Podcast
Questions and Answers
What type of cells primarily form connective tissue membranes?
What type of cells primarily form connective tissue membranes?
- Nerve cells
- Epithelial cells
- Connective tissue cells (correct)
- Muscle cells
Which of the following is NOT a type of epithelial membrane?
Which of the following is NOT a type of epithelial membrane?
- Mucous membrane
- Cutaneous membrane
- Synovial membrane (correct)
- Serous membrane
The serous membrane derives from which type of epithelium?
The serous membrane derives from which type of epithelium?
- Simple columnar epithelium
- Glandular epithelium
- Stratified squamous epithelium
- Mesothelium (correct)
How does synovial fluid contribute to joint function?
How does synovial fluid contribute to joint function?
Epithelial cells are derived from which of the following embryonic layers?
Epithelial cells are derived from which of the following embryonic layers?
What is the primary function of the basal lamina in epithelial tissues?
What is the primary function of the basal lamina in epithelial tissues?
Which of the following membranes is specifically associated with joint cavities?
Which of the following membranes is specifically associated with joint cavities?
Which feature distinguishes the apical surface of epithelial cells?
Which feature distinguishes the apical surface of epithelial cells?
What primary function does epithelial tissue serve in the body?
What primary function does epithelial tissue serve in the body?
Which type of muscle tissue is involuntary and found in the heart?
Which type of muscle tissue is involuntary and found in the heart?
What is the primary role of connective tissue in the body?
What is the primary role of connective tissue in the body?
What characteristic distinguishes nervous tissue from other types?
What characteristic distinguishes nervous tissue from other types?
Which tissue type is primarily responsible for voluntary movement?
Which tissue type is primarily responsible for voluntary movement?
What term describes the early developmental cells that can differentiate into any body cell type?
What term describes the early developmental cells that can differentiate into any body cell type?
Which type of epithelial tissue is known for its multiple layers?
Which type of epithelial tissue is known for its multiple layers?
What is histology the study of?
What is histology the study of?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Tissue Overview
- Tissue is a group of cells that share a common embryonic origin and work together to fulfill specific functions.
- Histoogy is the microscopic study of tissue structure, organization, and function.
Types of Tissues
-
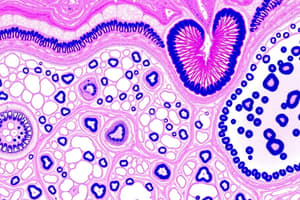
Epithelial Tissue (Epithelium)
- Covers exterior body surfaces and lines internal cavities and passageways.
- Forms certain glands involved in secretion.
-
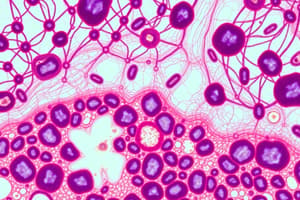
Connective Tissue
- Binds cells and organs, providing support, protection, and integration of body parts.
-
Muscle Tissue
- Excitable and responsive to stimulation.
- Has three main types:
- Skeletal (voluntary)
- Smooth
- Cardiac (found in the heart)
-
Nervous Tissue
- Also excitable, facilitating the propagation of nerve impulses for communication within the body.
Embryonic Origin of Tissues
- Originates from the zygote, which undergoes rapid cell division to form the embryo.
- Early embryonic cells are totipotent, meaning they can differentiate into any cell type.
- Three main cell lineages develop as cell proliferation progresses.
Tissue Membranes
- Tissue membranes are thin layers covering body surfaces, organs, and internal passageways.
- Two main types:
- Connective Tissue Membranes: Include synovial membranes and encapsulate organs, providing a protective layer.
- Epithelial Membranes: Composed of epithelium over a connective tissue layer.
Connective Tissue Membranes
- Formed solely from connective tissue, lining movable joints and organs such as the kidneys.
- Synovial Membrane: A type of connective tissue membrane that produces synovial fluid to reduce friction in joints.
Epithelial Membranes
- Composed of epithelial tissue and a surrounding layer of connective tissue.
- Mucous Membrane: Composite of connective and epithelial tissues, containing lamina propria for support.
- Serous Membrane: Composed of mesothelium supported by connective tissue; lines cavities and covers organs.
- Cutaneous Membrane (Skin): A stratified squamous epithelial layer that protects against environmental threats.
Epithelial Tissue Origin
- Epithelial cells originate from all three embryonic layers:
- Ectoderm: Forms the epithelia of skin and mucosal lining of mouth, nose, and anus.
- Endoderm: Lining of airways and most parts of the digestive system.
- Mesoderm: Vascular systems' lining (endothelium).
- Specialized structures called cell junctions form connections between adjacent cells.
- Epithelial cells are polarized, with the apical surface facing the external environment and a basal surface adjacent to underlying tissues.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.