Podcast
Questions and Answers
Where do the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC) and TCA cycle reactions occur?
Where do the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC) and TCA cycle reactions occur?
- Nucleus
- Cytosol
- Mitochondria (correct)
- Endoplasmic reticulum
What is the effect of malonate on the respiration process?
What is the effect of malonate on the respiration process?
- Accelerates respiration
- Has no effect on respiration
- Inhibits respiration (correct)
- Stimulates glycolysis
Which of the following compounds was shown to accelerate the rate of respiration according to the historical perspective?
Which of the following compounds was shown to accelerate the rate of respiration according to the historical perspective?
- Fructose
- Glucose
- Oxaloacetate (correct)
- Acetyl-CoA
What major pathway does the Krebs cycle serve in muscle tissue?
What major pathway does the Krebs cycle serve in muscle tissue?
Which enzymatic conversion was discovered by Krebs?
Which enzymatic conversion was discovered by Krebs?
Which substrate is directly involved in the transformation sequence: Succinate to Fumerate to Malate to Oxaloacetate?
Which substrate is directly involved in the transformation sequence: Succinate to Fumerate to Malate to Oxaloacetate?
What is the primary factor affecting the rate of oxygen consumption in the context of the Krebs cycle?
What is the primary factor affecting the rate of oxygen consumption in the context of the Krebs cycle?
Which year did Krebs elucidate the enzymatic conversion related to the cycle?
Which year did Krebs elucidate the enzymatic conversion related to the cycle?
Which enzyme is responsible for the formation of the Citroyl CoA intermediate in the TCA cycle?
Which enzyme is responsible for the formation of the Citroyl CoA intermediate in the TCA cycle?
What type of reaction does aconitase catalyze in the TCA cycle?
What type of reaction does aconitase catalyze in the TCA cycle?
Which of the following enzymes has two isoforms that differ in their electron acceptors?
Which of the following enzymes has two isoforms that differ in their electron acceptors?
What is the mechanism of reaction utilized by citrate synthase?
What is the mechanism of reaction utilized by citrate synthase?
Which reaction follows aconitase in the TCA cycle, driving the reaction forward?
Which reaction follows aconitase in the TCA cycle, driving the reaction forward?
Which substrate binds first to citrate synthase to initiate the reaction?
Which substrate binds first to citrate synthase to initiate the reaction?
Which enzyme is involved in the conversion of succinate to fumarate?
Which enzyme is involved in the conversion of succinate to fumarate?
Fumerase catalyzes which conversion in the TCA cycle?
Fumerase catalyzes which conversion in the TCA cycle?
What is the role of Thiamine pyrophosphate in the Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex?
What is the role of Thiamine pyrophosphate in the Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex?
Which enzyme in the Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex uses FAD as a bound cofactor?
Which enzyme in the Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex uses FAD as a bound cofactor?
What is a primary advantage of a multi-enzyme complex such as the Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex?
What is a primary advantage of a multi-enzyme complex such as the Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex?
What deficiency is directly linked to the disease Beriberi in animals?
What deficiency is directly linked to the disease Beriberi in animals?
Which substrate does the enzyme Dihydrolipoyl transacetylase use in the Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex?
Which substrate does the enzyme Dihydrolipoyl transacetylase use in the Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex?
Which of the following symptoms is NOT associated with Thiamine deficiency?
Which of the following symptoms is NOT associated with Thiamine deficiency?
How is Thiamine (Vitamin B1) primarily obtained by most vertebrates?
How is Thiamine (Vitamin B1) primarily obtained by most vertebrates?
Why is Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex critical for the brain's energy metabolism?
Why is Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex critical for the brain's energy metabolism?
Which complex is similar in mechanism to the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex?
Which complex is similar in mechanism to the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex?
What type of bond does Succinyl CoA have that is broken to form GTP?
What type of bond does Succinyl CoA have that is broken to form GTP?
Which enzyme is tightly bound to the inner mitochondrial membrane?
Which enzyme is tightly bound to the inner mitochondrial membrane?
Which enzyme has a high stereospecificity and does not recognize cis-Maleate?
Which enzyme has a high stereospecificity and does not recognize cis-Maleate?
What is the primary function of L-Malate Dehydrogenase in the citric acid cycle?
What is the primary function of L-Malate Dehydrogenase in the citric acid cycle?
Which of the following is NOT a rate-controlling enzyme in the citric acid cycle?
Which of the following is NOT a rate-controlling enzyme in the citric acid cycle?
Which mechanism is NOT used to regulate the activity of the citric acid cycle?
Which mechanism is NOT used to regulate the activity of the citric acid cycle?
Which pathway utilizes intermediates from the TCA cycle for biosynthesis?
Which pathway utilizes intermediates from the TCA cycle for biosynthesis?
Flashcards
What is the Krebs cycle?
What is the Krebs cycle?
A series of biochemical reactions that occur in the mitochondria of cells. It is the central pathway for the oxidation of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins to produce energy in the form of ATP.
Where does the Krebs cycle take place?
Where does the Krebs cycle take place?
The Krebs cycle is localized in the mitochondria, specifically in the mitochondrial matrix.
What is the role of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC)?
What is the role of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC)?
The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC) is a multi-enzyme complex responsible for converting pyruvate, the end product of glycolysis, into acetyl-CoA. This conversion is crucial for the entry of pyruvate into the Krebs cycle.
How does malonate affect the Krebs cycle?
How does malonate affect the Krebs cycle?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What's the significance of the Krebs cycle in cellular respiration?
What's the significance of the Krebs cycle in cellular respiration?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How is the Krebs cycle regulated?
How is the Krebs cycle regulated?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Who is the Krebs cycle named after?
Who is the Krebs cycle named after?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Who was Szent-Gyorgyi and what was his contribution to the Krebs cycle?
Who was Szent-Gyorgyi and what was his contribution to the Krebs cycle?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex (PDC)
Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex (PDC)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pyruvate Dehydrogenase (E1)
Pyruvate Dehydrogenase (E1)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dihydrolipoyl Transacetylase (E2)
Dihydrolipoyl Transacetylase (E2)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dihydrolipoyl Dehydrogenase (E3)
Dihydrolipoyl Dehydrogenase (E3)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thiamine Deficiency
Thiamine Deficiency
Signup and view all the flashcards
Beriberi
Beriberi
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thiamine Pyrophosphate (TPP)
Thiamine Pyrophosphate (TPP)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Brain's Glucose Metabolism
Brain's Glucose Metabolism
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Citrate Synthase?
What is Citrate Synthase?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does Aconitase do?
What does Aconitase do?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does Isocitrate Dehydrogenase do?
What does Isocitrate Dehydrogenase do?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does Alpha-ketoglutarate Dehydrogenase do?
What does Alpha-ketoglutarate Dehydrogenase do?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Succinyl-CoA Synthetase?
What is Succinyl-CoA Synthetase?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Succinate Dehydrogenase?
What is Succinate Dehydrogenase?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does Fumerase do?
What does Fumerase do?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does Malate Dehydrogenase do?
What does Malate Dehydrogenase do?
Signup and view all the flashcards
α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Succinyl CoA synthetase
Succinyl CoA synthetase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Succinate dehydrogenase
Succinate dehydrogenase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fumarase
Fumarase
Signup and view all the flashcards
L-Malate dehydrogenase
L-Malate dehydrogenase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Citrate synthase, Isocitrate dehydrogenase, α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
Citrate synthase, Isocitrate dehydrogenase, α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
Signup and view all the flashcards
How is the citric acid cycle regulated?
How is the citric acid cycle regulated?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What pathways utilize intermediates of the citric acid cycle?
What pathways utilize intermediates of the citric acid cycle?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Citric Acid Cycle
- The citric acid cycle, also known as the Krebs cycle or TCA cycle, is a crucial metabolic pathway in cells.
- It functions as a central hub for oxidizing carbon fuels (like acetyl CoA) and producing precursors for biosynthetic pathways.
- The cycle takes place in the mitochondria.
- Glycolysis occurs in the cytosol.
- Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC) and TCA cycle reactions take place within the mitochondria, using oxygen for oxidative phosphorylation to produce ATP.
- The consumption of oxygen during respiration depends on the rate of PDC and TCA reactions.
Discussion Points
- Krebs cycle location
- Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC)
- Krebs Cycle
- Regulation of the Krebs Cycle
Overview and Brief History
- The citric acid cycle is a central biochemical pathway in cells.
- Roundabouts function as hubs to facilitate traffic flow, similar to how the citric acid cycle functions as a hub for cellular processes.
- The citric acid cycle oxidizes carbon fuels, creating precursors for biosynthesis.
Reactions of Glycolysis and the Citric Acid Cycle
- Glycolysis occurs in the cytosol.
- Pyruvate dehydrogenase and TCA cycle reactions occur in the mitochondria.
- Mitochondria utilize oxygen for oxidative phosphorylation to generate ATP.
Citric Acid Cycle Stages
- Stage 1: Acetyl-CoA production occurs in the cytosol.
- Stage 2: Acetyl-CoA oxidation occurs in the mitochondria.
- Stage 3: Electron transport and oxidative phosphorylation (generating ATP) occur in the mitochondria.
Citric Acid Cycle (CAC) and Oxidative Phosphorylation
- The CAC proceeds through a series of eight enzyme-catalyzed reactions, using acetyl-CoA.
- FAD and NAD+ accept electrons from the CAC, carrying them to oxidative phosphorylation.
- 1 GTP, 2 CO2, and 8 electrons are generated per Acetyl CoA.
- Byproduct molecules like NADH and FAD deliver electrons to the electron-transport chain.
Historical Perspective
- 1930: Glycolysis, oxidation of glucose (using O2) was studied. Malonate was an inhibitor of succinate oxidation to fumarate.
- 1935: Szent-Gyorgyi showed small amounts of intermediates accelerated respiration. A sequence of interconversions of succinate, fumarate, malate and oxaloacetate was shown.
- 1936: Martius & Knoop identified a reaction sequence.
- 1937: Krebs elucidated the citric acid cycle and its role in pyruvate oxidation.
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1953
- Hans Adolf Krebs (discovery of the citric acid cycle) and Fritz Albert Lipmann were jointly awarded the Nobel Prize.
Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex (PDC)
- PDC is a multi-enzyme complex with three enzymes:
- E1: Pyruvate dehydrogenase (uses TPP as a cofactor).
- E2: Dihydrolipoyl transacetylase (lipoic acid and CoA as substrate)
- E3: Dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase (FAD and NAD+ as substrate).
- The enzymes work together non-covalently.
- Advantages of multi-enzyme complexes:
- Faster reactions (product of one enzyme is immediately substrate for next).
- Fewer side reactions.
- Coordinated control.
Reaction of Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex (PDC)
- Pyruvate is converted to Acetyl-CoA during this reaction.
- CO2 is released as a byproduct along with NADH and Acetyl-CoA.
Five Steps of Acetyl-CoA Formation
- Five steps convert pyruvate to acetyl-CoA.
- These steps require several cofactors.
Reaction of Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex (PDC) - detailed components
- The reaction involves pyruvate, NAD+, coenzyme A, CO2, and TPP.
- Pyruvate is decarboxylated and forms a hydroxyethyl-TPP intermediate.
- The reaction proceeds through further intermediates using lipoamide, and NAD+.
Coenzymes and Prosthetic Groups of Pyruvate Dehydrogenase
- Key cofactors for the PDC reaction include thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP), lipoic acid, CoA, FAD, and NAD.
Thiamin (Vitamin B1) Deficiency
- Deficiency causes beriberi in animals.
- TPP is a crucial cofactor in PDC function.
- Thiamin is required in diets for most vertebrates.
- Severe neurological issues result from its deficiency.
Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1929
- Christiaan Eijkman and Frederick Gowland Hopkins shared the prize for their discoveries of antineuritic and growth-stimulating vitamins.
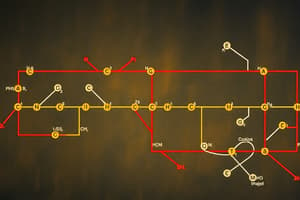
Reactions of the Citric Acid Cycle
- Citrate synthase: Formation of Citroyl CoA intermediate (induced fit model).
- Aconitase: Isomerization of citrate to isocitrate (dehydration/hydration steps).
- Isocitrate dehydrogenase: Oxidation of isocitrate to α-ketoglutarate (two forms – using NAD+ or NADP+).
- α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase: Oxidation of α-ketoglutarate to succinyl-CoA (a complex of three enzymes - similar to PDC).
- Succinyl-CoA synthetase: Conversion of succinyl-CoA to succinate (generating GTP).
- Succinate dehydrogenase: Oxidation of succinate to fumarate (FAD-dependent, membrane-bound).
- Fumarase: Hydration of fumarate to malate.
- Malate dehydrogenase: Oxidation of malate to oxaloacetate(NAD+ dependent).
Regulation of the Citric Acid Cycle (CAC)
- Rate-controlling enzymes include:
- Citrate synthase
- Isocitrate dehydrogenase
- α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
- Regulation occurs via:
- Substrate availability
- Product inhibition
- Allosteric inhibition/activation by other intermediates.
Pathways that utilize CAC Intermediates
- The CAC intermediates are used in other metabolic pathways like:
- Glucose biosynthesis (gluconeogenesis)
- Lipid biosynthesis
- Amino acid biosynthesis
- Porphyrin biosynthesis
- Complete oxidation of amino acids
Stoichiometry of Coenzyme Reduction and ATP Formation
- The table details the overall ATP and coenzyme production during glucose oxidation via glycolysis, PDC and the CAC, and oxidative phosphorylation.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.