Podcast
Questions and Answers
During the descent phase of a squat, which type of muscle action is primarily occurring in the quadriceps?
During the descent phase of a squat, which type of muscle action is primarily occurring in the quadriceps?
- Concentric
- Isometric
- Isokinetic
- Eccentric (correct)
Which of the following best describes a functional closed-chain movement involving the knee joint?
Which of the following best describes a functional closed-chain movement involving the knee joint?
- Supine straight leg raise exercise
- Standing calf raise exercise (correct)
- Lying hamstring curl exercise
- Seated knee extension exercise
What anatomical structure is located within the intercondylar notch of the distal femur?
What anatomical structure is located within the intercondylar notch of the distal femur?
- Lateral collateral ligament (LCL)
- Patellar tendon
- Medial collateral ligament (MCL)
- Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) (correct)
Which description accurately defines the patella's composition?
Which description accurately defines the patella's composition?
What is the primary function of the tibial tuberosity?
What is the primary function of the tibial tuberosity?
Which ligament has a direct attachment to the fibular head?
Which ligament has a direct attachment to the fibular head?
A patient presents with a Q angle of 25 degrees. What is the most likely implication of this measurement?
A patient presents with a Q angle of 25 degrees. What is the most likely implication of this measurement?
What is the clinical term for 'bowlegs,' characterized by a lateral angle greater than 180 degrees at the knee?
What is the clinical term for 'bowlegs,' characterized by a lateral angle greater than 180 degrees at the knee?
In a concentric contraction of the quadriceps during a leg extension exercise, what is the primary action occurring at the knee joint?
In a concentric contraction of the quadriceps during a leg extension exercise, what is the primary action occurring at the knee joint?
If an individual has a Q angle significantly higher than normal, which structure is most likely subjected to increased stress?
If an individual has a Q angle significantly higher than normal, which structure is most likely subjected to increased stress?
Which of the following describes the position of the knee in genu valgum?
Which of the following describes the position of the knee in genu valgum?
Where is the patella located in relation to the quadriceps tendon?
Where is the patella located in relation to the quadriceps tendon?
Which part of the femur articulates with the tibial plateau?
Which part of the femur articulates with the tibial plateau?
What is the clinical implication of observing a genu varum deformity in a patient?
What is the clinical implication of observing a genu varum deformity in a patient?
During knee extension, which action would be considered a concentric contraction for the quadriceps muscle group?
During knee extension, which action would be considered a concentric contraction for the quadriceps muscle group?
What is the primary function of the hyaline cartilage located on the posterior aspect of the patella?
What is the primary function of the hyaline cartilage located on the posterior aspect of the patella?
How does an increased Q angle typically affect the alignment and forces acting on the patella?
How does an increased Q angle typically affect the alignment and forces acting on the patella?
Which movement would primarily engage eccentric contractions of the quadriceps femoris?
Which movement would primarily engage eccentric contractions of the quadriceps femoris?
What is a key characteristic that defines a functional closed-chain exercise for the lower extremity?
What is a key characteristic that defines a functional closed-chain exercise for the lower extremity?
What is the primary anatomical feature located within the intercondylar notch of the femur?
What is the primary anatomical feature located within the intercondylar notch of the femur?
How does the Q angle influence patellofemoral joint mechanics?
How does the Q angle influence patellofemoral joint mechanics?
Which of the following is the clinical term for a condition characterized by the knees angling inward and touching when the ankles are separated?
Which of the following is the clinical term for a condition characterized by the knees angling inward and touching when the ankles are separated?
What muscle action occurs in the quadriceps during the upward phase of a squat exercise?
What muscle action occurs in the quadriceps during the upward phase of a squat exercise?
Which of the following is a hallmark characteristic of closed-chain exercises?
Which of the following is a hallmark characteristic of closed-chain exercises?
Which anatomical structure provides a direct attachment site for the patellar tendon?
Which anatomical structure provides a direct attachment site for the patellar tendon?
Lateral deviation with respect to alignment of the knee describes which condition?
Lateral deviation with respect to alignment of the knee describes which condition?
What is the consequence of a Q angle greater than 20°?
What is the consequence of a Q angle greater than 20°?
What is the role of hyaline cartilage on the posterior side of the patella?
What is the role of hyaline cartilage on the posterior side of the patella?
What movement is an example of a concentric action?
What movement is an example of a concentric action?
What is the normal range for the Q angle?
What is the normal range for the Q angle?
Which is NOT a part of the distal femur?
Which is NOT a part of the distal femur?
What is the articulation between the Tibia and the Femur referred to as?
What is the articulation between the Tibia and the Femur referred to as?
The medial and lateral convex surfaces of the distal femur are called what?
The medial and lateral convex surfaces of the distal femur are called what?
Which action describes someone rising from a lunge?
Which action describes someone rising from a lunge?
Which action describes someone controlling their descent into a lunge?
Which action describes someone controlling their descent into a lunge?
Laterally, the fibular head articulates with which structure?
Laterally, the fibular head articulates with which structure?
On which structure is hyaline cartilage found?
On which structure is hyaline cartilage found?
The tibial plateau provides a concave surface for articulation between which two structures?
The tibial plateau provides a concave surface for articulation between which two structures?
The tibial condyles are on which structure?
The tibial condyles are on which structure?
Which of the following is true about females, with respect to the Q angle?
Which of the following is true about females, with respect to the Q angle?
Flashcards
Eccentric Muscle Action
Eccentric Muscle Action
Muscle lengthens under tension, like lowering into a squat.
Concentric Muscle Action
Concentric Muscle Action
Muscle shortens under tension, like standing up from a squat.
Tibiofemoral Joint
Tibiofemoral Joint
The main knee joint, where the tibia and femur connect.
Functional Closed-Chain Movements
Functional Closed-Chain Movements
Signup and view all the flashcards
Distal Femur Condyles
Distal Femur Condyles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Intercondylar Notch
Intercondylar Notch
Signup and view all the flashcards
Femoral Epicondyles
Femoral Epicondyles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Patella
Patella
Signup and view all the flashcards
Patellar Articular Facets
Patellar Articular Facets
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tibial Plateau
Tibial Plateau
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tibial Tuberosity
Tibial Tuberosity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fibular Head
Fibular Head
Signup and view all the flashcards
Q Angle
Q Angle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pathological Q Angle
Pathological Q Angle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Genu Varum
Genu Varum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Genu Valgum
Genu Valgum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- Study notes on knee anatomy, biomechanics, and functional considerations.
Key Concepts
- Eccentric Muscle Actions: Muscles lengthen while contracting, exemplified by controlling the descent into a lunge.
- Concentric Muscle Actions: Muscles shorten while contracting, exemplified by rising from a lunge.
- Tibiofemoral Joint: The knee's primary joint, involving the articulation between the tibia and femur.
- Functional Closed-Chain Movements: Movements where the distal segment is fixed, such as the foot being on the ground during a lunge.
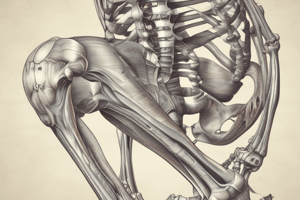
Osteology (Bone Structures)
- Distal Femur: Features medial and lateral convex condyles.
- Intercondylar Notch: Separates the condyles, and it allows passage for the cruciate ligaments.
- Epicondyles: Bony projections for ligament attachments.
- Patella: A triangular sesamoid bone within the quadriceps tendon.
- Patella: Includes medial, lateral, superior, and inferior articular facets.
- Patella: Has thick hyaline cartilage posteriorly.
- Proximal Tibia: Includes medial (larger) and lateral tibial condyles.
- Tibial Plateau: Concave surface for femoral articulation.
- Tibial Tuberosity: It is the attachment point for the patellar tendon.
- Fibula: The fibular head articulates with the tibia, and it is the attachment point for the lateral collateral ligament (LCL).
Arthrology (Joint Structures)
- Q Angle: Formed by the quadriceps tendon, patella tendon, and tibial tuberosity.
- Normal Q Angle: Approximately 12-20° (typically higher in females).
- Pathological Q Angle: Greater than 20°, increasing lateral force on the patella.
- Genu Varum (Bowlegs): Lateral angle is more than 180°.
- Genu Valgum (Knock Knees): Lateral angle is less than 180°.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.