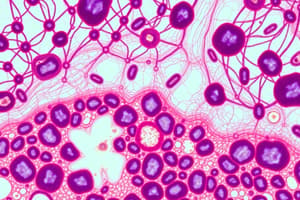
Podcast
Questions and Answers
What are the four primary tissue types?
What are the four primary tissue types?
- Nervous Tissue (correct)
- Connective Tissue (correct)
- Muscle Tissue (correct)
- Adipose Tissue
- Epithelial Tissue (correct)
What is the exposed surface of epithelial tissue called?
What is the exposed surface of epithelial tissue called?
apical surface
Epithelial tissue is avascular.
Epithelial tissue is avascular.
True (A)
What are the major functions of epithelial tissue?
What are the major functions of epithelial tissue?
Which type of epithelial tissue consists of a single layer of flat cells?
Which type of epithelial tissue consists of a single layer of flat cells?
Which type of gland produces hormones and does not have ducts?
Which type of gland produces hormones and does not have ducts?
What is connective tissue primarily composed of?
What is connective tissue primarily composed of?
What is one function of connective tissue?
What is one function of connective tissue?
Stratified epithelial tissue consists of a single layer of cells.
Stratified epithelial tissue consists of a single layer of cells.
Study Notes
Basic Types of Tissues
- Tissues consist of cells and an extracellular matrix.
- Four primary tissue types: Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, and Nervous.
Epithelial Tissue
- Also known as epithelium; covers and protects body surfaces; forms glands.
- Features apical surface (exposed) and basal surface (anchored to basement membrane).
- Avascular, meaning blood vessels do not penetrate the basement membrane.
- High regenerative capacity.
Functions of Epithelial Tissue
- Provides protection for underlying structures.
- Acts as a barrier to substances.
- Permits selective passage of substances.
- Secretes and absorbs various substances.
Classification of Epithelial Tissue by Shape
- Squamous: Flat or scale-like cells.
- Cuboidal: Cube-shaped, equally wide and tall.
- Columnar: Tall and thin cells, taller than they are wide.
Classification of Epithelial Tissue by Layers
- Simple Epithelium: Single layer of cells extending from basement membrane to free surface.
- Stratified Epithelium: Multiple layers; basal layer attaches to the membrane.
- Pseudostratified Epithelium: Appears layered due to varying cell heights but is a single layer.
- Transitional Epithelium: Changes shape from cuboidal to columnar to squamous-like when stretched.
Types of Simple Epithelium
- Simple Squamous Epithelium: Single layer of flat cells, ideal for filtration and diffusion.
- Simple Cuboidal Epithelium: Greater secretory capacity; found in glands.
- Simple Columnar Epithelium: Tall cells that secrete and absorb, playing a role in digestion and nutrient absorption.
- Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium: Appears layered; found in the respiratory tract.
Types of Stratified Epithelium
- Stratified Squamous Epithelium: Multiple layers; keratinized type forms outer skin; non-keratinized type found in mucosal surfaces.
- Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium: Rare; can be seen in sweat glands and some ducts.
- Stratified Columnar Epithelium: Multiple layers; located in mammary glands.
- Transitional Epithelium: Lines urinary tracts; adapts shape based on stretching.
Glands
- Composed of epithelium supported by connective tissue.
- Endocrine Glands: Produce hormones; lack ducts; have extensive blood vessel networks.
- Exocrine Glands: Produce secretions that enter ducts, such as saliva and sweat; classified by structure and secretion mode.
Connective Tissue
- Connects, supports, and binds other tissues; consists of cells separated by an abundant extracellular matrix.
- Functions include enclosing and separating tissues, holding them together, storing compounds, cushioning, insulating, transporting, and protecting.
Classification of Connective Tissue
- Differentiates between types based on structure and function, although specific types were not detailed in the provided text.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Related Documents
Description
Explore the fundamental types of tissues in histology, focusing on epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous tissues. This quiz will enhance your understanding of tissue structure and function, including the significance of the extracellular matrix. Perfect for students of biology or health sciences.