Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of saliva in digestion?
What is the primary function of saliva in digestion?
- Facilitating the absorption of proteins
- Breaking down fats into fatty acids
- Enhancing bone mineralization
- Regulating bacteria population (correct)
Which of the following substances is NOT found in gastric secretions?
Which of the following substances is NOT found in gastric secretions?
- Pepsinogen
- Hydrochloric acid
- Intrinsic factor
- Amylase (correct)
What role does intrinsic factor play in digestion?
What role does intrinsic factor play in digestion?
- Stimulates salivary amylase
- Neutralizes gastric acids
- Facilitates the absorption of vitamin B12 (correct)
- Activates pepsinogen to pepsin
Which type of cell in the gastric glands secretes hydrochloric acid?
Which type of cell in the gastric glands secretes hydrochloric acid?
What is the composition of saliva primarily aimed at?
What is the composition of saliva primarily aimed at?
Which gland secretes the hormone gastrin?
Which gland secretes the hormone gastrin?
What is the primary component of saliva that has minimal digestive enzyme activity?
What is the primary component of saliva that has minimal digestive enzyme activity?
Which of these is NOT a primary function of saliva?
Which of these is NOT a primary function of saliva?
What is the primary function of the gastrointestinal system?
What is the primary function of the gastrointestinal system?
Which of the following structures is part of the gastrointestinal tract?
Which of the following structures is part of the gastrointestinal tract?
What initiates carbohydrate digestion in the digestive system?
What initiates carbohydrate digestion in the digestive system?
What is the primary role of the muscular wall in the stomach?
What is the primary role of the muscular wall in the stomach?
Where does the majority of nutrient absorption occur in the gastrointestinal system?
Where does the majority of nutrient absorption occur in the gastrointestinal system?
Which component is secreted by gastric pits in the stomach?
Which component is secreted by gastric pits in the stomach?
What is the primary passage for food after chewing?
What is the primary passage for food after chewing?
Which organ is NOT classified as an accessory glandular organ?
Which organ is NOT classified as an accessory glandular organ?
Which layer of smooth muscle decreases the diameter of the lumen in the gastrointestinal tract?
Which layer of smooth muscle decreases the diameter of the lumen in the gastrointestinal tract?
What is the primary function of myenteric plexus in the gastrointestinal system?
What is the primary function of myenteric plexus in the gastrointestinal system?
Which of the following movements is characterized by pushing contents forward through the digestive tract?
Which of the following movements is characterized by pushing contents forward through the digestive tract?
What is the role of serosa in the gastrointestinal tract?
What is the role of serosa in the gastrointestinal tract?
Which type of contraction facilitates both digestion and absorption in the gastrointestinal tract?
Which type of contraction facilitates both digestion and absorption in the gastrointestinal tract?
What kind of muscle is primarily found in the gastrointestinal tract?
What kind of muscle is primarily found in the gastrointestinal tract?
Ingestion in the digestive system is defined as which of the following processes?
Ingestion in the digestive system is defined as which of the following processes?
Which layer of the gastrointestinal tract is responsible for the secretion of digestive juices?
Which layer of the gastrointestinal tract is responsible for the secretion of digestive juices?
What characterizes phasic contractions in the gastrointestinal tract?
What characterizes phasic contractions in the gastrointestinal tract?
How do interstitial cells of Cajal (ICC) function in the gastrointestinal motility?
How do interstitial cells of Cajal (ICC) function in the gastrointestinal motility?
What is the primary function of tonic contractions in the gastrointestinal tract?
What is the primary function of tonic contractions in the gastrointestinal tract?
Which of the following statements about slow waves in the gastrointestinal tract is true?
Which of the following statements about slow waves in the gastrointestinal tract is true?
What happens during the mixing in the antrum of the stomach?
What happens during the mixing in the antrum of the stomach?
What is the primary function of bile salts in digestion?
What is the primary function of bile salts in digestion?
What is the main requirement for the secretion of digestive juices in the gastrointestinal tract?
What is the main requirement for the secretion of digestive juices in the gastrointestinal tract?
What characterizes peristaltic waves in the GI tract?
What characterizes peristaltic waves in the GI tract?
How do monoglycerides and fatty acids enter absorptive cells?
How do monoglycerides and fatty acids enter absorptive cells?
What effect does the enteric nervous system (ENS) have on slow waves in the GI tract?
What effect does the enteric nervous system (ENS) have on slow waves in the GI tract?
What triggers the secretion of bile into the duodenum?
What triggers the secretion of bile into the duodenum?
What is the role of the sphincter of Oddi in digestion?
What is the role of the sphincter of Oddi in digestion?
Which of the following describes mechanical digestion?
Which of the following describes mechanical digestion?
What substances are secreted by the small intestine to aid in digestion?
What substances are secreted by the small intestine to aid in digestion?
What is the primary function of the enzymes present in the small intestine?
What is the primary function of the enzymes present in the small intestine?
What happens to bile when little or no food is present in the intestinal lumen?
What happens to bile when little or no food is present in the intestinal lumen?
Which structure in the gastrointestinal system is responsible for nutrient absorption and digestion?
Which structure in the gastrointestinal system is responsible for nutrient absorption and digestion?
What is the definition of digestion?
What is the definition of digestion?
What are the protective roles of the mucosa in the gastrointestinal tract?
What are the protective roles of the mucosa in the gastrointestinal tract?
What is one potential consequence of dysbiosis in the large intestine?
What is one potential consequence of dysbiosis in the large intestine?
Which layer of the gastrointestinal tract contains the submucosal plexus?
Which layer of the gastrointestinal tract contains the submucosal plexus?
What role do microvilli play in the small intestine?
What role do microvilli play in the small intestine?
What primarily gets absorbed in the large intestine?
What primarily gets absorbed in the large intestine?
What dietary component can ease movement through the large intestine and decrease constipation risk?
What dietary component can ease movement through the large intestine and decrease constipation risk?
Flashcards
Gastrointestinal system (GI system)
Gastrointestinal system (GI system)
The organ system responsible for acquiring nutrients and electrolytes from the external environment to maintain the body's internal balance.
GI tract
GI tract
The first part of the GI tract, where food enters the body. Structures include the mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, and anus.
Accessory Glandular Organs
Accessory Glandular Organs
Organs that support the GI tract in digestion, including salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, and exocrine and endocrine glands.
Digestion
Digestion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Saliva
Saliva
Signup and view all the flashcards
Salivary amylase
Salivary amylase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stomach
Stomach
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gastric pits
Gastric pits
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mucosa
Mucosa
Signup and view all the flashcards
Submucosa
Submucosa
Signup and view all the flashcards
Villi
Villi
Signup and view all the flashcards
Microvilli
Microvilli
Signup and view all the flashcards
Enterocytes
Enterocytes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Inner circumferential layer
Inner circumferential layer
Signup and view all the flashcards
Outer longitudinal layer
Outer longitudinal layer
Signup and view all the flashcards
Crypts
Crypts
Signup and view all the flashcards
Beneficial bacteria in the large intestine
Beneficial bacteria in the large intestine
Signup and view all the flashcards
Myenteric plexus
Myenteric plexus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dysbiosis
Dysbiosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
GI motility
GI motility
Signup and view all the flashcards
Propulsive movements
Propulsive movements
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mixing movements
Mixing movements
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tonic contraction
Tonic contraction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Digestive Secretion Volume
Digestive Secretion Volume
Signup and view all the flashcards
Saliva and Bacteria
Saliva and Bacteria
Signup and view all the flashcards
Digestive Enzymes in Saliva
Digestive Enzymes in Saliva
Signup and view all the flashcards
Parietal Cells and HCl
Parietal Cells and HCl
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chief Cells and Pepsinogen
Chief Cells and Pepsinogen
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gastrin and HCl Production
Gastrin and HCl Production
Signup and view all the flashcards
Intrinsic Factor and B12 Absorption
Intrinsic Factor and B12 Absorption
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mucus and Stomach Protection
Mucus and Stomach Protection
Signup and view all the flashcards
Interstitial cells of Cajal (ICC)
Interstitial cells of Cajal (ICC)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Phasic contractions
Phasic contractions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Slow waves
Slow waves
Signup and view all the flashcards
Enteric nervous system (ENS)
Enteric nervous system (ENS)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Secretion
Secretion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Antral contractions
Antral contractions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Emulsification
Emulsification
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chemical digestion
Chemical digestion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mechanical digestion
Mechanical digestion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cholecystokinin (CCK)
Cholecystokinin (CCK)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sphincter of Oddi
Sphincter of Oddi
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bile
Bile
Signup and view all the flashcards
Triglyceride digestion
Triglyceride digestion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Micelles
Micelles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Physiology (0603302) Ch. 6 Gastrointestinal System
- The gastrointestinal (GI) system is responsible for providing nutrients and electrolytes from the external environment to maintain homeostasis.
- The digestive system comprises two main parts: the GI tract and accessory glands.
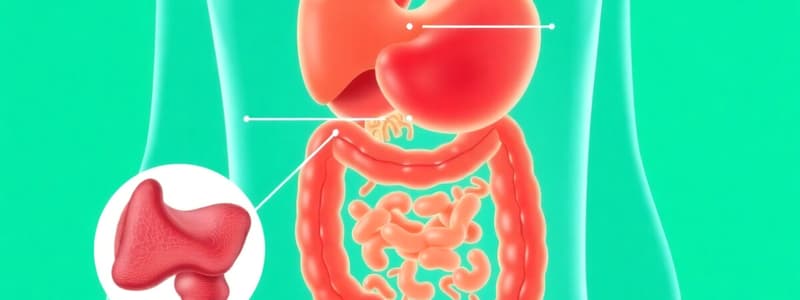
- The GI tract includes the mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, and anus.
- Accessory glands include the salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, and pancreas.
- The mouth contains muscles for mechanical digestion. Salivary glands produce saliva essential for lubrication, food degradation, and carbohydrate digestion, initiating with salivary amylase.
- Food passes through the pharynx, a passageway for both food and air.
- The esophagus carries food to the stomach by peristaltic contractions.
- The stomach contains a special lining to secrete digestive juices (pepsinogen, HCl) for protein digestion. Gastric pits originate digestive juices/enzymes.
- The stomach's muscular wall mechanically mixes food with digestive juices, and food passes through the pylorus sphincter to the small intestine.
- The small intestine, with enzymes from the pancreas and small intestine, further digests food; it contains villi cells that increase surface area for absorption. The villi and microvilli are lined with enterocytes.
- The large intestine absorbs water and electrolytes; beneficial bacteria produce vitamin K and some lipid molecules. Some diseases like diabetes and obesity may result from problems with gut bacteria.
- The large intestine facilitates the formation of feces. A high-fiber diet facilitates movement through the large intestine, potentially decreasing constipation risk.
- The GI system has four primary layers: Mucosa (innermost layer of epithelial cells, with protective, secretion, and absorption roles); Submucosa (beneath the mucosa, consisting of connective tissue, neurons, and blood vessels with GI tract distensibility and elasticity); Muscle (two layers of smooth muscle—inner circumferential and outer longitudinal layers); and Serosa (outermost layer of connective tissue).
- Motility involves phasic contractions (peristalsis and segmentation for rapid transport of food and nutrients, and tonic contractions (sphincter) for regulated and prolonged retention).
Processing of Food by the DS
- Ingestion is the process of eating.
- Digestion: Chemical and mechanical breakdown of food into absorbable units.
- Mechanical digestion prepares food for chemical digestion (chewing, mixing with saliva). Chemical digestion is achieved by enzymes in digestive juices.
GIT Secretion
- Digestive secretions are essential for digestion and absorption.
- The volume of digestive secretions is high compared to ingested fluids.
- Digestive fluid synthesis & secretion are controlled by endocrine, paracrine, and neural regulation.
- Saliva from the salivary glands (parotid, submandibular, and lingual glands) in the mouth is a mixed secretion, with proteins and water (parotid), and both mucus and enzyme amylase (submandibular and lingual). Saliva's functions include moistening for swallowing, neutralizing acids and bacteria, and initiating some digestion (minimal salivary amylase and lingual lipase).
- The stomach secretes HCL, Pepsinogen, mucus, and intrinsic factor. HCl activates Pepsinogen → Pepsin; mucus forms a protective barrier. Intrinsic factor combines with Vitamin B12 for absorption.
- Pancreatic secretions include proteases (cleave peptides), nucleases (hydrolyze DNA/RNA), elastases (digest collagen), phospholipases (split phospholipids), lipases (break triglycerides into glycerol +fatty acids), and amylase (starch to maltose + glucose). Pancreatic duct cells secrete bicarbonate, creating a neutral environment for pancreatic enzyme function.
Digestion: Overview (Table 14-5)
- Carbohydrate digestion begins in the mouth with salivary amylase. Disaccharidases in the small intestine complete carbohydrate breakdown to monosaccharides (particularly glucose).
- Protein digestion starts in the stomach with pepsin. Pancreatic proteases, aminopeptidases, and carboxypeptidases further break down proteins into peptides and then amino acids.
- Fat digestion involves emulsification by bile salts—forming micelles that increase lipase enzyme access to triglycerides—breaking down to monoglycerides and fatty acids, which are then absorbed by simple diffusion or by forming micelles.
Absorption
- The passage of digested food particles into blood and lymphatic systems.
- Most absorption happens in the small intestine.
Defecation
- Elimination of indigestible food substances.
Regulation of Gastrointestinal Tract Functions
- Intrinsic (in the GI wall) and extrinsic (external to GI wall) control systems regulate GI tract functions.
- Intrinsic control involves the enteric nervous system (ENS) and endocrine secretions (e.g., secretin, gastrin, CCK, GIP, and motilin), which respond to various stimuli within the digestive tract.
- Extrinsic control includes nerves (vagus and splanchnic) and hormones (e.g., aldosterone) that regulate GI function.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.