Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of epithelial tissue?
What is the primary function of epithelial tissue?
Which type of cell junction is primarily responsible for preventing leakage between epithelial cells?
Which type of cell junction is primarily responsible for preventing leakage between epithelial cells?
Desmosomes are characterized by their association with which structural components?
Desmosomes are characterized by their association with which structural components?
Which junction allows for direct communication between the cytoplasm of adjacent cells?
Which junction allows for direct communication between the cytoplasm of adjacent cells?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following is NOT a function of epithelial tissue?
Which of the following is NOT a function of epithelial tissue?
Signup and view all the answers
What type of epithelial tissue is characterized by layers of flattened cells?
What type of epithelial tissue is characterized by layers of flattened cells?
Signup and view all the answers
What role do occludins play in cell junctions?
What role do occludins play in cell junctions?
Signup and view all the answers
Which type of junction is primarily concentrated in tissues that undergo significant stretch or distortion?
Which type of junction is primarily concentrated in tissues that undergo significant stretch or distortion?
Signup and view all the answers
Which type of connective function is NOT identified in general descriptions of connective tissues?
Which type of connective function is NOT identified in general descriptions of connective tissues?
Signup and view all the answers
Which characteristic differentiates simple from stratified epithelial tissue?
Which characteristic differentiates simple from stratified epithelial tissue?
Signup and view all the answers
Which type of connective tissue is primarily responsible for binding tissues and surrounding blood vessels and nerves?
Which type of connective tissue is primarily responsible for binding tissues and surrounding blood vessels and nerves?
Signup and view all the answers
What characterizes dense, irregular connective tissue in comparison to dense, regular connective tissue?
What characterizes dense, irregular connective tissue in comparison to dense, regular connective tissue?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary function of fibroblasts in connective tissue?
What is the primary function of fibroblasts in connective tissue?
Signup and view all the answers
Which connective tissue type contains specialized cells called adipocytes?
Which connective tissue type contains specialized cells called adipocytes?
Signup and view all the answers
What component of connective tissue is NOT typically found in the matrix?
What component of connective tissue is NOT typically found in the matrix?
Signup and view all the answers
In which connective tissue type are collagenous fibers densely packed and arranged parallel to each other?
In which connective tissue type are collagenous fibers densely packed and arranged parallel to each other?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following is the main role of mast cells in connective tissue?
Which of the following is the main role of mast cells in connective tissue?
Signup and view all the answers
What type of connective tissue is characterized by easily stretched, irregularly arranged elastin fibrils?
What type of connective tissue is characterized by easily stretched, irregularly arranged elastin fibrils?
Signup and view all the answers
Which type of connective tissue provides support and forms attachments with a matrix that includes chondroitin sulfate?
Which type of connective tissue provides support and forms attachments with a matrix that includes chondroitin sulfate?
Signup and view all the answers
Which cell type is responsible for producing antibodies in connective tissue?
Which cell type is responsible for producing antibodies in connective tissue?
Signup and view all the answers
What function is primarily associated with cuboidal epithelium?
What function is primarily associated with cuboidal epithelium?
Signup and view all the answers
Which type of epithelium is characterized by cells that appear to be in multiple layers but actually contact the basement membrane?
Which type of epithelium is characterized by cells that appear to be in multiple layers but actually contact the basement membrane?
Signup and view all the answers
What describes the merocrine mechanism of secretion?
What describes the merocrine mechanism of secretion?
Signup and view all the answers
Which type of glandular epithelium releases products directly into the bloodstream?
Which type of glandular epithelium releases products directly into the bloodstream?
Signup and view all the answers
What is a key distinguishing feature of transitional epithelium?
What is a key distinguishing feature of transitional epithelium?
Signup and view all the answers
What type of cell is primarily associated with the function of producing mucus in the respiratory tract?
What type of cell is primarily associated with the function of producing mucus in the respiratory tract?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following is an example of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium?
Which of the following is an example of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following structures is primarily lined by ciliated columnar epithelium?
Which of the following structures is primarily lined by ciliated columnar epithelium?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the main role of connective tissue within the body?
What is the main role of connective tissue within the body?
Signup and view all the answers
What type of epithelium is typically found lining the small intestine?
What type of epithelium is typically found lining the small intestine?
Signup and view all the answers
Which type of cartilage is primarily responsible for providing flexibility and support in structures such as the outer ear?
Which type of cartilage is primarily responsible for providing flexibility and support in structures such as the outer ear?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary structural component of bone matrix that contributes to its rigidity?
What is the primary structural component of bone matrix that contributes to its rigidity?
Signup and view all the answers
Which term describes muscle tissue that is striated, involuntary, and contains intercalated discs?
Which term describes muscle tissue that is striated, involuntary, and contains intercalated discs?
Signup and view all the answers
Which type of connective tissue is characterized as a highly specialized fluid, with formed elements like erythrocytes and platelets?
Which type of connective tissue is characterized as a highly specialized fluid, with formed elements like erythrocytes and platelets?
Signup and view all the answers
What type of muscle is non-striated and found in the walls of hollow organs such as the GI tract?
What type of muscle is non-striated and found in the walls of hollow organs such as the GI tract?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the role of canaliculi in bone tissue?
What is the role of canaliculi in bone tissue?
Signup and view all the answers
Which category of connective tissue includes intervertebral discs and the pubic symphysis?
Which category of connective tissue includes intervertebral discs and the pubic symphysis?
Signup and view all the answers
What distinguishes compact bone from spongy bone?
What distinguishes compact bone from spongy bone?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following statements accurately describes muscle tissue?
Which of the following statements accurately describes muscle tissue?
Signup and view all the answers
What type of tissue primarily helps in the transmission of signals throughout the body?
What type of tissue primarily helps in the transmission of signals throughout the body?
Signup and view all the answers
Study Notes
Introduction to Histology
- Histology is the study of tissues, which are groups of similar cells performing a common function.
- Four general classes of tissues:
- Epithelial: Covers body surfaces and lines ducts/cavities.
- Connective: Binds, supports, and protects structures.
- Muscle: Responsible for movement and generating pressure.
- Nervous: Involved in regulation and communication.
Cell Junctions
- Points of contact between cells; classified into three main types:
- Tight junctions (occluding junctions)
- Located at the apical border of epithelial cells.
- Function includes creating a liquid-tight barrier and establishing cell membrane domains (basolateral & apical).
- Anchoring junctions
- Desmosomes: Act as rivets, anchored by intermediate filaments and use cadherins for adhesion.
- Adherens junctions: Anchored by actin filaments, concentrated in areas undergoing stress, also use cadherins.
- Communicating junctions (gap junctions)
- Allow cytoplasmic continuity and act as low-resistance pathways for intracellular signaling.
- Composed of sets of connexins forming connexons, creating channels.
- Tight junctions (occluding junctions)
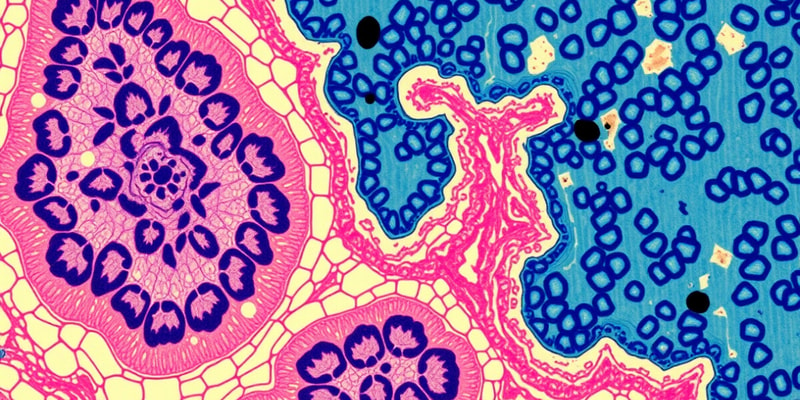
Epithelial Tissue
- Functions include physical protection, permeability control, sensation, and secretion.
- Characteristics:
- Membranous structure: Simple vs. stratified, with apical & basal borders.
- Non-vascularized and mitotically active.
- Types of epithelial tissue:
- Simple:
- Squamous: Flattened cells for filtration/diffusion (e.g. lung alveoli).
- Cuboidal: Cube-shaped for secretion/absorption (e.g. kidney tubules).
- Columnar: Tall cells for secretion/absorption (e.g. small intestine).
- Ciliated columnar: Cilia present (e.g. uterine tubes).
- Pseudostratified ciliated columnar: All cells touch basement membrane; not all reach the apical surface (e.g. trachea).
- Stratified:
- Squamous: Can be keratinized (e.g. skin) or non-keratinized (e.g. oral cavity).
- Cuboidal: Rare, typically two or more layers, found in sweat and salivary glands.
- Transitional: Specialized to accommodate stretching (e.g. bladder).
- Simple:
Glandular Epithelium
- Functions to produce and secrete substances.
- Types:
- Ducts: Endocrine (ductless, secreted into the blood) and exocrine (released via ducts).
- Cellular organization: Unicellular (e.g. goblet cells) or multicellular (simple and compound).
- Mechanisms of secretion:
- Merocrine: Exocytosis (e.g. salivary glands).
- Apocrine: Part of the apical cell is sloughed (e.g. mammary glands).
- Holocrine: Entire cell is sloughed (e.g. sebaceous glands).
Connective Tissue
- Functions include binding tissue, support, energy storage, and erythrocyte production.
- Consists of cells dispersed in a matrix comprising ground substance and protein fibers.
- Lacks free surfaces and is typically highly vascularized.
- Major cell types:
- Fibroblasts (produce fibers), macrophages (engulf bacteria), plasma cells (produce antibodies), and mast cells (produce histamines).
- Matrix components include glycosaminoglycans (GAG) and three types of fibers:
- Collagenous, elastic, and reticular.
Types of Connective Tissue
- Loose (areolar): Binds tissues, surrounds blood vessels, provides elasticity and support.
- Dense regular: Parallel collagen fibers found in tendons and ligaments.
- Dense irregular: Randomly packed collagen fibers in the dermis and organ capsules.
- Elastic: Contains elastin fibers, found in arteries and bronchi.
- Reticular: Thin collagen fibers, found in lymph nodes, liver, spleen, and basement membranes.
- Adipose tissue: Insulates and stores energy, composed of adipocytes.
- Cartilage: Supports and forms attachments, characterized by chondrocytes within lacunae.
- Types include:
- Hyaline: Flexible, with fine collagen fibers (e.g. articular surfaces).
- Fibrocartilage: Supports under compression (e.g. intervertebral discs).
- Elastic: Flexible (e.g. outer ear).
- Types include:
Bone
- Most rigid connective tissue containing osteocytes in lacunae, surrounded by concentric layers of matrix called lamellae.
- Matrix consists primarily of calcium hydroxyapatite and collagen fibers.
- Types of bone:
- Compact: Outer hard layer, covered by periosteum.
- Spongy: Inner porous tissue, highly vascularized, providing space for marrow.
Vascular Tissue
- Specialized fluid tissue and a type of connective tissue.
- Components include:
- Formed elements: Erythrocytes, leukocytes, and platelets.
- Plasma: Liquid component of blood.
Muscle Tissue
- Characterized by its ability to contract and facilitate movement.
- Types of muscle tissue:
- Skeletal: Striated, voluntary, and multinucleated.
- Cardiac: Striated, involuntary, contains intercalated discs for communication.
- Smooth: Non-striated, involuntary, found in various organs.
Nervous Tissue
- Divided into central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and peripheral nervous system.
- Composed of neurons and glial cells, with specific roles in communication and signaling.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Related Documents
Description
This quiz covers the essential concepts of histology, focusing on the study of tissues and their classifications. Explore the four main types of tissues: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous, along with their functions and characteristics. Reference material includes MTT and BB, enhancing your understanding of cell junctions and tissue organization.