Podcast
Questions and Answers
A company aims to increase its market share in a slow-growing market where it already holds a dominant position. According to the BCG matrix, which strategy would be MOST suitable?
A company aims to increase its market share in a slow-growing market where it already holds a dominant position. According to the BCG matrix, which strategy would be MOST suitable?
- Invest heavily in research and development to transform the product into a 'Star'.
- Divest the product, as it is likely a 'Dog'.
- Milk the product for cash, as it is likely a 'Cash Cow'. (correct)
- Increase promotion and lower prices to turn it into a 'Question Mark'.
Which of the following BEST describes the relationship between customer needs, wants, and demands?
Which of the following BEST describes the relationship between customer needs, wants, and demands?
- Needs are satisfied by demands, which are specific expressions of wants.
- Needs are basic human requirements; wants are shaped by culture and personality, and demands are wants backed by purchasing power. (correct)
- Wants are basic human requirements; needs are shaped by individual personality, and demands are wants backed by purchasing power.
- Demands are basic human requirements; wants are shaped by culture and personality, and needs are wants backed by purchasing power.
A new tech company has developed a groundbreaking AI product. They decide to initially focus their marketing efforts on early adopters within the tech industry, rather than the mass market. Which element of the STP framework are they primarily addressing?
A new tech company has developed a groundbreaking AI product. They decide to initially focus their marketing efforts on early adopters within the tech industry, rather than the mass market. Which element of the STP framework are they primarily addressing?
- Positioning
- Targeting (correct)
- Product
- Segmentation
Which of the following scenarios BEST exemplifies 'customer delight'?
Which of the following scenarios BEST exemplifies 'customer delight'?
A small business owner is struggling to define their company's mission. Which question should they answer FIRST to establish a clear and effective mission statement?
A small business owner is struggling to define their company's mission. Which question should they answer FIRST to establish a clear and effective mission statement?
A company is considering expanding its product line into a new market. Which of the following questions BEST represents the 'Place' element of the 4Ps?
A company is considering expanding its product line into a new market. Which of the following questions BEST represents the 'Place' element of the 4Ps?
A company notices that while its sales are increasing, its overall market share is declining. What is the MOST likely explanation for this situation?
A company notices that while its sales are increasing, its overall market share is declining. What is the MOST likely explanation for this situation?
A company decides to focus on Market Penetration according to The Product-Market Growth Matrix. Which action aligns with this decision?
A company decides to focus on Market Penetration according to The Product-Market Growth Matrix. Which action aligns with this decision?
A company is deciding whether to launch an existing product in a new geographical region. Which market growth strategy are they employing?
A company is deciding whether to launch an existing product in a new geographical region. Which market growth strategy are they employing?
Which component of the marketing environment includes factors such as population age, income distribution, and education levels?
Which component of the marketing environment includes factors such as population age, income distribution, and education levels?
What is the primary distinction between primary and secondary data in marketing research?
What is the primary distinction between primary and secondary data in marketing research?
A marketing manager needs to quickly gather insights into consumer perceptions of a new product idea. Which primary data collection method would be most suitable for this initial exploration?
A marketing manager needs to quickly gather insights into consumer perceptions of a new product idea. Which primary data collection method would be most suitable for this initial exploration?
In the context of consumer behavior, which of the following is the best example of an 'experiential' source of information?
In the context of consumer behavior, which of the following is the best example of an 'experiential' source of information?
A consumer is buying a new laptop. They decide that having a long battery life is the single most important factor. They only consider laptops that meet a minimum battery life threshold, regardless of other features. Which decision-making rule are they using?
A consumer is buying a new laptop. They decide that having a long battery life is the single most important factor. They only consider laptops that meet a minimum battery life threshold, regardless of other features. Which decision-making rule are they using?
A customer buys a new car but immediately starts to second-guess their decision after seeing a negative review online. This scenario best exemplifies what concept?
A customer buys a new car but immediately starts to second-guess their decision after seeing a negative review online. This scenario best exemplifies what concept?
A consumer routinely purchases the same brand of coffee beans without much thought or research. This is an example of what buying behavior?
A consumer routinely purchases the same brand of coffee beans without much thought or research. This is an example of what buying behavior?
Which concept suggests that the pain of losing $100 is psychologically greater than the pleasure of gaining $100?
Which concept suggests that the pain of losing $100 is psychologically greater than the pleasure of gaining $100?
What is a key element of Disney's marketing strategy that drives customer loyalty?
What is a key element of Disney's marketing strategy that drives customer loyalty?
GoPro's marketing strategy relies heavily on:
GoPro's marketing strategy relies heavily on:
Beyond Meat appeals to consumers by emphasizing which core values?
Beyond Meat appeals to consumers by emphasizing which core values?
The 'STP' in marketing stands for which of the following?
The 'STP' in marketing stands for which of the following?
Which analytical tool helps companies assess their Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats?
Which analytical tool helps companies assess their Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats?
Which type of exam question assesses the ability to recall facts and definitions?
Which type of exam question assesses the ability to recall facts and definitions?
Flashcards
What is Marketing?
What is Marketing?
Creating value for customers and building strong relationships to capture value in return.
Marketing Process
Marketing Process
Understanding needs, designing a strategy, creating a program, and building relationships.
Needs, Wants, and Demands
Needs, Wants, and Demands
Basic requirements (needs) shaped by culture (wants) backed by purchasing power (demands).
STP (Segmentation, Targeting, Positioning)
STP (Segmentation, Targeting, Positioning)
Signup and view all the flashcards
4Ps of Marketing
4Ps of Marketing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Customer Satisfaction and Delight
Customer Satisfaction and Delight
Signup and view all the flashcards
Company Mission
Company Mission
Signup and view all the flashcards
Market Share
Market Share
Signup and view all the flashcards
Market Development
Market Development
Signup and view all the flashcards
Product Development
Product Development
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diversification
Diversification
Signup and view all the flashcards
Microenvironment
Microenvironment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Macroenvironment
Macroenvironment
Signup and view all the flashcards
SWOT Analysis
SWOT Analysis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Primary Data
Primary Data
Signup and view all the flashcards
Secondary Data
Secondary Data
Signup and view all the flashcards
Customer Stimuli
Customer Stimuli
Signup and view all the flashcards
Compensatory Decision Making
Compensatory Decision Making
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lexicographic Decision Rule
Lexicographic Decision Rule
Signup and view all the flashcards
Elimination by Aspects
Elimination by Aspects
Signup and view all the flashcards
Postpurchase Dissonance
Postpurchase Dissonance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Complex Buying Behavior
Complex Buying Behavior
Signup and view all the flashcards
Prospect Theory
Prospect Theory
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
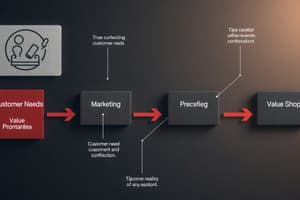
- Marketing involves creating value for customers and building customer relationships to capture value in return.
- Marketing involves understanding customer needs and delivering solutions, not just selling products.
The Marketing Process
- Understand customer needs.
- Design a customer-driven marketing strategy.
- Create an integrated marketing program.
- Build strong customer relationships.
Customer Needs, Wants, and Demands
- Needs are basic human requirements (e.g., food, water).
- Wants are shaped by culture and individual personality (e.g., desire for a specific brand of food).
- Demands are wants backed by purchasing power.
STP (Segmentation, Targeting, Positioning)
- Segmentation divides the market into distinct groups with different needs and behaviors.
- Targeting involves selecting the market segments to serve.
- Positioning is how a company wants consumers to perceive its product or brand.
4Ps of Marketing (Product, Price, Place, Promotion)
- Product refers to what you offer to satisfy customer needs.
- Price is the cost customers pay for the product.
- Place refers to how the product is distributed to customers.
- Promotion includes activities to raise awareness and persuade customers to buy.
Customer Satisfaction and Delight
- Customer satisfaction means meeting or exceeding customer expectations.
- Customer delight means going beyond customer expectations to create a memorable experience.
Company Mission and Business Definition
- A company’s mission defines its purpose, objectives, and strategy.
- The company mission answers why the company exists and what it aims to accomplish.
Market Share
- Market share is the percentage of total sales in an industry or market held by a company.
- A higher market share signifies a dominant position.
BCG Matrix
- The Boston Consulting Group (BCG) matrix analyzes a company’s product portfolio.
- Stars have high growth and market share.
- Cash Cows have low growth but high market share.
- Question Marks have high growth but low market share.
- Dogs have low growth and low market share.
Product-Market Growth Matrix
- This matrix helps companies identify growth opportunities based on current and new markets and products.
- Market Penetration involves selling more of existing products in existing markets.
- Market Development involves introducing existing products to new markets.
- Product Development means creating new products for existing markets.
- Diversification means introducing new products to new markets.
Microenvironment
- Includes forces close to the company that affect its ability to serve customers.
- Includes the company itself, its suppliers, marketing intermediaries, competitors, and customers.
Macroenvironment
- Includes broader forces that impact the company.
- Includes demographic, economic, natural, technological, political, and cultural factors.
SWOT Analysis
- SWOT analysis assesses a company’s internal Strengths and Weaknesses, and external Opportunities and Threats.
Marketing Research Process
- Marketing research involves identifying problems, collecting data, analyzing the information, and using findings to make informed decisions.
Research Objectives
- Clear objectives should guide research design.
- These include exploratory, descriptive, and causal research objectives.
Primary Data and Secondary Data
- Primary data is collected for a specific research project (e.g., surveys, interviews).
- Secondary data is previously collected for another purpose (e.g., reports, census data).
Primary Data Collection Methods
- Common methods include surveys, focus groups, and observation.
- Surveys involve structured questionnaires used to collect data from a large audience.
- Focus groups refer to small group discussions to explore attitudes and perceptions.
- Observation is when watching consumer behavior to gain insights.
Primary vs. Secondary Data
- Primary data is specific to the research problem, while secondary data is more readily available.
- Primary data can be expensive and time-consuming, while secondary data may not always be directly relevant.
Customer Needs and Stimuli
- External stimuli (advertisements, word of mouth) trigger a customer’s needs, influencing their buying decisions.
Information Search
- Consumers look for information to make an informed decision.
- Sources include personal (friends, family), commercial (advertising), public (reviews), and experiential (trying the product).
Evaluation of Alternatives
- Consumers evaluate alternatives based on various criteria (e.g., price, quality, features).
Compensatory Decision Making
- Consumers weigh the pros and cons of different options.
- Strengths in one area can compensate for weaknesses in another.
Non-Compensatory Decision Making
- Consumers use rigid rules to make decisions.
- Lexicographic Decision Rule involves choosing the alternative with the highest rating on the most important attribute.
- Elimination by Aspects involves rejecting alternatives that do not meet a certain threshold on key attributes.
Two-Stage Decision Making
- Involves an initial screening (eliminating options).
- Followed by a more detailed comparison of the remaining options.
Postpurchase Dissonance
- Consumers may feel regret or doubt after a purchase.
- It may be caused by conflicting information or expectations.
Types of Buying Behavior
- Complex Buying Behavior: High involvement, significant differences between alternatives.
- Dissonance-Reducing Buying Behavior: High involvement, few differences between alternatives.
- Habitual Buying Behavior: Low involvement, few differences between alternatives.
- Variety-Seeking Buying Behavior: Low involvement, significant differences between alternatives.
Prospect Theory
- People value gains and losses differently.
- Losses have a greater psychological impact than gains.
Case Study: Walt Disney World
- Marketing Strategy: Disney uses emotional connections and immersive experiences to drive customer loyalty.
- Key Takeaway: Delight customers by going beyond satisfaction.
Case Study: GoPro
- Marketing Strategy: GoPro leverages user-generated content to inspire new customers.
- Key Takeaway: Engage customers through content and community to build brand loyalty.
Case Study: Beyond Meat
- Marketing Strategy: Beyond Meat uses health-conscious messaging and environmental sustainability to attract consumers.
- Key Takeaway: Target specific consumer values, such as health and sustainability, to differentiate products.
Exam Review Key Concepts
- The marketing process flows from analyzing customer needs to building relationships.
- STP refers to market segmentation, targeting, and positioning.
- The 4Ps of Marketing: Product, Price, Place, Promotion.
- The BCG Matrix has four types of products: stars, cash cows, question marks, and dogs.
- SWOT Analysis identifies strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
- Primary data is collected for a specific purpose, while secondary data was previously collected for another purpose.
- Consumer behavior involves decision-making processes, buying behavior, and the impact of stimuli on choices.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
Marketing focuses on creating value for customers and building strong relationships to capture value in return. This involves understanding customer needs, designing effective marketing strategies. Segmentation, targeting and positioning are important steps. The marketing mix consists of the 4Ps: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion.