Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the difference in partial pressure of oxygen between the alveoli and the blood of the pulmonary capillaries?
What is the difference in partial pressure of oxygen between the alveoli and the blood of the pulmonary capillaries?
- 40 mm Hg
- 104 mm Hg
- 10 mm Hg
- 64 mm Hg (correct)
What is the partial pressure of oxygen in the alveoli?
What is the partial pressure of oxygen in the alveoli?
- 45 mm Hg
- 40 mm Hg
- 104 mm Hg (correct)
- 100 mm Hg
What is the partial pressure of carbon dioxide in the blood of the capillary?
What is the partial pressure of carbon dioxide in the blood of the capillary?
- 50 mm Hg
- 55 mm Hg
- 45 mm Hg (correct)
- 40 mm Hg
What is the term for gas exchange that occurs at the level of body tissues?
What is the term for gas exchange that occurs at the level of body tissues?
Why is the solubility of carbon dioxide greater than that of oxygen?
Why is the solubility of carbon dioxide greater than that of oxygen?
What is the partial pressure of oxygen in tissues?
What is the partial pressure of oxygen in tissues?
What causes oxygen to dissociate from hemoglobin and diffuse out of the blood?
What causes oxygen to dissociate from hemoglobin and diffuse out of the blood?
What is the color of blood returning to the heart?
What is the color of blood returning to the heart?
What is the direction of oxygen diffusion across the respiratory membrane?
What is the direction of oxygen diffusion across the respiratory membrane?
What is the relative concentration of oxygen and carbon dioxide that diffuse across the respiratory membrane?
What is the relative concentration of oxygen and carbon dioxide that diffuse across the respiratory membrane?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Diseases of the Lungs
- Some diseases affect one or more bronchopulmonary segments, which can be surgically removed with little influence on neighboring segments.
- A pulmonary lobule is a subdivision of the lung formed as the bronchi branch into bronchioles.
- Each lobule receives its own large bronchiole that has multiple branches.
- An interlobular septum is a wall of connective tissue that separates lobules from one another.
Blood Supply of the Lungs
- The lungs together receive the total cardiac output of 5 L/min.
- The pulmonary circulation is a low-pressure, low-resistance system with a systolic/diastolic pressure of 25/10 mmHg and a mean pressure of 15 mmHg.
- The lungs contain 450 ml of blood, which is 12% of the total blood volume.
- The capillary network in the lungs is more dense than elsewhere to provide a large interface for gas exchange.
- The pulmonary arterioles constrict in response to a fall in PO2 or a rise in PCO2.
- Blood is preferentially distributed to dependent parts of the lungs.
Pulmonary Artery and Capillary Network
- The pulmonary artery arises from the pulmonary trunk and carries deoxygenated blood to the alveoli.
- The pulmonary artery branches multiple times, following the bronchi, and each branch becomes progressively smaller in diameter.
- One arteriole and an accompanying venule supply and drain one pulmonary lobule.
- The pulmonary capillary network consists of tiny vessels with very thin walls that lack smooth muscle fibers.
- The capillaries branch and follow the bronchioles and alveoli, forming the respiratory membrane.
Nervous Innervation of the Lungs
- The parasympathetic system causes bronchoconstriction, whereas the sympathetic nervous system stimulates bronchodilation.
- The pulmonary plexus is a region on the lung root formed by the entrance of the nerves at the hilum.
- Sensory nerve fibers arise from the vagus nerve and the second to fifth thoracic ganglia.
Pleura of the Lungs
- Each lung is enclosed within a cavity surrounded by the pleura.
- The pleura is a serous membrane that surrounds the lung.
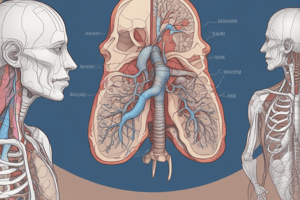
Gas Exchange
- There is a drastic difference in the partial pressure of oxygen in the alveoli (104 mmHg) versus in the blood of the pulmonary capillaries (40 mmHg).
- This difference creates a strong pressure gradient that causes oxygen to rapidly cross the respiratory membrane into the blood.
- The partial pressure of carbon dioxide in the blood of the capillary (45 mmHg) is higher than in the alveoli (40 mmHg).
- Carbon dioxide has a higher solubility than oxygen in both blood and alveolar fluids.
Internal Respiration
- Internal respiration is gas exchange that occurs at the level of body tissues.
- Gas exchange occurs as simple diffusion due to a partial pressure gradient.
- The partial pressure of oxygen in tissues is low (about 40 mmHg), causing oxygen to dissociate from hemoglobin and diffuse into the tissues.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.