Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary goal of treatment in pneumonia?
What is the primary goal of treatment in pneumonia?
- Minimize morbidity
- Eradicate offending organism
- Prevent aspiration
- Achieve complete clinical cure (correct)
What is the purpose of oxygen therapy in pneumonia?
What is the purpose of oxygen therapy in pneumonia?
- To prevent aspiration
- To eradicate the offending organism
- To reduce fever
- To improve oxygenation (correct)
What is the key factor in selecting antibiotic therapy for pneumonia?
What is the key factor in selecting antibiotic therapy for pneumonia?
- Type of pneumonia (correct)
- Patient age
- Type of antibiotic
- Duration of treatment
What is the expected timeline for full recovery from pneumonia?
What is the expected timeline for full recovery from pneumonia?
What is monitored during treatment of pneumonia?
What is monitored during treatment of pneumonia?
What is one way to prevent VAP?
What is one way to prevent VAP?
What is the purpose of vaccination in pneumonia prevention?
What is the purpose of vaccination in pneumonia prevention?
What is the purpose of bronchodilators in pneumonia treatment?
What is the purpose of bronchodilators in pneumonia treatment?
What are the 3rd and 4th most common causes of death?
What are the 3rd and 4th most common causes of death?
What is the annual incidence of pneumonia reported per 10,000 adults?
What is the annual incidence of pneumonia reported per 10,000 adults?
What is the most common cause of pneumonia and mortality due to LRTIs?
What is the most common cause of pneumonia and mortality due to LRTIs?
What happens to the alveoli in pneumonia?
What happens to the alveoli in pneumonia?
How can microorganisms bypass the normal protective mechanism to gain access to the lower respiratory tract?
How can microorganisms bypass the normal protective mechanism to gain access to the lower respiratory tract?
What can depress mucociliary transport?
What can depress mucociliary transport?
How can viruses and bacteria suppress the antibacterial activity of the lung?
How can viruses and bacteria suppress the antibacterial activity of the lung?
What is the result of impairment in the normal defense mechanism?
What is the result of impairment in the normal defense mechanism?
What is a common respiratory symptom of the clinical presentation?
What is a common respiratory symptom of the clinical presentation?
What is a diagnostic test used to determine the presence of bacteria in the blood?
What is a diagnostic test used to determine the presence of bacteria in the blood?
What is the primary characteristic that distinguishes atypical CAP from typical CAP?
What is the primary characteristic that distinguishes atypical CAP from typical CAP?
What is a non-respiratory symptom of the clinical presentation?
What is a non-respiratory symptom of the clinical presentation?
Which of the following bacteria is associated with hospital-acquired pneumonia?
Which of the following bacteria is associated with hospital-acquired pneumonia?
What is a complication of the clinical presentation?
What is a complication of the clinical presentation?
What is the name of the type of pneumonia that occurs when a patient who is at risk of aspiration develops pneumonia and anaerobic pathogens from the digestive tract are implicated?
What is the name of the type of pneumonia that occurs when a patient who is at risk of aspiration develops pneumonia and anaerobic pathogens from the digestive tract are implicated?
What is a diagnostic test used to examine the lungs?
What is a diagnostic test used to examine the lungs?
Which of the following is NOT a typical symptom of typical CAP?
Which of the following is NOT a typical symptom of typical CAP?
What is the primary pathogen associated with ventilator-associated pneumonia?
What is the primary pathogen associated with ventilator-associated pneumonia?
What is a laboratory test used to determine the number of white blood cells?
What is a laboratory test used to determine the number of white blood cells?
What is the primary source of pathogens implicated in aspiration pneumonia?
What is the primary source of pathogens implicated in aspiration pneumonia?
What is a sign of the clinical presentation?
What is a sign of the clinical presentation?
What is a diagnostic test used to examine the airways?
What is a diagnostic test used to examine the airways?
Which of the following is a common complication of aspiration pneumonia?
Which of the following is a common complication of aspiration pneumonia?
What is the classification of CAP based on?
What is the classification of CAP based on?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Lower Respiratory Tract Infections (LRTIs)
- LRTIs, including COPD and acute exacerbation of chronic lung diseases, are the 3rd and 4th most common causes of death worldwide.
- They are caused by viral or bacterial infections, with an annual incidence of 24.8 per 10,000 adults, and a higher incidence in patients over 65 years old.
Pneumonia
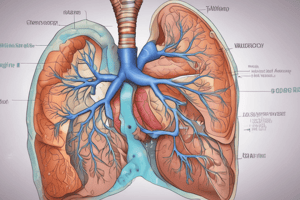
- Pneumonia is a bacterial or viral infection of the lungs, causing the alveoli to fill with pus and become solid.
- Pathogens can bypass the normal protective mechanisms to gain access to the lower respiratory tract through inhalation, hematogenous seeding, or aspiration of oropharyngeal contents.
- Impairments in the normal defense mechanism, such as depressed mucociliary transport, can increase the risk of developing pneumonia.
Pneumonia Classification
- Pneumonia can be classified as community-acquired or hospital-acquired, with different types of causative pathogens, including aerobic bacteria, atypical bacteria, and viruses.
- Ventilator-associated pneumonia is a type of hospital-acquired pneumonia caused by pathogens such as Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Enterobacter species.
Community-Acquired Pneumonia (CAP)
- CAP can be classified as typical or atypical, based on patient presentation, clinical observations, and course of the disease.
- Typical CAP is associated with acute fever, chills, pleuritic chest pain, and productive cough, while atypical CAP is associated with myalgias, fever without chills, headache, and unproductive cough.
- Aspiration pneumonia is a type of CAP that occurs when a patient at risk of aspiration develops pneumonia, often with anaerobic pathogens from the digestive tract.
Signs and Symptoms
- Symptoms of pneumonia include respiratory symptoms such as cough, shortness of breath, and difficulty breathing, as well as non-respiratory symptoms such as fever, fatigue, sweats, headache, and myalgias.
- Signs of pneumonia include temperature, increased respiratory rate, cyanosis, and diminished breath sounds.
Diagnosis
- Diagnosis of pneumonia involves laboratory tests, diagnostic tests, and microbiological tests, including chest X-ray, CT scan, sputum gram stain and culture, and blood culture.
Risk Factors
- Risk factors for pneumonia include age, underlying medical conditions, and impaired defense mechanisms.
Complications
- Complications of pneumonia include bacteremia, difficulty breathing, fluid accumulation around the lungs, and lung abscess.
Treatment
- Goals of treatment include eradicating the offending organism, achieving complete clinical cure, and minimizing associated morbidity.
- Treatment involves non-pharmacological therapy, such as oxygen, mechanical ventilation, and fluid resuscitation, as well as pharmacologic therapy, including antibiotics and bronchodilators.
- Antibiotic selection depends on the type of pneumonia, patient factors, and severity of disease presentation.
Monitoring and Prevention
- Monitoring involves tracking improvements or worsening of clinical symptoms and laboratory and diagnostic parameters.
- Prevention involves vaccination, immune prophylaxis, and minimizing the risk of developing ventilator-associated pneumonia.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.