucose utilization?
In the fed state, which process is NOT stimulated to increase glucose utilization?
What is the primary effect of glycogen storage in the liver and muscles?
What is the primary effect of glycogen storage in the liver and muscles?
Which hormone-related response occurs when blood glucose levels drop?
Which hormone-related response occurs when blood glucose levels drop?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
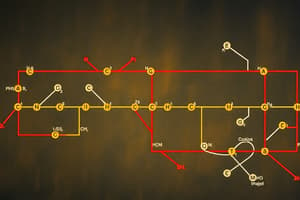
Pyruvate Metabolism
- Acetyl-CoA is the primary product of pyruvate conversion under aerobic conditions.
- Ethanol is an end product of alcoholic fermentation.
- Lactic acid fermentation occurs when pyruvate is converted to lactate.
- Pyruvate is a key intermediate in carbohydrate metabolism, linking glycolysis to the Krebs cycle.
- Glucose transporters (GLUTs) facilitate the movement of glucose across cell membranes, allowing cells to take up glucose for energy production.
Krebs Cycle & Energy Production
- Catabolic reactions break down complex molecules into simpler ones, releasing energy.
- The succinyl CoA synthetase reaction in the Krebs cycle produces ATP through substrate-level phosphorylation.
- Two cycles of the Krebs cycle yield 24 ATP molecules from the complete oxidation of two acetyl CoA.
- The complete oxidation of glucose yields a total of 38 ATP molecules, considering both glycolysis and the Krebs cycle.
- The glycerol 3-phosphate shuttle transfers electrons from cytosolic NADH to complex II in the electron transport chain.
- The malate-aspartate shuttle is responsible for transferring electrons from cytosolic NADH to complex I in the electron transport chain, increasing ATP yield.
- The Krebs cycle mainly involves energy conversion from chemical bonds to electron carriers, generating reducing power.
- The Krebs cycle's oxidation of isocitrate, α-ketoglutarate, and malate leads to the generation of NADH.
- The Krebs cycle plays a central role in cellular respiration by oxidizing acetyl CoA and producing ATP, electron carriers, and precursor metabolites for biosynthesis.
- The Krebs cycle involves substrate-level phosphorylation, where ATP is directly produced from the breakdown of a high-energy substrate.
- Acetyl CoA, derived from carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins, enters the Krebs cycle.
- Glycolysis and the Krebs cycle combined directly produce 4 ATP molecules from one molecule of glucose.
- The Krebs cycle is amphibolic because it participates in both catabolism (breakdown) and anabolism (synthesis) by providing intermediates for other metabolic pathways.
- Succinyl CoA acts as an important high-energy substrate in substrate-level phosphorylation during the Krebs cycle.
- Enzymes are located in the mitochondria, enabling efficient ATP production in the Krebs cycle due to the close proximity of electron transport chain components.
- NADH and FADH2, generated during the Krebs cycle, carry electrons to the electron transport chain for oxidative phosphorylation.
Glycolysis & Glycogen Metabolism
- Hexokinase converts glucose into glucose-6-phosphate during glycolysis.
- Glycogen phosphorylase is absent from muscle and adipose tissue.
- The Cori cycle involves lactate produced in muscles being transported to the liver, where it's converted back to glucose and released into the bloodstream.
- Glycogen is a branched polymer of glucose that serves as a storage form of glucose in animals.
- Glycogen synthase is primarily responsible for the synthesis of glycogen from glucose.
- Glycogenolysis is the process of breaking down glycogen back into glucose.
- Gluconeogenesis is the metabolic pathway involved in synthesizing glucose from non-carbohydrate precursors.
- During intense exercise, muscles utilize glucose faster than they can receive it from the bloodstream, leading to lactate production and its conversion to glucose in the liver through the Cori cycle, recycling glucose for muscle use.
- Gluconeogenesis occurs when the liver and kidneys synthesize glucose from non-carbohydrate precursors, like amino acids and glycerol.
- Insulin is the primary hormone involved in lowering blood glucose levels.
- When blood glucose concentration exceeds the kidney threshold, excess glucose is excreted in urine.
- Gluconeogenesis is stimulated during fasting to increase blood glucose levels.
- Lipids stored in adipose tissues are broken down into fatty acids and glycerol, which can be used for energy or converted to glucose.
- In the fed state, glycogen synthesis is stimulated to store excess glucose.
- Glycogen storage in the liver and muscles provides a readily available source of glucose for energy needs.
- When blood glucose levels drop, glucagon is released, stimulating glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis to increase blood glucose levels.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.