Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the term used to describe a single layer of flat, scale-like epithelial cells?
What is the term used to describe a single layer of flat, scale-like epithelial cells?
- Simple Columnar
- Simple Cuboidal
- Simple Squamous (correct)
- Stratified Squamous
Which structure is found on the surface of ciliated epithelial cells and helps in moving substances like mucus?
Which structure is found on the surface of ciliated epithelial cells and helps in moving substances like mucus?
- Cilia (correct)
- Basement Membrane
- Keratin
- Microvilli
What is the primary function of microvilli in epithelial cells?
What is the primary function of microvilli in epithelial cells?
- Increase surface area for absorption (correct)
- Filtration of blood
- Protection from damage
- Secretion of mucus
Which type of epithelial tissue has a centrally located, round nucleus and is cube-shaped?
Which type of epithelial tissue has a centrally located, round nucleus and is cube-shaped?
In which organ are simple squamous epithelial cells primarily found for effective diffusion?
In which organ are simple squamous epithelial cells primarily found for effective diffusion?
Which of the following statements is true regarding keratin in epithelial tissues?
Which of the following statements is true regarding keratin in epithelial tissues?
What characterizes stratified epithelium as compared to simple epithelium?
What characterizes stratified epithelium as compared to simple epithelium?
What is the smallest unit of living matter in the hierarchy of biological organization?
What is the smallest unit of living matter in the hierarchy of biological organization?
Which of the following tissues is avascular and does not have blood supply?
Which of the following tissues is avascular and does not have blood supply?
What is the main function of the basement membrane in epithelial tissue?
What is the main function of the basement membrane in epithelial tissue?
Which of the following correctly describes the process of classifying types of epithelium?
Which of the following correctly describes the process of classifying types of epithelium?
What color does hematoxylin stain the nuclei in histological slides?
What color does hematoxylin stain the nuclei in histological slides?
Which of the following is NOT one of the four basic tissues in the body?
Which of the following is NOT one of the four basic tissues in the body?
What is the primary function of simple columnar epithelium?
What is the primary function of simple columnar epithelium?
What characterizes stratified squamous epithelium?
What characterizes stratified squamous epithelium?
Where would you typically find transitional epithelium?
Where would you typically find transitional epithelium?
What is the structure of pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium?
What is the structure of pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium?
What is a key function of stratified squamous epithelium?
What is a key function of stratified squamous epithelium?
Which epithelium type is primarily responsible for mucus propulsion in the respiratory tract?
Which epithelium type is primarily responsible for mucus propulsion in the respiratory tract?
What type of epithelium is found lining the gastrointestinal tract from the stomach to the anus?
What type of epithelium is found lining the gastrointestinal tract from the stomach to the anus?
What best describes the cells at the apical layer of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium?
What best describes the cells at the apical layer of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium?
What is the significance of microvilli in simple columnar epithelium?
What is the significance of microvilli in simple columnar epithelium?
What type of connective tissue is characterized by collagen fibers arranged in all directions for strength?
What type of connective tissue is characterized by collagen fibers arranged in all directions for strength?
Which type of cartilage is known to provide flexibility and is found in the ear and epiglottis?
Which type of cartilage is known to provide flexibility and is found in the ear and epiglottis?
Osteoblasts are responsible for which function in bone tissue?
Osteoblasts are responsible for which function in bone tissue?
Which type of muscle tissue is voluntary and features long, striated, and multinucleated fibers?
Which type of muscle tissue is voluntary and features long, striated, and multinucleated fibers?
What is the primary component of the extracellular matrix in blood?
What is the primary component of the extracellular matrix in blood?
Which cell type in cartilage is responsible for maintaining the extracellular matrix?
Which cell type in cartilage is responsible for maintaining the extracellular matrix?
What type of connective tissue is mainly responsible for energy storage, padding, and insulation?
What type of connective tissue is mainly responsible for energy storage, padding, and insulation?
What is the main function of osteoclasts in bone tissue?
What is the main function of osteoclasts in bone tissue?
What is the primary function of fibroblasts in connective tissue proper?
What is the primary function of fibroblasts in connective tissue proper?
How does the structure of epithelial tissue differ from that of connective tissue?
How does the structure of epithelial tissue differ from that of connective tissue?
Which type of connective tissue cell is responsible for storing fat?
Which type of connective tissue cell is responsible for storing fat?
What role do mast cells play in connective tissue?
What role do mast cells play in connective tissue?
What is the main characteristic of the extracellular matrix in connective tissue?
What is the main characteristic of the extracellular matrix in connective tissue?
Which type of collagen is the most abundant protein found in the body?
Which type of collagen is the most abundant protein found in the body?
What is the function of the ground substance in connective tissue?
What is the function of the ground substance in connective tissue?
Which of the following is a primary type of connective tissue derived from mesenchyme?
Which of the following is a primary type of connective tissue derived from mesenchyme?
What type of connective tissue is characterized by a loose arrangement of fibers and cells?
What type of connective tissue is characterized by a loose arrangement of fibers and cells?
Which type of cell in connective tissue is primarily involved in immune responses and phagocytosis?
Which type of cell in connective tissue is primarily involved in immune responses and phagocytosis?
Study Notes
Hierarchical Organization of Living Matter
- Cells are the smallest units of living matter, with approximately one trillion in the human body.
- Grouping of similar cells forms tissues, defined as a collection of cells organized for a common purpose.
- Four basic tissue types in the body: epithelium, connective, muscle, and nervous.
- Tissues aggregate to form organs, which are groups of tissues working together, like the heart and kidneys.
- Organ systems are formed by assembling organs for specific functions, e.g., cardiovascular and respiratory systems.
- The entirety of organ systems combined forms an organism.
Introduction to Histology
- Histology is the study of tissues, focusing on the four basic types.
- Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining is the most common staining method in histology.
- Hematoxylin stains nuclei purple, while eosin stains proteins pink, aiding in cellular component identification.
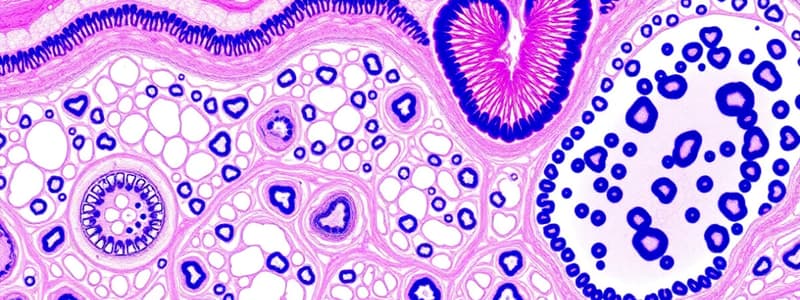
Epithelium Overview
- Epithelium serves as glandular tissue, lining organ lumens and body cavities, and covering external body surfaces.
- Comprises cells anchored to a basement membrane with distinct apical (top) and basal (bottom) surfaces.
- Avascular tissue type, meaning it lacks blood vessels and has very little extracellular matrix (ECM).
Classification of Epithelial Tissue
- Classifications based on cell layers and shapes:
- Simple Epithelia: Single cell layer (e.g., simple squamous, cuboidal, or columnar).
- Stratified Epithelia: Multiple cell layers (e.g., stratified squamous).
- Shapes:
- Squamous: Flat, scale-like cells.
- Cuboidal: Cube-shaped cells with round nuclei.
- Columnar: Tall, thin cells with basally located nuclei.
Specific Types of Epithelial Tissue
- Simple Squamous Epithelium: Thin and ideal for diffusion, found in alveoli and capillaries; facilitates gas exchange and filtration.
- Simple Cuboidal Epithelium: Cube-shaped cells aiding in absorption and secretion; often present in kidney tubules and glands.
- Simple Columnar Epithelium: Tall cells often with microvilli or cilia; important in absorption and secretion, located in the GI tract.
- Stratified Squamous Epithelium: Multiple layers for protection against abrasion; keratinized form protects skin, while non-keratinized lines cavities like the esophagus.
- Transitional Epithelium: Urinary epithelium that stretches; found in bladder and ureters.
- Pseudostratified Ciliated Columnar Epithelium: Appears stratified due to varied cell heights but is a single layer; functions in secretion and cilia-mediated transport of mucus.
Connective Tissue Overview
- Derived from mesenchyme, connective tissue includes four main types: connective tissue proper, cartilage, bone, and blood.
- Characterized by a few scattered cells in a large extracellular matrix, providing varying degrees of support and connectivity.
- Unlike epithelial cells, connective tissue cells are not tightly packed and feature extensive intercellular spaces.### Connective Tissue Overview
- Connective tissues primarily consist of cells surrounded by an extracellular matrix.
- Main categories include connective tissue proper, cartilage, bone, and blood.
Connective Tissue Proper
- Fibroblasts are the primary cells that synthesize collagen, elastin fibers, and ground substance.
- Adipocytes are fat cells that store lipids in a single droplet and are prominent in adipose tissue.
- Macrophages phagocytize microorganisms and damaged tissues, playing a critical role in the immune response.
- Mast cells release histamine, promoting vascular leakiness during inflammatory responses.
- Extracellular matrix includes ground substance (amorphous material) and fibers (primarily collagen and elastin), essential for structure and function.
Types of Connective Tissue Proper
- Loose Connective Tissue (Areolar): Supports epithelial tissues and cushions organs.
- Dense Irregular Connective Tissue: Provides strength in all directions, found in dermis and organ submucosa.
- Dense Regular Connective Tissue: Provides strength in one direction, seen in tendons with parallel collagen fibers.
- Adipose Tissue: Composed of adipocytes for energy storage, insulation, and padding, primarily found in the hypodermis.
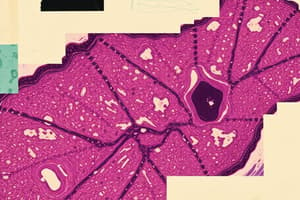
Cartilage
- Composed of chondroblasts and mature chondrocytes; has minimal blood supply, leading to slow healing.
- Hyaline Cartilage: Found in ribs (costal cartilage) and ends of long bones (articular cartilage).
- Elastic Cartilage: Contains high elastin concentration; located in the ear and epiglottis for flexibility.
- Fibrocartilage: Has the highest concentration of collagen fibers, found in intervertebral discs and menisci for strength and shock absorption.
Bone Tissue
- Contains:
- Osteoblasts: Build and secrete bone matrix.
- Osteocytes: Mature osteoblasts that maintain bone matrix, residing in lacunae.
- Osteoclasts: Break down bone matrix, regulating calcium levels in the blood.
- Extracellular matrix is rich in calcium and phosphate, providing structure and rigidity.
Blood
- A liquid connective tissue with red blood cells (RBCs) for oxygen transport, white blood cells (WBCs) for immune defense, and platelets for blood clotting.
- Plasma serves as the extracellular matrix, composed mainly of water and clotting factors.
Muscle Tissue
- Comprised of contractile cells; categorized into skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle.
Skeletal Muscle
- Voluntary, striated, multinucleated fibers; attached to bones.
- Surrounded by connective tissue layers (endomysium, perimysium, epimysium) for structure and function.
Cardiac Muscle
- Involuntary, striated with intercalated discs that allow coordinated contractions.
- Found exclusively in the myocardium (heart wall).
Smooth Muscle
- Involuntary, non-striated cells; contracts without conscious thought.
- Located in the walls of hollow organs (e.g., stomach, intestines, blood vessels).
Nervous Tissue
- Composed of neurons (functional cells) and glial cells (supporting cells).
Neurons
- Consist of dendrites (receive signals), axons (transmit signals), and synapses (junctions between neurons).
- Classified into sensory neurons (towards CNS), motor neurons (away from CNS), and interneurons (connect sensory and motor).
Glial Cells
- Support neurons, provide physical and metabolic maintenance.
- Oligodendrocytes: Produce myelin in the CNS.
- Schwann Cells: Produce myelin in the PNS.
- Additional types:
- Astrocytes: Regulate electrical impulses and support the blood-brain barrier.
- Ependymal Cells: Line brain ventricles and facilitate cerebrospinal fluid circulation.
- Microglia: Immune cells that act as macrophages within the CNS.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
This tutorial provides a basic introduction to histology, highlighting the hierarchical organization of living matter and the four basic tissue types. For a more in-depth understanding, viewers are encouraged to visit Dr. Kathy Moore's histology resources. This session aims to lay the groundwork for further studies in histology.