Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the respiratory bronchiole?
What is the primary function of the respiratory bronchiole?
- To facilitate gaseous exchange (correct)
- To warm and humidify the air
- To produce mucus to trap pathogens
- To filter out dust and other particles
What is the approximate diameter of the bronchioles?
What is the approximate diameter of the bronchioles?
- 1 micrometre
- 1 millimetre (correct)
- 1 centimetre
- 1 nanometre
What is the function of the pulmonary arteries?
What is the function of the pulmonary arteries?
- To carry oxygenated blood to the heart
- To carry deoxygenated blood to the alveoli (correct)
- To carry nutrient-rich blood to the lungs
- To carry waste products away from the lungs
Why do the conducting portions of the airways need their own oxygen-rich supply of blood?
Why do the conducting portions of the airways need their own oxygen-rich supply of blood?
What is the purpose of the alveoli?
What is the purpose of the alveoli?
How many alveoli are present in each lung?
How many alveoli are present in each lung?
Why are the pulmonary veins located at a distance from the bronchial tree?
Why are the pulmonary veins located at a distance from the bronchial tree?
What is the term for the final bronchiole that leads to the alveoli?
What is the term for the final bronchiole that leads to the alveoli?
What is the primary function of the nasal cavities and paranasal sinuses in the upper respiratory tract?
What is the primary function of the nasal cavities and paranasal sinuses in the upper respiratory tract?
Which of the following is NOT a protective mechanism of the airway?
Which of the following is NOT a protective mechanism of the airway?
What is the correct sequence of events in the cough reflex?
What is the correct sequence of events in the cough reflex?
Which of the following cartilages is NOT part of the larynx?
Which of the following cartilages is NOT part of the larynx?
What is the purpose of the laryngeal inlet?
What is the purpose of the laryngeal inlet?
Why is an inhaled foreign object more likely to be found in the right lung?
Why is an inhaled foreign object more likely to be found in the right lung?
What is a complication of viral infections that can lead to inflammation of the nose, ear, and throat?
What is a complication of viral infections that can lead to inflammation of the nose, ear, and throat?
During influenza or COVID-19 infection, what causes the lungs to become inflamed and clog the airways?
During influenza or COVID-19 infection, what causes the lungs to become inflamed and clog the airways?
What is the function of the respiratory bronchioles and alveoli?
What is the function of the respiratory bronchioles and alveoli?
What is the role of alveolar type 2 cells in the alveoli?
What is the role of alveolar type 2 cells in the alveoli?
What is the purpose of the conchae in the nasal cavities?
What is the purpose of the conchae in the nasal cavities?
What is the main function of the nasal cavities?
What is the main function of the nasal cavities?
What is the purpose of the mucus glands and serous glands in the nasal cavities?
What is the purpose of the mucus glands and serous glands in the nasal cavities?
Why is the mouth not considered a respiratory organ?
Why is the mouth not considered a respiratory organ?
What is the primary function of macrophages in the respiratory system?
What is the primary function of macrophages in the respiratory system?
What is the primary mechanism of the mucociliary elevator in the respiratory tract?
What is the primary mechanism of the mucociliary elevator in the respiratory tract?
Which type of cells are responsible for producing antibodies in the respiratory system?
Which type of cells are responsible for producing antibodies in the respiratory system?
What is the primary function of the cough reflex in the respiratory system?
What is the primary function of the cough reflex in the respiratory system?
What is the primary stimulus for the cough reflex in the respiratory system?
What is the primary stimulus for the cough reflex in the respiratory system?
What is the role of the vagus nerve in the cough reflex?
What is the role of the vagus nerve in the cough reflex?
What is the primary function of polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMN) in the respiratory system?
What is the primary function of polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMN) in the respiratory system?
What is the primary location of the epithelial cells that permit gas exchange in the respiratory system?
What is the primary location of the epithelial cells that permit gas exchange in the respiratory system?
What is the common cause of death among rock stars mentioned in the content?
What is the common cause of death among rock stars mentioned in the content?
What is the purpose of placing a patient in the recovery position?
What is the purpose of placing a patient in the recovery position?
What is the most common place for obstruction in the airway?
What is the most common place for obstruction in the airway?
What is the procedure that involves penetration of the cricothyroid membrane with a sharp implement?
What is the procedure that involves penetration of the cricothyroid membrane with a sharp implement?
What is the importance of maintaining patency of the air opening in cricothyroidotomy?
What is the importance of maintaining patency of the air opening in cricothyroidotomy?
What is the risk of excessive drinking, according to the content?
What is the risk of excessive drinking, according to the content?
Why is it important to avoid damage to the thyroid gland during cricothyroidotomy?
Why is it important to avoid damage to the thyroid gland during cricothyroidotomy?
What is the result of twisting the sharp implement during cricothyroidotomy?
What is the result of twisting the sharp implement during cricothyroidotomy?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
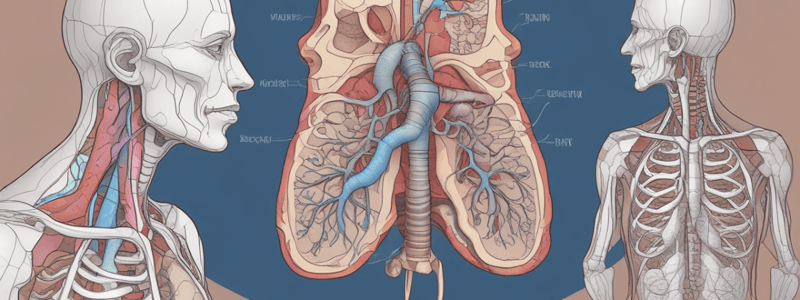
Upper Respiratory Tract
- The upper respiratory tract includes the nasal cavities, paranasal sinuses, larynx, and trachea.
- The respiratory functions of the nasal cavities and paranasal sinuses include warming, moistening, and filtering the inspired air.
- The nasal cavities are surrounded by blood vessels that exchange heat with each breath.
Nasal Cavities
- The nasal cavities are divided by a midline septum.
- The lateral walls of the nasal cavities have folds called conchae, which resemble the shape of a conical shell.
- The nasal cavities contain mucus glands and serous glands that humidify the inspired air.
- The nasal cavities are more efficient at heat and moisture exchange than the mouth.
Paranasal Sinuses
- The paranasal sinuses are extensions of the nasal cavities.
- They connect with the nasal cavities and are involved in the respiratory process.
Conducting Versus Respiratory Zones
- The conducting portion of the airway runs from the trachea to the terminal bronchioles.
- The respiratory bronchioles and alveoli are capable of gaseous exchange.
- Alveoli are lined by alveolar type 1 and alveolar type 2 cells, with the latter producing surfactant to reduce surface tension.
Pulmonary Circulation
- The pulmonary circulation supplies the lungs with deoxygenated blood.
- The pulmonary trunk emerges from the right ventricle and divides into the right and left pulmonary arteries.
- The pulmonary arteries carry deoxygenated blood to the alveoli, where gas exchange takes place.
- Oxygenated blood is then carried back to the left atrium of the heart via the pulmonary veins.
Bronchial Arteries
- The bronchial arteries supply oxygen-rich blood to the conducting portions of the airways.
- The walls of the conducting airways are too thick to permit diffusion, so they require their own oxygen-rich supply.
Immune Cells of the Airways
- Macrophages and immune cells can usually deal with microorganisms that enter the airways.
- Once the microorganism is phagocytosed, the macrophage presents microbial antigens on the surface to activate B and T cells.
- Activated B and T cells produce more antibody and/or activate the macrophage.
Coughing
- The cough reflex is a mechanism for clearance of the lungs.
- There are four distinct phases to a normal cough: irritation, inspiration, compression, and expulsion.
- The cough reflex can be triggered by inflammatory, mechanical, chemical, or thermal stimuli.
Larynx
- The larynx is a vital structure that protects the lungs.
- The larynx contains cartilages and membranes that play a crucial role in the respiratory process.
- The laryngeal inlet is a narrow passage that allows air to enter the lungs.
- An emergency laryngotomy may be required if the glottis is obstructed.
Emergency Laryngotomy
- The procedure involves penetration of the cricothyroid membrane with a sharp implement to establish an airway.
- Care must be taken to avoid damage to the thyroid gland.
- The patency of the opening needs to be maintained to prevent obstruction.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.