Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the upper respiratory tract?
What is the primary function of the upper respiratory tract?
- To regulate pH levels
- To exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide
- To warm, humidify, and filter the air we breathe (correct)
- To conduct air to the lungs
Which of the following is NOT a part of the lower respiratory tract?
Which of the following is NOT a part of the lower respiratory tract?
- Trachea
- Alveoli
- Pharynx (correct)
- Bronchioles
What is the main function of the lungs?
What is the main function of the lungs?
- To filter out dust and debris
- To regulate breathing
- To exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide (correct)
- To warm and humidify the air
Which muscle is primarily responsible for breathing?
Which muscle is primarily responsible for breathing?
Where does gas exchange occur in the respiratory system?
Where does gas exchange occur in the respiratory system?
What is the function of the epiglottis?
What is the function of the epiglottis?
What influences the regulation of breathing?
What influences the regulation of breathing?
What is the function of the intercostal muscles?
What is the function of the intercostal muscles?
What is the brainstem's role in breathing?
What is the brainstem's role in breathing?
What is transported to the heart after gas exchange occurs?
What is transported to the heart after gas exchange occurs?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Overview
- The respiratory system is a complex biological system that brings oxygen into the body and removes carbon dioxide.
- It consists of the upper and lower respiratory tracts, lungs, and breathing muscles.
Upper Respiratory Tract
- Includes the:
- Nose and mouth (entry points for air)
- Pharynx (throat)
- Larynx (voice box)
- Epiglottis ( flap that separates the trachea and esophagus)
- Functions:
- Warms, humidifies, and filters the air we breathe
- Contains small hair-like structures called cilia that help remove dust and debris
Lower Respiratory Tract
- Includes the:
- Trachea (windpipe)
- Bronchi (tubes that branch off from the trachea)
- Bronchioles (smaller tubes that branch off from the bronchi)
- Alveoli (tiny air sacs where gas exchange occurs)
- Functions:
- Conducts air to the lungs
- Allows for gas exchange between the air we breathe and the bloodstream
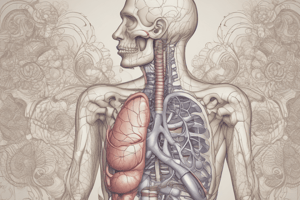
Lungs
- Located in the chest cavity, protected by the rib cage
- Functions:
- Exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide through the process of respiration
- Regulate pH levels by removing excess hydrogen ions
Breathing Muscles
- Includes the:
- Diaphragm (main muscle of breathing, located below the lungs)
- Intercostal muscles (muscles between the ribs)
- Accessory muscles (neck, back, and abdominal muscles that assist with breathing)
- Functions:
- Contract and relax to expand and deflate the lungs
- Allow for inhalation and exhalation
Gas Exchange
- Occurs in the alveoli, where oxygen diffuses into the bloodstream and carbon dioxide diffuses out
- Oxygen-rich blood is transported to the heart and then to the rest of the body
- Carbon dioxide-rich blood is transported to the lungs, where it is exhaled out of the body
Regulation of Breathing
- Controlled by the:
- Brainstem (regulates automatic breathing)
- Cerebral cortex (regulates voluntary breathing)
- Influenced by factors such as:
- Carbon dioxide levels
- Oxygen levels
- pH levels
- Emotional state (e.g. anxiety, excitement)
Respiratory System
- Complex biological system that brings oxygen into the body and removes carbon dioxide
Upper Respiratory Tract
- Includes nose and mouth as entry points for air
- Includes pharynx (throat), larynx (voice box), and epiglottis (flap that separates trachea and esophagus)
- Functions: warms, humidifies, and filters the air we breathe
- Contains small hair-like structures called cilia that help remove dust and debris
Lower Respiratory Tract
- Includes trachea (windpipe), bronchi (tubes that branch off from trachea), bronchioles (smaller tubes that branch off from bronchi), and alveoli (tiny air sacs where gas exchange occurs)
- Functions: conducts air to the lungs and allows for gas exchange between the air we breathe and the bloodstream
Lungs
- Located in the chest cavity, protected by the rib cage
- Functions: exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide through the process of respiration, and regulate pH levels by removing excess hydrogen ions
Breathing Muscles
- Includes diaphragm (main muscle of breathing, located below the lungs), intercostal muscles (muscles between the ribs), and accessory muscles (neck, back, and abdominal muscles that assist with breathing)
- Functions: contract and relax to expand and deflate the lungs, allowing for inhalation and exhalation
Gas Exchange
- Occurs in the alveoli, where oxygen diffuses into the bloodstream and carbon dioxide diffuses out
- Oxygen-rich blood is transported to the heart and then to the rest of the body
- Carbon dioxide-rich blood is transported to the lungs, where it is exhaled out of the body
Regulation of Breathing
- Controlled by the brainstem (regulates automatic breathing) and cerebral cortex (regulates voluntary breathing)
- Influenced by factors such as carbon dioxide levels, oxygen levels, pH levels, and emotional state
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.