Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary role of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis?
What is the primary role of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis?
- Regulating reproductive functions. (correct)
- Controlling sleep cycles.
- Regulating blood sugar levels.
- Managing digestive processes.
Which of the following hormones is directly produced by the hypothalamus and initiates the HPG axis cascade?
Which of the following hormones is directly produced by the hypothalamus and initiates the HPG axis cascade?
- Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH).
- Luteinizing hormone (LH).
- Testosterone.
- Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH). (correct)
What feedback mechanism is primarily employed by gonadal steroids on the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary?
What feedback mechanism is primarily employed by gonadal steroids on the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary?
- Neutral feedback.
- Negative feedback. (correct)
- Positive feedback.
- Variable feedback.
In males, what is the primary hormone produced by the testes?
In males, what is the primary hormone produced by the testes?
What enzyme is responsible for converting testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT) in target cells?
What enzyme is responsible for converting testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT) in target cells?
What is the role of the scrotal sac in mammalian spermatogenesis?
What is the role of the scrotal sac in mammalian spermatogenesis?
Which cell type directly supports gametogenesis within the testes?
Which cell type directly supports gametogenesis within the testes?
What stage of spermatogenesis involves cells that have entered meiosis I?
What stage of spermatogenesis involves cells that have entered meiosis I?
What role do Leydig cells play in the endocrine control of spermatogenesis?
What role do Leydig cells play in the endocrine control of spermatogenesis?
What is the primary function of DHT (dihydrotestosterone) in male development?
What is the primary function of DHT (dihydrotestosterone) in male development?
Which hormones are primarily produced by the ovaries?
Which hormones are primarily produced by the ovaries?
Which ovarian structure primarily secretes progesterone during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle?
Which ovarian structure primarily secretes progesterone during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle?
What event is triggered by sustained high levels of estradiol, leading to a surge release of LH/FSH?
What event is triggered by sustained high levels of estradiol, leading to a surge release of LH/FSH?
Which phase of the uterine cycle involves the shedding of the endometrial lining due to steroid withdrawal?
Which phase of the uterine cycle involves the shedding of the endometrial lining due to steroid withdrawal?
What process is initiated by the LH surge during the luteal phase of the ovarian cycle?
What process is initiated by the LH surge during the luteal phase of the ovarian cycle?
During fetal development, what genetic factor primarily determines sex?
During fetal development, what genetic factor primarily determines sex?
What is the typical chromosomal configuration for a female?
What is the typical chromosomal configuration for a female?
Which duct system develops into the male internal genitalia?
Which duct system develops into the male internal genitalia?
What hormone secreted by Sertoli cells prompts the regression of the paramesonephric ducts in male fetal development?
What hormone secreted by Sertoli cells prompts the regression of the paramesonephric ducts in male fetal development?
What external genitalia development occurs in females in the absence of DHT?
What external genitalia development occurs in females in the absence of DHT?
What is the first event differentiating cell types after fertilization?
What is the first event differentiating cell types after fertilization?
Which structure gives rise to the placenta?
Which structure gives rise to the placenta?
Which term refers to the delivery of the baby during parturition?
Which term refers to the delivery of the baby during parturition?
Which hormone is involved in positive feedback loop?
Which hormone is involved in positive feedback loop?
If an individual has a loss-of-function mutation in the $5\alpha$-reductase gene, what outcome would you predict?
If an individual has a loss-of-function mutation in the $5\alpha$-reductase gene, what outcome would you predict?
A researcher is studying the effect of a new drug on the HPG axis. They observe that the drug leads to a significant decrease in LH and FSH secretion. Which of the following is the most likely mechanism of action of this drug?
A researcher is studying the effect of a new drug on the HPG axis. They observe that the drug leads to a significant decrease in LH and FSH secretion. Which of the following is the most likely mechanism of action of this drug?
A clinician observes that a male patient has normal testosterone levels but exhibits signs of androgen insensitivity. Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause?
A clinician observes that a male patient has normal testosterone levels but exhibits signs of androgen insensitivity. Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause?
A woman is experiencing irregular menstrual cycles and is found to have consistently low progesterone levels during the luteal phase. Which of the following ovarian structures is most likely malfunctioning?
A woman is experiencing irregular menstrual cycles and is found to have consistently low progesterone levels during the luteal phase. Which of the following ovarian structures is most likely malfunctioning?
A researcher discovers that a specific chemical can disrupt the tight junctions between Sertoli cells in the testes. What is the most likely consequence of this disruption?
A researcher discovers that a specific chemical can disrupt the tight junctions between Sertoli cells in the testes. What is the most likely consequence of this disruption?
A patient has a genetic condition where their cells cannot convert cholesterol into pregnenolone. What steroid derivatives will the patient be unable to produce?
A patient has a genetic condition where their cells cannot convert cholesterol into pregnenolone. What steroid derivatives will the patient be unable to produce?
A woman is given a drug that increases the amount of prostogesterone at the end of her cycle. Which of the following outcomes is most likely?
A woman is given a drug that increases the amount of prostogesterone at the end of her cycle. Which of the following outcomes is most likely?
Which statement is correct of the urinary and reproductive system interaction?
Which statement is correct of the urinary and reproductive system interaction?
What is a consequence of blocking aromatase activity?
What is a consequence of blocking aromatase activity?
Flashcards
GnRH
GnRH
A hormone released by the hypothalamus that stimulates the anterior pituitary to release LH and FSH.
LH and FSH
LH and FSH
Hormones released by the anterior pituitary that act on the gonads.
Spermatogenesis
Spermatogenesis
The process of sperm production in the testes.
Sertoli cells
Sertoli cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Leydig cells
Leydig cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Testosterone
Testosterone
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dihydrotestosterone (DHT)
Dihydrotestosterone (DHT)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oogenesis
Oogenesis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Endometrium
Endometrium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Myometrium
Myometrium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Antrum
Antrum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Follicular phase
Follicular phase
Signup and view all the flashcards
"LH surge"
"LH surge"
Signup and view all the flashcards
Luteal Phase
Luteal Phase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Luteal regression
Luteal regression
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fertilization
Fertilization
Signup and view all the flashcards
Inner cell mass
Inner cell mass
Signup and view all the flashcards
Trophectoderm
Trophectoderm
Signup and view all the flashcards
Parturition
Parturition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oxytocin
Oxytocin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Gonadal (HPG) Axis
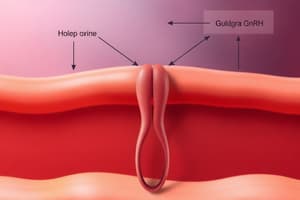
- GnRH, gonadotropin-releasing hormone, is produced in the hypothalamus.
- LH stands for luteinizing hormone.
- FSH stands for follicle-stimulating hormone.
- Somatic cell types depend on whether the gonad is male or female.
- Somatic cells support gametogenesis directly or through steroids.
- Actions outside gonads are supported by steroid cell types
Steroidogenic Pathway
- Adione = androstenedione.
- DHEA = dehydroepiandrosterone.
- DHT = dihydrotestosterone.
Feedback Regulation
- The main hormone product of the testes is testosterone (an androgen)
- Testosterone converts to DHT within target cells.
- The main hormone product of the ovaries is estradiol (an estrogen) and progesterone (a progestin).
- All gonadal steroids mediate negative feedback at the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary, except estradiol under certain conditions.
- Sustained high levels of estradiol will trigger surge release of LH/FSH which is positive feedback.
Human Male Reproductive System
- Testicular migration into the scrotal sac is a feature of some species of mammals; this requires testosterone.
- Normal spermatogenesis requires a temperature 2-3° less than body temperature in some species.
- Failure of the testes to descend results in cryptorchidism.
- The testes contain seminiferous tubules where sperm develop, and the epididymis and vas deferens for sperm storage and transport.
- In spermatogenesis, spermatogonia undergo mitotic division, primary spermatocytes enter meiosis I, secondary spermatocytes initiate meiosis II, and spermatids complete meiosis.
Spermatozoan Structure
- The head of a spermatozoan encapsulates the acrosome which contains enzymes to aid fertilization, and also contains the nucleus.
- The mid-piece contains mitochondrial spirals.
- The tail contains microtubules for propulsion, which is also known as the flagellum.
Endocrine Control of Spermatogenesis
- GnRH influences the anterior pituitary to release FSH and LH.
- FSH and LH stimulate the production of testosterone in Leydig cells.
- Sertoli cells produce products needed in spermatogenesis.
Testicular Androgens
- Testicular androgens have a negative feedback control on LH/FSH and GnRH.
- The primary sex characteristics supported by testicular androgens are the development and maintenance of internal and external genitalia, and spermatogenesis.
- Secondary sexual characteristics promoted by testicular androgens are protein synthesis and muscle growth.
- The main secreted steroid is testosterone, which is converted to DHT in target cells, which has a higher affinity for the androgen receptor.
- DHT, versus testosterone, is required for differentiation of external genitalia during development, also development and support of accessory sex glands.
- Related traits that DHT also plays a role in are male pattern baldness, acne, and facial hair.
Human Female Reproductive System
- The ovaries connect to the uterus via the fallopian tubes.
- The endometrium is the inner lining of the uterus, with the myometrium smooth muscle of the uterus.
Ovarian Structures
- Oocytes are located within follicles, starting as a primordial follicle, maturing into primary, secondary, and tertiary follicles,.
- During ovulation, the oocyte is released from a ruptured follicle.
- After the egg is released, the corpus luteum and regressing corpus luteum remain.
Follicular Phase
- The follicular phase begins with luteal regression, low ovarian steroids, which causes menses.
- In the ovary, a selected follicle begins to grow and secretes estrogen.
- Sustained exposure to high estrogen, when progesterone is low, causes a massive release of gonadotropins, the "LH surge," which results in ovulation.
- Part of endometrial lining sheds during steroid withdrawal, causes menses in the uterus.
- Rising estrogen from a maturing follicle stimulates regrowth of the lining in the "proliferative phase."
Luteal Phase
- The luteal phase begins with the LH surge, which triggers ovulation.
- The oocyte escapes the ovary, completes meiosis I in response to the LH surge, then arrests in meiosis II.
- Somatic cells of the ovulatory follicle transform into luteal cells forming a solid, progesterone-secreting structure called "luteinization".
- High ovarian steroids suppress gonadotropins, preventing the growth of large follicles.
- In the absence of pregnancy, luteal regression occurs after ~12 days.
- Under the influence of progesterone and estrogen, the uterus is prepared for pregnancy resulting in the "secretory phase".
- Luteal regression causes steroid withdrawal, leading to menses.
Genetic Sex Determination in Fetal Development
- Chromosomal sex is determined at fertilization
- Female parent is XX
- Male Parent is XY
- Female offspring inherit XX
- Male offspring inherits XY
- Urinary and reproductive systems are inter-related during sex determination
Embryonic Development
- In early development, there are indifferent gonads.
- Males retain the mesonephric duct, while females retain the paramesonephric duct.
- There are three sets of kidneys, the first two sets degenerate.
- Each sex forms para mesonephric ducts, but only in females.
- Males use ductwork left from the primitive kidney, called the mesonephric duct.
- Females use parallel ductwork, called the paramesonephric duct.
Development of Internal Genitalia
- In males, Wolffian structures persist, while Mullerian ducts degenerate.
- In females, Mullerian ducts persist, and Wolffian ducts degenerate.
- Wolffian derivatives include the epididymis, vas deferens and accessory sex glands such as the prostate.
- Mullerian derivatives include the fallopian tubes, uterus, cervix and upper vagina.
Sexual Differentiation
- Sry is the master transcription factor expressed by pre-Sertoli cells.
- Sertoli cells secrete anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH).
- Testosterone from Leydig cells acts on the mesonephric (Wolffian) duct and develops the male tract.
Signalling Involved in Reproductive Development
- To build a 'bipotential' gonad: germ cell precursors arrive and somatic cells organize around them.
- Somatic cells in testes express Sry.
- In the presence of no Sry an ovary will form.
- Presence of Sry cells yields a testis.
- Sertoli cells release AMH
- Female external genitalia has a retained Mullerian duct
Disorders of Sexual Differentiation
- Consequences of mutations for XY individuals with a loss of function in 5α-reductase, or mutations that cause a loss of function in the androgen receptor may cause disorders of sexual differentiation.
Fertilization-Parturition
- The inner cell mass and trophectoderm are the first differentiated cell types in mammalian embryos.
- The placental membrane is derived from the trophectoderm, and the embryo proper is derived from the inner cell mass.
Parturition
- Parturition involves cervical softening ('ripening'), initiation of rhythmic uterine contractions, delivery of the baby, and expulsion of the placenta.
- Parturition is controlled by a sequential cascade of hormones; however, the exact hormones and cascade vary among species of mammals.
- A consistent finding is positive feedback/neuroendocrine reflex involving oxytocin.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.