Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following structures is NOT part of the lower limb skeleton?
Which of the following structures is NOT part of the lower limb skeleton?
- Tibia
- Femur
- Pelvic girdle
- Humerus (correct)
Approximately how many bones are in the lower limb?
Approximately how many bones are in the lower limb?
- 30 (correct)
- 38
- 34
- 26
Which of the following is a region of the lower limb?
Which of the following is a region of the lower limb?
- Gluteal (correct)
- Thoracic
- Brachial
- Cervical
What two bones make up the pelvic girdle?
What two bones make up the pelvic girdle?
Which of the following bones is NOT fused to form the hip bone?
Which of the following bones is NOT fused to form the hip bone?
What is the function of the pelvic girdle?
What is the function of the pelvic girdle?
What is the acetabulum?
What is the acetabulum?
What is the name given to the cavity in the lower part of the trunk of the human body?
What is the name given to the cavity in the lower part of the trunk of the human body?
The human pelvic anatomy is a compromise between what two requirements?
The human pelvic anatomy is a compromise between what two requirements?
Which of the following is a characteristic of the male pelvis compared to the female pelvis?
Which of the following is a characteristic of the male pelvis compared to the female pelvis?
Which of the following is the longest and strongest bone in the body?
Which of the following is the longest and strongest bone in the body?
Which of the following is found on the proximal end of the femur?
Which of the following is found on the proximal end of the femur?
What structure is found on the shaft of the Femur?
What structure is found on the shaft of the Femur?
Which of the following is a common site for fractures of the femur?
Which of the following is a common site for fractures of the femur?
What is the general shape of the patella?
What is the general shape of the patella?
On which surface of the patella is the smooth, oval articulation located?
On which surface of the patella is the smooth, oval articulation located?
What is the apex of the patella?
What is the apex of the patella?
The patella is embedded in the quadriceps femoris tendon and is the __________ sesamoid bone in the body.
The patella is embedded in the quadriceps femoris tendon and is the __________ sesamoid bone in the body.
Flashcards
Pelvic Girdle Definition
Pelvic Girdle Definition
The pelvic girdle transfers the weight of the upper body to the lower limbs and consists of two hip bones.
Hip Bone Composition
Hip Bone Composition
A hip bone consists of three fused bones: ilium, ischium, and pubis.
Acetabulum Function
Acetabulum Function
The acetabulum is the socket on the hip bone that forms the hip joint with the femur.
False vs. True Pelvis
False vs. True Pelvis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pelvic Adaptation Factors
Pelvic Adaptation Factors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Femur Definition
Femur Definition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Femur Proximal End
Femur Proximal End
Signup and view all the flashcards
Femur Shaft Features
Femur Shaft Features
Signup and view all the flashcards
Femur Distal End
Femur Distal End
Signup and view all the flashcards
Patella Definition
Patella Definition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Patella Functions
Patella Functions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Patella Surfaces
Patella Surfaces
Signup and view all the flashcards
Patella Surface Texture
Patella Surface Texture
Signup and view all the flashcards
False Pelvis Location
False Pelvis Location
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- Lecture 7 is on the Skeleton of the Lower Limb I, by C. Mupfiga from the University of the Western Cape
Lower Limb Skeleton
- Consists of 30 bones adapted for weight-bearing and locomotion.
- Includes the pelvic girdle, hip bone, femur, patella, tibia, fibula, tarsals, metatarsals, and the phalanges
- Regions are gluteal, thigh, leg, ankle, and foot
- Adapted for weight-bearing, locomotion, and bipedal posture
- Bones of the pelvic girdle and lower limb are more massive than their homologues of the upper limb
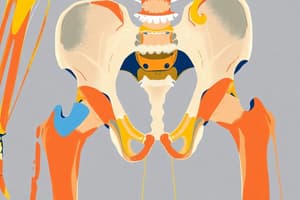
Pelvic Girdle
- Transfers the weight of the upper body to the lower limbs
- The pelvic girdle consists of 2 hip bones, each with 3 fused bones: ilium, ischium, and pubis
- Along with the sacrum and coccyx, they form a bowl-shaped region called the pelvis
- Each hip bone is large, flattened, and irregularly shaped
- The right and left hip bones meet anteriorly, forming the lateral and anterior walls of the pelvic cavity
- The 3 parts (ilium, ischium, and pubis) merge at the acetabulum, forming the hip joint with the femur
- Functions of the pelvic girdle include supporting and protecting abdominal and pelvic organs and the developing foetus
- Attaches lower limbs to the trunk, and transmits weight of upper body from vertebral column to lower limbs
- The pelvis, resembles a basin, a bony ring between the vertebral column and lower limbs
- Divided by the pelvic brim into a false pelvis and true pelvis
- The false pelvis is an expanded portion of the cavity lying above the pelvic brim
- The true pelvis is situated below the pelvic brim and consists of an inlet, outlet, and cavity
- Human pelvic anatomy must allow for both bipedalism and childbirth, which results in a narrower pelvic outlet for humans, potentially causing pain and difficulty during childbirth
Femur
- It is the longest and strongest bone of the skeleton
- In the erect posture, it is slightly inclined medially
- The proximal end consists of the head, neck, greater and lesser trochanter, intertrochanteric crest and line
- The shaft: linea aspera, gluteal tuberosity, popliteal surface
- The distal end consists of medial and lateral condyles, intercondylar fossa, patellar surface
Femoral Fractures
- The neck of the femur is most frequently fractured because it is the narrowest and weakest part of the bone
- Lies at an angle to the line of weight-bearing
- It becomes increasingly vulnerable with age, especially in females, secondary to osteoporosis
- Fractures of the femoral shaft result from direct trauma sustained by the bone resulting from falls
Patella
- A flat triangular bone situated anterior to distal end of femur
- The anterior surface is roughened
- The posterior surface is smooth and oval; has medial and lateral facets which articulate with condyles of femur
- Borders include a superior base border, medial and lateral borders
- The apex is pointed inferiorly
- It is a roughly triangular sesamoid bone embedded in the tendon of the quadriceps femoris muscle
- Largest sesamoid bone
- It protects the tendon against friction and increases mechanical advantage by changing the direction of pull
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.