Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of fibrocytes in connective tissue?
What is the primary function of fibrocytes in connective tissue?
- Secrete the ground substance
- Facilitate tissue repair
- Supply nutrients to the tissue
- Secrete the fibres (correct)
Which of the following types of connective tissue is NOT classified as proper connective tissue?
Which of the following types of connective tissue is NOT classified as proper connective tissue?
- Adipose connective tissue
- Fibrous connective tissue
- Areolar connective tissue
- Cartilage (correct)
What type of fibre runs in bundles and is characteristic of the connective tissue?
What type of fibre runs in bundles and is characteristic of the connective tissue?
- Reticular fibres
- Yellow (Elastic) fibres
- Mucous fibres
- Collagenous fibres (correct)
What role do mast cells play in connective tissue?
What role do mast cells play in connective tissue?
Which type of tissue is involved in the formation of organs from groups of similar cells?
Which type of tissue is involved in the formation of organs from groups of similar cells?
Which type of connective tissue consists of fat cells loaded with fat globules?
Which type of connective tissue consists of fat cells loaded with fat globules?
What type of cartilage is characterized by a solid and clear matrix, with chondrocytes arranged singly or in groups?
What type of cartilage is characterized by a solid and clear matrix, with chondrocytes arranged singly or in groups?
Which type of muscle tissue is involved in involuntary movements and is found in the walls of hollow organs?
Which type of muscle tissue is involved in involuntary movements and is found in the walls of hollow organs?
Which type of blood cell is characterized by a round, biconcave shape and is non-nucleated?
Which type of blood cell is characterized by a round, biconcave shape and is non-nucleated?
Which white blood cells are characterized by the presence of visible granules in their cytoplasm?
Which white blood cells are characterized by the presence of visible granules in their cytoplasm?
Flashcards
Histology Definition
Histology Definition
The study of tissues in the body.
Tissue
Tissue
A group of similar cells working together for a specific function.
Areolar Connective Tissue (Proper)
Areolar Connective Tissue (Proper)
Connective tissue with fibers (collagen and elastic) and cells (fibrocytes, mast cells).
Connective Tissue Types
Connective Tissue Types
Signup and view all the flashcards
Connective Tissue Components
Connective Tissue Components
Signup and view all the flashcards
Macrophage
Macrophage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Adipose Connective Tissue
Adipose Connective Tissue
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hyaline Cartilage
Hyaline Cartilage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Erythrocytes (RBCs)
Erythrocytes (RBCs)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Skeletal Muscle
Skeletal Muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Introduction to Histology
- Histology is the study of tissues.
- Cells are the smallest functional units of the body.
- Cells group to form tissues, each with specialized functions.
- Tissues group to form organs, and organs work together in systems.
Types of Tissues
- Tissues are collections of cells with similar structures and common functions.
- Major tissue types: epithelial, connective, muscular, and nervous.
Epithelial Tissues
- Characteristics: Cells are tightly packed with little intercellular space, lying on a basement membrane.
- Functions: Protection of organs, secretion (e.g., stomach acid), absorption (e.g., intestines), and waste removal (e.g., sweat).
Types of Epithelial Tissue Cells
- Squamous: Flattened.
- Cuboidal: Cube-shaped.
- Columnar: Tall and column-shaped.
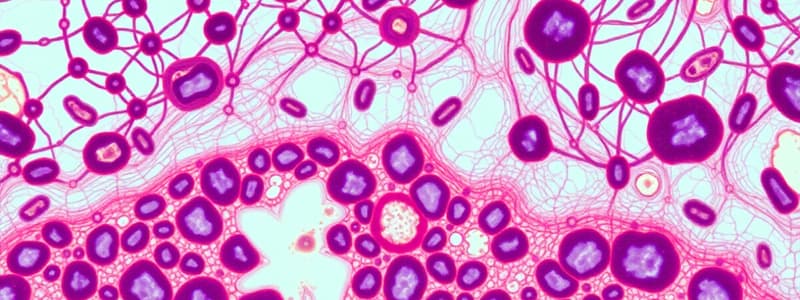
Connective Tissues
- Characteristics: Cells are spaced widely apart and have a matrix (intercellular substance) around the cells. The matrix varies greatly between the different connective tissues.
- Components: Fibroblasts, fat cells, macrophages, leukocytes, and mast cells.
- Functions: Support, transportation of materials, storage of energy, protection, and insulation.
Types of Connective Tissues
- Proper connective tissue: Areolar, adipose, mucous.
- Skeletal connective tissue: Cartilage (hyaline, elastic, calcified).
- Vascular connective tissue: Blood and Lymph.
Areolar Connective Tissue
- Loose connective tissue
- Contains collagenous fibers, elastic fibers, and cells.
Adipose Connective Tissue
- Fat cells are loaded with fat globules.
Mucous Connective Tissue
- Semi-fluid or gelatinous matrix containing white fibers and fibroblasts.
- Example: Umbilical cord.
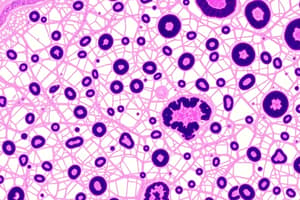
Cartilage
- Made of chondrocytes within a solid matrix.
- Types: Hyaline, elastic, calcified.
Fluid Connective Tissues
- Blood and lymph: Liquid tissues flowing in vessels.
- Blood constituents: Erythrocytes (RBCs), Leucocytes (WBCs), and blood platelets.
- Erythrocytes are round, biconcave, non-nucleated.
- Leucocytes are larger, nucleated, and exhibit amoeboid movement
- Types of leucocytes: Granulocytes (e.g., neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils) and Agranulocytes (e.g., lymphocytes, monocytes)
Muscular Tissues
- Form muscles.
- Types: Smooth, skeletal, and cardiac.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.