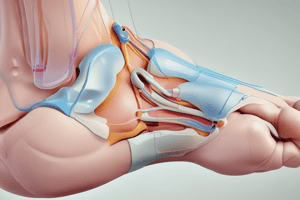
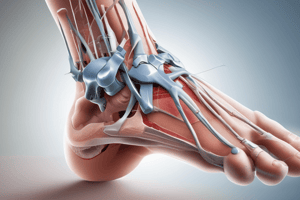
Podcast
Questions and Answers
In the context of normal first ray function during gait, what is the most critical biomechanical event facilitated by plantarflexion of the first ray?
In the context of normal first ray function during gait, what is the most critical biomechanical event facilitated by plantarflexion of the first ray?
- Maximization of subtalar joint pronation, facilitating shock absorption and internal rotation of the tibia.
- Attenuation of ground reaction force through increased contact area of the lateral metatarsals.
- Enhancement of tibialis anterior moment arm, optimizing ankle dorsiflexion during swing phase.
- Removal of supinatus/forefoot varus, thereby enabling the windlass mechanism for efficient propulsion. (correct)
Which of the following represents the most biomechanically cohesive rationale for the constraint in hallux dorsiflexion observed in functional hallux limitus?
Which of the following represents the most biomechanically cohesive rationale for the constraint in hallux dorsiflexion observed in functional hallux limitus?
- Progressive ankylosis of the sesamoid apparatus restricting the excursion of the flexor hallucis longus tendon.
- Adaptive shortening of the extensor hallucis longus tendon resulting in a fixed plantarflexed position of the hallux.
- Inadequate first ray plantarflexion during the propulsive phase, leading to jamming of the metatarsal head against the proximal phalanx. (correct)
- Development of a traction spur on the dorsal aspect of the metatarsal head, physically impeding dorsiflexion.
In the context of surgical management for hallux rigidus, which biomechanical principle is most directly addressed by a decompression osteotomy of the first metatarsal?
In the context of surgical management for hallux rigidus, which biomechanical principle is most directly addressed by a decompression osteotomy of the first metatarsal?
- Enhancement of the windlass mechanism by increasing the mechanical advantage of the flexor hallucis longus.
- Reduction of intra-articular pressure within the first metatarsophalangeal joint, thereby increasing dorsiflexion. (correct)
- Restoration of the normal parabola of the metatarsal cascade to equally distribute plantar pressure.
- Attenuation of intrinsic muscular imbalances that exacerbate hallux abduction and pronation.
What is the most critical consideration when contemplating a Valenti procedure for hallux rigidus, given its potential impact on future surgical options?
What is the most critical consideration when contemplating a Valenti procedure for hallux rigidus, given its potential impact on future surgical options?
When considering the biomechanical ramifications of a Keller resection arthroplasty for end-stage hallux rigidus, what represents the most significant long-term compensatory mechanism that contributes to the procedure's eventual failure?
When considering the biomechanical ramifications of a Keller resection arthroplasty for end-stage hallux rigidus, what represents the most significant long-term compensatory mechanism that contributes to the procedure's eventual failure?
In the selection of an appropriate implant for first MTPJ arthroplasty, what is the MOST critical long-term biomechanical consideration regarding the material properties of the implant relative to native cartilage?
In the selection of an appropriate implant for first MTPJ arthroplasty, what is the MOST critical long-term biomechanical consideration regarding the material properties of the implant relative to native cartilage?
Which of the following represents the most compelling rationale against performing a chondroplasty in isolation for hallux rigidus?
Which of the following represents the most compelling rationale against performing a chondroplasty in isolation for hallux rigidus?
In the context of the Drago, Oloff, and Jacobs classification, what is the MOST pivotal clinical distinction between Stage 1 (Functional Limitus) and Stage 2 (Adaptation) hallux rigidus that dictates treatment strategy?
In the context of the Drago, Oloff, and Jacobs classification, what is the MOST pivotal clinical distinction between Stage 1 (Functional Limitus) and Stage 2 (Adaptation) hallux rigidus that dictates treatment strategy?
Considering the long-term biomechanical consequences, which of the following complications is MOST directly attributable to over-compression during a first MTPJ arthrodesis?
Considering the long-term biomechanical consequences, which of the following complications is MOST directly attributable to over-compression during a first MTPJ arthrodesis?
What is the primary biomechanical rationale for incorporating a reverse Morton's extension in orthotic management of functional hallux limitus?
What is the primary biomechanical rationale for incorporating a reverse Morton's extension in orthotic management of functional hallux limitus?
Following a cheilectomy procedure: While it may be generally true it can increase patient symptoms if the joint is deteriorated, what is the most precise underlying biomechanical concern that contributes?
Following a cheilectomy procedure: While it may be generally true it can increase patient symptoms if the joint is deteriorated, what is the most precise underlying biomechanical concern that contributes?
What is the most substantiated long-term risk associated with utilizing metallic hemi-implants in first MTPJ arthroplasty, particularly concerning implant longevity and the potential need for revision surgery?
What is the most substantiated long-term risk associated with utilizing metallic hemi-implants in first MTPJ arthroplasty, particularly concerning implant longevity and the potential need for revision surgery?
What is the most critical biomechanical implication of a long first metatarsal relative to a short second metatarsal in the context of hallux rigidus etiology?
What is the most critical biomechanical implication of a long first metatarsal relative to a short second metatarsal in the context of hallux rigidus etiology?
What is the most crucial factor in orthotic casting for hallux limitus?
What is the most crucial factor in orthotic casting for hallux limitus?
What is the rationale for a Lapidus procedure in the treatment of hallux rigidus?
What is the rationale for a Lapidus procedure in the treatment of hallux rigidus?
What is the MOST concerning complication specific to the Kessel & Bonney procedure regarding potential future surgical interventions?
What is the MOST concerning complication specific to the Kessel & Bonney procedure regarding potential future surgical interventions?
In a patient presenting with hallux rigidus and radiographic evidence of metatarsus primus elevatus, which additional clinical finding would most strongly advocate for a plantarflexory osteotomy of the first metatarsal as opposed to simple cheilectomy?
In a patient presenting with hallux rigidus and radiographic evidence of metatarsus primus elevatus, which additional clinical finding would most strongly advocate for a plantarflexory osteotomy of the first metatarsal as opposed to simple cheilectomy?
When contemplating an arthrodiastasis procedure for a patient with hallux rigidus, what is the MOST significant theoretical advantage concerning cartilage regeneration?
When contemplating an arthrodiastasis procedure for a patient with hallux rigidus, what is the MOST significant theoretical advantage concerning cartilage regeneration?
What is the MOST concerning aspect of flexible silicone implants?
What is the MOST concerning aspect of flexible silicone implants?
What is the Youngswick osteotomy?
What is the Youngswick osteotomy?
When a patient presents with late stage hallux rigidus accompanied by severe angular deformity at the first MTPJ, what is most appropriate given the primary goals of arthrodesis?
When a patient presents with late stage hallux rigidus accompanied by severe angular deformity at the first MTPJ, what is most appropriate given the primary goals of arthrodesis?
A 71-year-old obese female presents with right foot pain. Radiographs reveal late-stage hallux rigidus. She has a history of midfoot arthritis and equinus. What initial treatment approach would address the collective pathologies?
A 71-year-old obese female presents with right foot pain. Radiographs reveal late-stage hallux rigidus. She has a history of midfoot arthritis and equinus. What initial treatment approach would address the collective pathologies?
A 66-year-old female presents with right big toe joint pain, having undergone bunion surgery two years prior. Now exhibits functional limitus and NC sag. Initial treatment includes OTC orthotics, but what is the MOST appropriate next step?
A 66-year-old female presents with right big toe joint pain, having undergone bunion surgery two years prior. Now exhibits functional limitus and NC sag. Initial treatment includes OTC orthotics, but what is the MOST appropriate next step?
A 63-year-old female smoker presents with left big toe joint pain. Exam reveals 15° of motion with crepitus. Radiographs reveal MTPJ arthrosis and rigidity. What MOST important treatment option should be considered initially?
A 63-year-old female smoker presents with left big toe joint pain. Exam reveals 15° of motion with crepitus. Radiographs reveal MTPJ arthrosis and rigidity. What MOST important treatment option should be considered initially?
A 29-year-old female presents with right big toe joint pain following prior surgery and is found to have a mal-positioned implant, lytic changes, a short first metatarsal, and you suspect she was a poor candidate. After removal of the implant which approach is MOST definitive approach considering her bone stock and age?
A 29-year-old female presents with right big toe joint pain following prior surgery and is found to have a mal-positioned implant, lytic changes, a short first metatarsal, and you suspect she was a poor candidate. After removal of the implant which approach is MOST definitive approach considering her bone stock and age?
An 80-year-old female presents with left big toe joint pain after two prior foot surgeries. Exam reveals hallux extensus and 5° of motion and second metatarsal pain. What MOST appropriate treatment option for this patient?
An 80-year-old female presents with left big toe joint pain after two prior foot surgeries. Exam reveals hallux extensus and 5° of motion and second metatarsal pain. What MOST appropriate treatment option for this patient?
Which of the following statements best articulates the relationship between first ray hypermobility and the pathomechanics of hallux rigidus?
Which of the following statements best articulates the relationship between first ray hypermobility and the pathomechanics of hallux rigidus?
During normal gait, what is the primary biomechanical function facilitated by the sliding motion within the first MTPJ complex, subsequent to the initial rolling phase?
During normal gait, what is the primary biomechanical function facilitated by the sliding motion within the first MTPJ complex, subsequent to the initial rolling phase?
What is the most critical biomechanical determinant of success following a first MTPJ cheilectomy procedure?
What is the most critical biomechanical determinant of success following a first MTPJ cheilectomy procedure?
When evaluating a patient with hallux rigidus, which physical examination finding would suggest that an isolated cheilectomy may be insufficient?
When evaluating a patient with hallux rigidus, which physical examination finding would suggest that an isolated cheilectomy may be insufficient?
What is the primary advantage of using a cannulated screw system during first MTPJ hemiarthroplasty?
What is the primary advantage of using a cannulated screw system during first MTPJ hemiarthroplasty?
In which clinical scenario might an arthrodiastasis procedure be considered as a potentially joint-sparing option?
In which clinical scenario might an arthrodiastasis procedure be considered as a potentially joint-sparing option?
What is the BEST treatment option given the need for clean MTPJ?
What is the BEST treatment option given the need for clean MTPJ?
When should the Valenti procedure be used?
When should the Valenti procedure be used?
What is the MOST concerning with the Keller/Valenti?
What is the MOST concerning with the Keller/Valenti?
Of the metallic hemi-implant, which has dorsal elevation?
Of the metallic hemi-implant, which has dorsal elevation?
What do the base resurfacing systems do?
What do the base resurfacing systems do?
When do we do the Keller?
When do we do the Keller?
What surgical procedure can be done after the implant?
What surgical procedure can be done after the implant?
Considering the interplay between arthrodiastasis and cartilage homeostasis, what is the MOST critical cellular mechanism believed to be stimulated by intermittent joint distraction that potentiates chondrogenesis in the first MTPJ?
Considering the interplay between arthrodiastasis and cartilage homeostasis, what is the MOST critical cellular mechanism believed to be stimulated by intermittent joint distraction that potentiates chondrogenesis in the first MTPJ?
In cases of hallux rigidus secondary to metatarsus primus elevatus, which surgical intervention offers the MOST biomechanically sound approach to restore first ray purchase during the propulsive phase of gait, while simultaneously addressing sagittal plane malalignment?
In cases of hallux rigidus secondary to metatarsus primus elevatus, which surgical intervention offers the MOST biomechanically sound approach to restore first ray purchase during the propulsive phase of gait, while simultaneously addressing sagittal plane malalignment?
During orthotic fabrication for functional hallux limitus, what specific biomechanical modification MOST effectively mitigates the pathological jamming of the first MTPJ during dorsiflexion, assuming a pronated foot type with forefoot supinatus?
During orthotic fabrication for functional hallux limitus, what specific biomechanical modification MOST effectively mitigates the pathological jamming of the first MTPJ during dorsiflexion, assuming a pronated foot type with forefoot supinatus?
When contemplating surgical intervention for hallux rigidus in a high-performance athlete, which joint-sparing procedure offers the MOST favorable biomechanical trade-off between preserving motion and preventing the long-term sequelae of altered gait mechanics?
When contemplating surgical intervention for hallux rigidus in a high-performance athlete, which joint-sparing procedure offers the MOST favorable biomechanical trade-off between preserving motion and preventing the long-term sequelae of altered gait mechanics?
In managing hallux rigidus, what represents the PRIMARY advantage of employing a distal metatarsal plantarflexion osteotomy, such as the Youngswick modification, over a simple cheilectomy in patients exhibiting metatarsus primus elevatus?
In managing hallux rigidus, what represents the PRIMARY advantage of employing a distal metatarsal plantarflexion osteotomy, such as the Youngswick modification, over a simple cheilectomy in patients exhibiting metatarsus primus elevatus?
In the context of end-stage hallux rigidus management, what is the MOST significant long-term biomechanical concern associated with Keller resection arthroplasty regarding its impact on adjacent structures and overall foot function?
In the context of end-stage hallux rigidus management, what is the MOST significant long-term biomechanical concern associated with Keller resection arthroplasty regarding its impact on adjacent structures and overall foot function?
When considering first MTPJ implant arthroplasty for hallux rigidus, what constitutes the MOST critical factor influencing long-term implant survivorship and patient satisfaction, considering the biomechanical demands during gait?
When considering first MTPJ implant arthroplasty for hallux rigidus, what constitutes the MOST critical factor influencing long-term implant survivorship and patient satisfaction, considering the biomechanical demands during gait?
In a patient presenting with hallux rigidus and radiographic evidence of a significantly long first metatarsal relative to the second, which surgical strategy would MOST effectively address the pathomechanical etiology while optimizing first MTPJ range of motion?
In a patient presenting with hallux rigidus and radiographic evidence of a significantly long first metatarsal relative to the second, which surgical strategy would MOST effectively address the pathomechanical etiology while optimizing first MTPJ range of motion?
What is the MOST crucial biomechanical consideration when determining the optimal degree of plantarflexion achieved during a first MTPJ arthrodesis for end-stage hallux rigidus, aiming to restore optimal gait mechanics and minimize secondary complications?
What is the MOST crucial biomechanical consideration when determining the optimal degree of plantarflexion achieved during a first MTPJ arthrodesis for end-stage hallux rigidus, aiming to restore optimal gait mechanics and minimize secondary complications?
Which statement BEST encapsulates the theoretical advantage of an arthrodiastasis procedure in early-stage hallux rigidus regarding the restoration of joint homeostasis and cartilage regeneration?
Which statement BEST encapsulates the theoretical advantage of an arthrodiastasis procedure in early-stage hallux rigidus regarding the restoration of joint homeostasis and cartilage regeneration?
During the biomechanical assessment of a patient for hallux rigidus, what clinical finding would MOST strongly contraindicate isolated cheilectomy as a viable long-term solution?
During the biomechanical assessment of a patient for hallux rigidus, what clinical finding would MOST strongly contraindicate isolated cheilectomy as a viable long-term solution?
In the context of orthotic management for hallux limitus, what is the MOST critical biomechanical rationale for incorporating a reverse Morton's extension?
In the context of orthotic management for hallux limitus, what is the MOST critical biomechanical rationale for incorporating a reverse Morton's extension?
Which of the following statements BEST encapsulates the primary biomechanical impact of the Lapidus procedure when utilized in the context of hallux rigidus associated with underlying structural instability?
Which of the following statements BEST encapsulates the primary biomechanical impact of the Lapidus procedure when utilized in the context of hallux rigidus associated with underlying structural instability?
In planning a cheilectomy for hallux rigidus, what intraoperative assessment provides the MOST reliable indication that adequate decompression has been achieved, thereby maximizing the potential for increased range of motion?
In planning a cheilectomy for hallux rigidus, what intraoperative assessment provides the MOST reliable indication that adequate decompression has been achieved, thereby maximizing the potential for increased range of motion?
Considering the properties of synthetic cartilage implants, what represents the MOST significant long-term limitation regarding their application in first MTPJ arthroplasty for hallux rigidus?
Considering the properties of synthetic cartilage implants, what represents the MOST significant long-term limitation regarding their application in first MTPJ arthroplasty for hallux rigidus?
What is the MOST critical biomechanical determinant of successful and sustained pain relief following a cheilectomy procedure for hallux rigidus?
What is the MOST critical biomechanical determinant of successful and sustained pain relief following a cheilectomy procedure for hallux rigidus?
In the context of orthotic casting for hallux limitus, what is the MOST critical manual maneuver required to optimize first ray function during the casting process?
In the context of orthotic casting for hallux limitus, what is the MOST critical manual maneuver required to optimize first ray function during the casting process?
Within the context of the Drago, Oloff, and Jacobs classification, what pathological feature distinguishes Stage 2 (Adaptation) hallux rigidus from Stage 3 (Deterioration), directly influencing surgical decision-making?
Within the context of the Drago, Oloff, and Jacobs classification, what pathological feature distinguishes Stage 2 (Adaptation) hallux rigidus from Stage 3 (Deterioration), directly influencing surgical decision-making?
When performing a Youngswick osteotomy for hallux rigidus, what is the MOST crucial intraoperative radiographic parameter to assess in order to prevent iatrogenic over-shortening of the first metatarsal?
When performing a Youngswick osteotomy for hallux rigidus, what is the MOST crucial intraoperative radiographic parameter to assess in order to prevent iatrogenic over-shortening of the first metatarsal?
What is the MOST significant biomechanical disadvantage associated with the Valenti procedure in the surgical management of hallux rigidus?
What is the MOST significant biomechanical disadvantage associated with the Valenti procedure in the surgical management of hallux rigidus?
In the surgical treatment of hallux rigidus, which statement BEST articulates the primary rationale for performing a decompression osteotomy of the first metatarsal?
In the surgical treatment of hallux rigidus, which statement BEST articulates the primary rationale for performing a decompression osteotomy of the first metatarsal?
When managing hallux rigidus with a Keller resection arthroplasty, what is the MOST critical factor to consider in order to minimize the likelihood of subsequent transfer lesion development to the lesser metatarsals?
When managing hallux rigidus with a Keller resection arthroplasty, what is the MOST critical factor to consider in order to minimize the likelihood of subsequent transfer lesion development to the lesser metatarsals?
When selecting between metallic hemi-implants for first MTPJ arthroplasty, what is the MOST pertinent biomechanical advantage of a dorsal elevation design?
When selecting between metallic hemi-implants for first MTPJ arthroplasty, what is the MOST pertinent biomechanical advantage of a dorsal elevation design?
Within the array of surgical options for hallux rigidus, in what specific clinical scenario would arthrodiastasis be MOST strongly considered as a potentially joint-sparing intervention?
Within the array of surgical options for hallux rigidus, in what specific clinical scenario would arthrodiastasis be MOST strongly considered as a potentially joint-sparing intervention?
Of the various joint destructive procedures available for end-stage hallux rigidus, what is the MOST concerning aspect regarding the Keller/Valenti?
Of the various joint destructive procedures available for end-stage hallux rigidus, what is the MOST concerning aspect regarding the Keller/Valenti?
When considering postoperative management following a cheilectomy for hallux rigidus, what rehabilitation strategy is MOST critical for optimizing long-term outcomes and functional recovery?
When considering postoperative management following a cheilectomy for hallux rigidus, what rehabilitation strategy is MOST critical for optimizing long-term outcomes and functional recovery?
In the context of the first MTPJ range of motion (ROM), what is the MOST consequential biomechanical characteristic of the first 20-30° of hallux dorsiflexion during gait?
In the context of the first MTPJ range of motion (ROM), what is the MOST consequential biomechanical characteristic of the first 20-30° of hallux dorsiflexion during gait?
During assessment for hallux rigidus, what clinical sign primarily differentiates functional hallux limitus from structural hallux rigidus?
During assessment for hallux rigidus, what clinical sign primarily differentiates functional hallux limitus from structural hallux rigidus?
Considering the various treatment options for hallux rigidus, in which of the following scenarios would chondroplasty be MOST appropriately utilized?
Considering the various treatment options for hallux rigidus, in which of the following scenarios would chondroplasty be MOST appropriately utilized?
When evaluating a patient with hallux rigidus, which long-term sequela is MOST directly associated with over-compression during first MTPJ arthrodesis?
When evaluating a patient with hallux rigidus, which long-term sequela is MOST directly associated with over-compression during first MTPJ arthrodesis?
What is the MOST crucial biomechanical justification for performing a Lapidus procedure in the context of hallux rigidus management?
What is the MOST crucial biomechanical justification for performing a Lapidus procedure in the context of hallux rigidus management?
Which aspect of flexible silicone implants is MOST concerning when considering long-term outcomes in first MTPJ arthroplasty?
Which aspect of flexible silicone implants is MOST concerning when considering long-term outcomes in first MTPJ arthroplasty?
Considering normal first ray anatomy and function during gait, what primary pathomechanical effect results from an excessively rigid plantar fascia?
Considering normal first ray anatomy and function during gait, what primary pathomechanical effect results from an excessively rigid plantar fascia?
What is the PRIMARY biomechanical concern when incorporating a Morton’s extension for hallux rigidus?
What is the PRIMARY biomechanical concern when incorporating a Morton’s extension for hallux rigidus?
According to the principles governing first ray biomechanics, which statement accurately describes the role of the peroneus longus tendon in mitigating the development of hallux rigidus?
According to the principles governing first ray biomechanics, which statement accurately describes the role of the peroneus longus tendon in mitigating the development of hallux rigidus?
What surgical approach represents the MOST biomechanically rational choice for a 29-year-old female with hallux rigidus, lytic changes to bone and a mal-positioned implant?
What surgical approach represents the MOST biomechanically rational choice for a 29-year-old female with hallux rigidus, lytic changes to bone and a mal-positioned implant?
In the scenario of an 80-year-old female patient, previously treated with multiple surgeries, how would one address pain with hallux extensus?
In the scenario of an 80-year-old female patient, previously treated with multiple surgeries, how would one address pain with hallux extensus?
In the context of first MTPJ arthrodesis, what is the MOST critical factor in determining optimal sagittal plane positioning to ensure a plantigrade foot and avoid compensatory pathology in adjacent structures?
In the context of first MTPJ arthrodesis, what is the MOST critical factor in determining optimal sagittal plane positioning to ensure a plantigrade foot and avoid compensatory pathology in adjacent structures?
When performing a Youngswick osteotomy for hallux rigidus associated with metatarsus primus elevatus, what is the MOST biomechanically relevant parameter to evaluate intraoperatively via fluoroscopy to mitigate the risk of adverse sequelae?
When performing a Youngswick osteotomy for hallux rigidus associated with metatarsus primus elevatus, what is the MOST biomechanically relevant parameter to evaluate intraoperatively via fluoroscopy to mitigate the risk of adverse sequelae?
In the management of a patient with hallux rigidus, exhibiting radiographic evidence of metatarsus primus elevatus and a clinically evident, structurally shortened first metatarsal, what surgical strategy would be MOST biomechanically sound to re-establish appropriate first ray purchase during the propulsive phase of gait?
In the management of a patient with hallux rigidus, exhibiting radiographic evidence of metatarsus primus elevatus and a clinically evident, structurally shortened first metatarsal, what surgical strategy would be MOST biomechanically sound to re-establish appropriate first ray purchase during the propulsive phase of gait?
Following a technically successful cheilectomy for hallux rigidus, a patient continues to experience pain during terminal stance. Advanced imaging reveals the presence of a previously undetected intra-articular osteochondral lesion on the plantar aspect of the first metatarsal head. What secondary pathomechanical consequence MOST directly explains the patient's persistent symptoms?
Following a technically successful cheilectomy for hallux rigidus, a patient continues to experience pain during terminal stance. Advanced imaging reveals the presence of a previously undetected intra-articular osteochondral lesion on the plantar aspect of the first metatarsal head. What secondary pathomechanical consequence MOST directly explains the patient's persistent symptoms?
In the context of Keller resection arthroplasty as a salvage procedure for end-stage hallux rigidus, what is the MOST critical intraoperative factor that determines the long-term biomechanical stability of the first ray and minimizes proximal migration of the hallux?
In the context of Keller resection arthroplasty as a salvage procedure for end-stage hallux rigidus, what is the MOST critical intraoperative factor that determines the long-term biomechanical stability of the first ray and minimizes proximal migration of the hallux?
In the context of first ray anatomy and function, which of the following statements most accurately describes the biomechanical consequence of an elevated metatarsus primus?
In the context of first ray anatomy and function, which of the following statements most accurately describes the biomechanical consequence of an elevated metatarsus primus?
In the radiographic assessment of hallux rigidus, the presence of a 'flag sign' at the first metatarsal head suggests a primary etiology of STJ supination.
In the radiographic assessment of hallux rigidus, the presence of a 'flag sign' at the first metatarsal head suggests a primary etiology of STJ supination.
Describe the biomechanical rationale for employing a reverse Morton's extension orthotic modification in the conservative management of functional hallux limitus.
Describe the biomechanical rationale for employing a reverse Morton's extension orthotic modification in the conservative management of functional hallux limitus.
According to the Drago, Oloff, & Jacobs classification, Stage III hallux rigidus is characterized by severe flattening of the first metatarsal head, dorsal osteophytosis, asymmetric joint space narrowing, degeneration of articular cartilage, ______, subchondral cystic formation, and pain on full ROM.
According to the Drago, Oloff, & Jacobs classification, Stage III hallux rigidus is characterized by severe flattening of the first metatarsal head, dorsal osteophytosis, asymmetric joint space narrowing, degeneration of articular cartilage, ______, subchondral cystic formation, and pain on full ROM.
Match each surgical procedure for hallux rigidus with its primary biomechanical objective:
Match each surgical procedure for hallux rigidus with its primary biomechanical objective:
Which of the following represents the most critical consideration in determining the suitability of a joint-salvage procedure versus a joint-destructive procedure for hallux rigidus?
Which of the following represents the most critical consideration in determining the suitability of a joint-salvage procedure versus a joint-destructive procedure for hallux rigidus?
The primary goal of a Lapidus procedure in the context of hallux rigidus is to directly address intra-articular pathology within the MTPJ through joint debridement and resurfacing.
The primary goal of a Lapidus procedure in the context of hallux rigidus is to directly address intra-articular pathology within the MTPJ through joint debridement and resurfacing.
Explain the biomechanical principles underlying the potential for central metatarsalgia following a Keller resection arthroplasty for hallux rigidus.
Explain the biomechanical principles underlying the potential for central metatarsalgia following a Keller resection arthroplasty for hallux rigidus.
In the context of interpositional arthroplasty for hallux rigidus, a significant limitation of many implant designs is the large discrepancy in the ______ of cartilage versus the implant material, potentially leading to implant subsidence and adjacent joint degeneration.
In the context of interpositional arthroplasty for hallux rigidus, a significant limitation of many implant designs is the large discrepancy in the ______ of cartilage versus the implant material, potentially leading to implant subsidence and adjacent joint degeneration.
Match the following surgical procedures used for hallux rigidus with their respective primary advantages and disadvantages:
Match the following surgical procedures used for hallux rigidus with their respective primary advantages and disadvantages:
Which of the following biomechanical factors is LEAST likely to contribute directly to the development of hallux limitus?
Which of the following biomechanical factors is LEAST likely to contribute directly to the development of hallux limitus?
In a patient presenting with radiographic evidence of Stage 2 hallux rigidus according to the Drago, Oloff, and Jacobs classification, a cheilectomy alone is typically sufficient to restore near-normal first MTPJ range of motion and prevent disease progression irrespective of underlying biomechanical abnormalities.
In a patient presenting with radiographic evidence of Stage 2 hallux rigidus according to the Drago, Oloff, and Jacobs classification, a cheilectomy alone is typically sufficient to restore near-normal first MTPJ range of motion and prevent disease progression irrespective of underlying biomechanical abnormalities.
Describe the key operative steps required to perform a Youngswick osteotomy for hallux limitus, emphasizing the importance of maintaining intrinsic stability.
Describe the key operative steps required to perform a Youngswick osteotomy for hallux limitus, emphasizing the importance of maintaining intrinsic stability.
Arthrodiastasis for hallux rigidus involves external fixation and distraction of the joint to promote cartilage regeneration; however, its efficacy is predicated upon the absence of significant ______ and adequate patient compliance with a prolonged fixation period.
Arthrodiastasis for hallux rigidus involves external fixation and distraction of the joint to promote cartilage regeneration; however, its efficacy is predicated upon the absence of significant ______ and adequate patient compliance with a prolonged fixation period.
Match each surgical procedure for hallux rigidus with the most appropriate postoperative management strategy:
Match each surgical procedure for hallux rigidus with the most appropriate postoperative management strategy:
Which of the following statements most accurately reflects the potential drawbacks of a first MTPJ implant arthroplasty in the treatment of advanced hallux rigidus?
Which of the following statements most accurately reflects the potential drawbacks of a first MTPJ implant arthroplasty in the treatment of advanced hallux rigidus?
A first MTPJ fusion performed in excessive dorsiflexion is unlikely to produce any significant functional limitations, as the compensatory mechanisms of the lesser metatarsals can adequately accommodate changes in weight distribution during gait.
A first MTPJ fusion performed in excessive dorsiflexion is unlikely to produce any significant functional limitations, as the compensatory mechanisms of the lesser metatarsals can adequately accommodate changes in weight distribution during gait.
In a revision scenario following a failed first MTPJ implant arthroplasty for hallux rigidus, articulate the key considerations that would guide your decision-making between conversion to arthrodesis versus a revision implant procedure.
In a revision scenario following a failed first MTPJ implant arthroplasty for hallux rigidus, articulate the key considerations that would guide your decision-making between conversion to arthrodesis versus a revision implant procedure.
A Kessel-Bonney osteotomy, indicated for hallux limitus, is a ______ osteotomy of the proximal phalanx that aims to decompress the MTPJ and improve dorsiflexion, primarily through altered joint mechanics.
A Kessel-Bonney osteotomy, indicated for hallux limitus, is a ______ osteotomy of the proximal phalanx that aims to decompress the MTPJ and improve dorsiflexion, primarily through altered joint mechanics.
Match the clinical presentation characteristics with the most likely stage of hallux rigidus according to the Drago, Oloff, and Jacobs classification.
Match the clinical presentation characteristics with the most likely stage of hallux rigidus according to the Drago, Oloff, and Jacobs classification.
A patient presents with a long first metatarsal relative to the second, and clinical signs of functional hallux limitus. Which of the following orthotic modifications would be MOST appropriate to address the biomechanical fault?
A patient presents with a long first metatarsal relative to the second, and clinical signs of functional hallux limitus. Which of the following orthotic modifications would be MOST appropriate to address the biomechanical fault?
The presence of a dorsal bunion in conjunction with hallux limitus conclusively indicates the presence of an osseous equinus, necessitating immediate surgical intervention to prevent further joint degeneration.
The presence of a dorsal bunion in conjunction with hallux limitus conclusively indicates the presence of an osseous equinus, necessitating immediate surgical intervention to prevent further joint degeneration.
A patient with stage 3 hallux rigidus who is not a candidate for fusion is scheduled for a Valenti procedure. Describe the critical steps to take to ensure post operative managment.
A patient with stage 3 hallux rigidus who is not a candidate for fusion is scheduled for a Valenti procedure. Describe the critical steps to take to ensure post operative managment.
After a cheilectomy, drilling the subchondral bone stimulates bleeding to promote _________ ___________.
After a cheilectomy, drilling the subchondral bone stimulates bleeding to promote _________ ___________.
Match each case presentation to the appropriate stage of hallux rigidus according to the D,O,J classification.
Match each case presentation to the appropriate stage of hallux rigidus according to the D,O,J classification.
A 75-year-old female presents with hallux rigidus and significant dorsiflexion stiffness with imaging revealing stage 4 changes. What surgical procedure?
A 75-year-old female presents with hallux rigidus and significant dorsiflexion stiffness with imaging revealing stage 4 changes. What surgical procedure?
A reverse Mortons extension will plantarflex the hallux.
A reverse Mortons extension will plantarflex the hallux.
What direction should a surgeon aim to plantarflex the first ray?
What direction should a surgeon aim to plantarflex the first ray?
If the STJ is locked or held in neutral position while plantarflexting the first ray, then the term supination/forefoot varus is considered __________.
If the STJ is locked or held in neutral position while plantarflexting the first ray, then the term supination/forefoot varus is considered __________.
Indicate the correct amount of dorsiflexion required with MTPJ fusion.
Indicate the correct amount of dorsiflexion required with MTPJ fusion.
A patient presents with pain and limited movement in their great toe joint, a condition diagnosed as hallux rigidus. Radiographs reveal joint space narrowing, osteophyte formation, and subchondral sclerosis. Based on the Drago, Oloff, and Jacobs classification, which stage of hallux rigidus aligns with these findings?
A patient presents with pain and limited movement in their great toe joint, a condition diagnosed as hallux rigidus. Radiographs reveal joint space narrowing, osteophyte formation, and subchondral sclerosis. Based on the Drago, Oloff, and Jacobs classification, which stage of hallux rigidus aligns with these findings?
A first MTPJ fusion aims to relieve pain and improve function by preserving the range of motion of the first metatarsophalangeal joint, while eliminating painful bone-on-bone contact.
A first MTPJ fusion aims to relieve pain and improve function by preserving the range of motion of the first metatarsophalangeal joint, while eliminating painful bone-on-bone contact.
After performing a cheilectomy, bone drilling can improve
After performing a cheilectomy, bone drilling can improve
A hallux rigidus patient has a long first metatarsal in realtion to the second and signs of functional hallux limitus. The correct offloading in this case requires a reverse ______ extension to enhance first ray ______.
A hallux rigidus patient has a long first metatarsal in realtion to the second and signs of functional hallux limitus. The correct offloading in this case requires a reverse ______ extension to enhance first ray ______.
Match functional/structural
Match functional/structural
When it comes to MTPJ fusion, the positioning is ___________
When it comes to MTPJ fusion, the positioning is ___________
Keller arthroplasty is generally recommended for high impact patients.
Keller arthroplasty is generally recommended for high impact patients.
What is not the goal with cheilectomies for joint clean up?
What is not the goal with cheilectomies for joint clean up?
Keller Arthroplasty makes revision to fusion ______ ______.
Keller Arthroplasty makes revision to fusion ______ ______.
Which statement most accurately delineates the biomechanical transition within the first metatarsophalangeal joint (MTPJ) during normal dorsiflexion?
Which statement most accurately delineates the biomechanical transition within the first metatarsophalangeal joint (MTPJ) during normal dorsiflexion?
In the context of hallux rigidus etiology, 'metatarsus primus elevatus' is solely a functional biomechanical phenomenon, independent of structural osseous variations.
In the context of hallux rigidus etiology, 'metatarsus primus elevatus' is solely a functional biomechanical phenomenon, independent of structural osseous variations.
According to the Drago, Oloff, and Jacobs classification, Stage III hallux rigidus is characterized by severe flattening of the first metatarsal head, dorsal osteophytosis, asymmetric joint space narrowing, degeneration of articular cartilage, crepitus, subchondral cystic formation, and pain on ______ ROM.
According to the Drago, Oloff, and Jacobs classification, Stage III hallux rigidus is characterized by severe flattening of the first metatarsal head, dorsal osteophytosis, asymmetric joint space narrowing, degeneration of articular cartilage, crepitus, subchondral cystic formation, and pain on ______ ROM.
Explain the rationale behind plantarflexing the first ray during orthotic casting for functional hallux limitus, and detail its impact on sagittal plane joint motion.
Explain the rationale behind plantarflexing the first ray during orthotic casting for functional hallux limitus, and detail its impact on sagittal plane joint motion.
Match the following surgical procedures for hallux rigidus with their primary biomechanical rationale
Match the following surgical procedures for hallux rigidus with their primary biomechanical rationale
The Valenti procedure is universally recognized as a joint salvage technique that consistently preserves native joint mechanics and is easily reversible to arthrodesis.
The Valenti procedure is universally recognized as a joint salvage technique that consistently preserves native joint mechanics and is easily reversible to arthrodesis.
Which of the following statements most accurately reflects the rationale behind the Morton's extension modification in orthotic management of hallux limitus?
Which of the following statements most accurately reflects the rationale behind the Morton's extension modification in orthotic management of hallux limitus?
In the context of first metatarsophalangeal joint (MTPJ) arthrodesis for hallux rigidus, what specific biomechanical complications may arise from excessive dorsiflexion of the hallux, and how are these typically managed?
In the context of first metatarsophalangeal joint (MTPJ) arthrodesis for hallux rigidus, what specific biomechanical complications may arise from excessive dorsiflexion of the hallux, and how are these typically managed?
A Youngswick osteotomy, characterized by a decompression osteotomy and an Austin osteotomy with an extra parallel cut dorsally, is primarily indicated for long first metatarsals exhibiting mild ____.
A Youngswick osteotomy, characterized by a decompression osteotomy and an Austin osteotomy with an extra parallel cut dorsally, is primarily indicated for long first metatarsals exhibiting mild ____.
Chondroplasty is considered a definitive standalone surgical intervention for hallux rigidus, effectively addressing its underlying biomechanical etiologies.
Chondroplasty is considered a definitive standalone surgical intervention for hallux rigidus, effectively addressing its underlying biomechanical etiologies.
When evaluating a patient with hallux rigidus, which radiographic finding is most indicative of a late-stage degenerative joint process according to the Drago, Oloff, & Jacobs classification?
When evaluating a patient with hallux rigidus, which radiographic finding is most indicative of a late-stage degenerative joint process according to the Drago, Oloff, & Jacobs classification?
Describe the critical steps involved in performing an orthotic casting for a patient with functional hallux limitus, emphasizing the importance of subtalar joint (STJ) and midtarsal joint manipulation.
Describe the critical steps involved in performing an orthotic casting for a patient with functional hallux limitus, emphasizing the importance of subtalar joint (STJ) and midtarsal joint manipulation.
In cases of hallux rigidus, performing a Keller resection arthroplasty in a patient with continued external rotation could result in metatarsalgia, unless the patient is ______.
In cases of hallux rigidus, performing a Keller resection arthroplasty in a patient with continued external rotation could result in metatarsalgia, unless the patient is ______.
A Lapidus procedure is contraindicated in patients presenting with a structurally normal first metatarsal, irrespective of the severity of their hallux rigidus.
A Lapidus procedure is contraindicated in patients presenting with a structurally normal first metatarsal, irrespective of the severity of their hallux rigidus.
Which statement best characterizes the primary limitation associated with the use of first metatarsophalangeal joint (MTPJ) implant arthroplasty in the management of advanced hallux rigidus?
Which statement best characterizes the primary limitation associated with the use of first metatarsophalangeal joint (MTPJ) implant arthroplasty in the management of advanced hallux rigidus?
Detail the surgical technique and expected biomechanical outcomes of a Kessel-Bonney osteotomy for hallux rigidus, including its specific advantages and potential complications.
Detail the surgical technique and expected biomechanical outcomes of a Kessel-Bonney osteotomy for hallux rigidus, including its specific advantages and potential complications.
In the context of arthrodiastasis for hallux rigidus, the procedure aims to nourish cartilage via disuse of the subchondral plate, giving the cartilage a ______.
In the context of arthrodiastasis for hallux rigidus, the procedure aims to nourish cartilage via disuse of the subchondral plate, giving the cartilage a ______.
Reverse Morton's extension is designed to limit first ray plantarflexion.
Reverse Morton's extension is designed to limit first ray plantarflexion.
What is the typical sequence of management for a 71-year-old obese female patient (Case #1) presenting with late-stage 3 hallux rigidus, ankle equinus, and concurrent naviculocuneiform (NC) joint arthrosis?
What is the typical sequence of management for a 71-year-old obese female patient (Case #1) presenting with late-stage 3 hallux rigidus, ankle equinus, and concurrent naviculocuneiform (NC) joint arthrosis?
A 66-year-old female presents with hallux limitus after a previous bunion surgery for the right foot. What distinct clinical and radiographic findings would suggest a diagnosis of 'functional limitus' as opposed to structural rigidus in this patient?
A 66-year-old female presents with hallux limitus after a previous bunion surgery for the right foot. What distinct clinical and radiographic findings would suggest a diagnosis of 'functional limitus' as opposed to structural rigidus in this patient?
Which surgical treatment of hallux rigidus would be the least appropriate for a long 1st metatarsal bone with mild presentation of MPE?
Which surgical treatment of hallux rigidus would be the least appropriate for a long 1st metatarsal bone with mild presentation of MPE?
An 80-year-old is being seen for post-op treatment on their left foot. The patient tells you they sought a 2nd opinion but was treated elsewhere. The radiographic results show MTPJ has 5 degrees of motion w/ a hallux extensus as well as sub 2nd metatarsal pain. What treatment options are available?
An 80-year-old is being seen for post-op treatment on their left foot. The patient tells you they sought a 2nd opinion but was treated elsewhere. The radiographic results show MTPJ has 5 degrees of motion w/ a hallux extensus as well as sub 2nd metatarsal pain. What treatment options are available?
For a patient with hallux rigidus caused by pronation leading to dorsiflexion of the first metatarsal, a foot orthotic would need to ___ the first metatarsal to reduce the symptoms.
For a patient with hallux rigidus caused by pronation leading to dorsiflexion of the first metatarsal, a foot orthotic would need to ___ the first metatarsal to reduce the symptoms.
Which of the following arthroplasty procedures is least suited for an active athlete?
Which of the following arthroplasty procedures is least suited for an active athlete?
A first MTPJ implant arthroplasty with a large discrepancy in the modulus of elasticity in comparison to cobalt chromiums biomechanical structure could cause long-term sesamoiditis due to the stress fractures the discrepancy may cause.
A first MTPJ implant arthroplasty with a large discrepancy in the modulus of elasticity in comparison to cobalt chromiums biomechanical structure could cause long-term sesamoiditis due to the stress fractures the discrepancy may cause.
State three different radiographic findings that would cause a doctor to identify a patient as having hallux rigidus.
State three different radiographic findings that would cause a doctor to identify a patient as having hallux rigidus.
Match each stage of the Drago, Oloff, & Jacobs Classification with its corresponding treatment consideration.
Match each stage of the Drago, Oloff, & Jacobs Classification with its corresponding treatment consideration.
In order to determine the amount of motion available at a patients 1st MTPJ you assess the range of motion. What numbers (in degrees) should the ROM be to identify normal ROM?
In order to determine the amount of motion available at a patients 1st MTPJ you assess the range of motion. What numbers (in degrees) should the ROM be to identify normal ROM?
Functional hallux limitus shows decreased hallux dorsiflexion only when the forefoot is unloaded.
Functional hallux limitus shows decreased hallux dorsiflexion only when the forefoot is unloaded.
Arthrodial joints aid movement with ___.
Arthrodial joints aid movement with ___.
Identify which cases in series of 5 would be most appropriate for you to use custom methods rather than over-the-counter (OTC) methods.
Identify which cases in series of 5 would be most appropriate for you to use custom methods rather than over-the-counter (OTC) methods.
Match the treatment plan that coincides with what pathology is occurring.
Match the treatment plan that coincides with what pathology is occurring.
What causes the proximal phalanx sublux plantarly?
What causes the proximal phalanx sublux plantarly?
Compression occurs at the beginning range of motion.
Compression occurs at the beginning range of motion.
When a patient has a painful 1st metatarsophalangeal joint, the strategy is to ___ range of motion.
When a patient has a painful 1st metatarsophalangeal joint, the strategy is to ___ range of motion.
A 29-year-old presents but "isn't exactly sure" what surgery they received on their foot. They have had the surgery, have limited dorsiflexion, mal-positioned implant, lytic changes and poor patient selection. As a doctor, what issues do you know you will face when creating a treatment plan?
A 29-year-old presents but "isn't exactly sure" what surgery they received on their foot. They have had the surgery, have limited dorsiflexion, mal-positioned implant, lytic changes and poor patient selection. As a doctor, what issues do you know you will face when creating a treatment plan?
Match the following surgical procedures with their primary purpose in addressing hallux rigidus:
Match the following surgical procedures with their primary purpose in addressing hallux rigidus:
Which of the following factors in the assessment of hallux rigidus are related to etiology of the disease? (Select all that apply)
Which of the following factors in the assessment of hallux rigidus are related to etiology of the disease? (Select all that apply)
In the context of first MTPJ biomechanics, which statement most accurately describes the functional interplay between the windlass mechanism and the role of the plantar aponeurosis during the propulsive phase of gait, considering the influence of subtalar joint (STJ) pronation and its impact on first ray stability and MTPJ dorsiflexion?
In the context of first MTPJ biomechanics, which statement most accurately describes the functional interplay between the windlass mechanism and the role of the plantar aponeurosis during the propulsive phase of gait, considering the influence of subtalar joint (STJ) pronation and its impact on first ray stability and MTPJ dorsiflexion?
In the context of hallux rigidus etiopathogenesis, the presence of metatarsus primus elevatus invariably implies a structurally fixed sagittal plane deformity, categorically precluding any functional biomechanical influence or compensatory mechanism.
In the context of hallux rigidus etiopathogenesis, the presence of metatarsus primus elevatus invariably implies a structurally fixed sagittal plane deformity, categorically precluding any functional biomechanical influence or compensatory mechanism.
In patients presenting with hallux rigidus, describe the parameters for differentiating a Youngswick osteotomy candidate from a Kessel & Bonney candidate.
In patients presenting with hallux rigidus, describe the parameters for differentiating a Youngswick osteotomy candidate from a Kessel & Bonney candidate.
The Drago, Oloff, & Jacobs Classification of Hallux Rigidus categorizes Stage 4 as ______.
The Drago, Oloff, & Jacobs Classification of Hallux Rigidus categorizes Stage 4 as ______.
Match each surgical procedure for hallux rigidus with its primary biomechanical goal:
Match each surgical procedure for hallux rigidus with its primary biomechanical goal:
What is the normal range of motion (ROM) for the first metatarsophalangeal joint (MTPJ)?
What is the normal range of motion (ROM) for the first metatarsophalangeal joint (MTPJ)?
Hallux rigidus is characterized by an increased range of motion in the first MTP joint.
Hallux rigidus is characterized by an increased range of motion in the first MTP joint.
Which of the following is a characteristic radiographic finding associated with hallux rigidus?
Which of the following is a characteristic radiographic finding associated with hallux rigidus?
Elevation of the first metatarsal, known as metatarsus primus __________, is a potential cause of hallux rigidus.
Elevation of the first metatarsal, known as metatarsus primus __________, is a potential cause of hallux rigidus.
Match each stage of the Drago, Oloff, & Jacobs classification of hallux rigidus with its corresponding characteristic:
Match each stage of the Drago, Oloff, & Jacobs classification of hallux rigidus with its corresponding characteristic:
According to the Drago, Oloff, & Jacobs classification, which stage of hallux rigidus involves obliteration of the joint space?
According to the Drago, Oloff, & Jacobs classification, which stage of hallux rigidus involves obliteration of the joint space?
Orthotics are generally considered to be more effective for structural hallux rigidus than for functional hallux limitus.
Orthotics are generally considered to be more effective for structural hallux rigidus than for functional hallux limitus.
Which of the following is a common surgical treatment option for hallux rigidus?
Which of the following is a common surgical treatment option for hallux rigidus?
What is the primary goal of performing a cheilectomy in the treatment of hallux rigidus?
What is the primary goal of performing a cheilectomy in the treatment of hallux rigidus?
Which of the following is a characteristic of functional hallux limitus?
Which of the following is a characteristic of functional hallux limitus?
A Youngswick osteotomy is primarily performed to lengthen the first metatarsal.
A Youngswick osteotomy is primarily performed to lengthen the first metatarsal.
Which of the following best describes the purpose of arthrodiastasis in treating hallux rigidus?
Which of the following best describes the purpose of arthrodiastasis in treating hallux rigidus?
A Keller resection arthroplasty involves:
A Keller resection arthroplasty involves:
A Lapidus procedure primarily addresses pathology at the metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint.
A Lapidus procedure primarily addresses pathology at the metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint.
In the context of orthotic management for hallux rigidus, what is the purpose of a reverse Morton's extension?
In the context of orthotic management for hallux rigidus, what is the purpose of a reverse Morton's extension?
The term 'metatarsus primus _________' refers to the elevation of the first metatarsal bone.
The term 'metatarsus primus _________' refers to the elevation of the first metatarsal bone.
Which of the following represents a joint-destructive procedure for hallux rigidus?
Which of the following represents a joint-destructive procedure for hallux rigidus?
The primary motion at the first MTPJ is purely a rolling motion.
The primary motion at the first MTPJ is purely a rolling motion.
Which of the following is NOT a potential etiology of hallux rigidus?
Which of the following is NOT a potential etiology of hallux rigidus?
According to one presentation slide, what type of implant is noted to potentially sink into the metaphyseal bone?
According to one presentation slide, what type of implant is noted to potentially sink into the metaphyseal bone?
What is a potential complication associated with a Keller resection arthroplasty, involving pain in the lesser metatarsals?
What is a potential complication associated with a Keller resection arthroplasty, involving pain in the lesser metatarsals?
A Lapidus procedure is commonly performed to directly address pathology within the first MTPJ.
A Lapidus procedure is commonly performed to directly address pathology within the first MTPJ.
What range of motion at the 1st MTPJ could indicate the need for joint-destructive treatment?
What range of motion at the 1st MTPJ could indicate the need for joint-destructive treatment?
In orthotic casting for hallux rigidus, plantarflexing the first ray is _________ to first ray function.
In orthotic casting for hallux rigidus, plantarflexing the first ray is _________ to first ray function.
Which of the following surgical procedures for hallux rigidus involves the removal of osteophytes from the metatarsal head and proximal phalanx?
Which of the following surgical procedures for hallux rigidus involves the removal of osteophytes from the metatarsal head and proximal phalanx?
A 'V' cut in the sagittal plane removing the majority of the MTPJ characterizes the Keller procedure.
A 'V' cut in the sagittal plane removing the majority of the MTPJ characterizes the Keller procedure.
Among the presented surgical treatment options for hallux rigidus, which is LEAST likely to be performed in isolation?
Among the presented surgical treatment options for hallux rigidus, which is LEAST likely to be performed in isolation?
Which of the following surgical options for hallux rigidus is particularly indicated for adolescents?
Which of the following surgical options for hallux rigidus is particularly indicated for adolescents?
What is the 'gold standard' surgical treatment for hallux rigidus?
What is the 'gold standard' surgical treatment for hallux rigidus?
A 71-year-old female presents with right foot pain. Examination reveals no ROM with forefoot loaded, 40° when unloaded, pain at the dorsal aspect on palpation and mild crepitus. Radiographs reveal 1st MTPJ arthrosis and NC arthrosis w/sag. According to the Drago, Oloff and Jacobs Classification, in which stage does this patient fall within?
A 71-year-old female presents with right foot pain. Examination reveals no ROM with forefoot loaded, 40° when unloaded, pain at the dorsal aspect on palpation and mild crepitus. Radiographs reveal 1st MTPJ arthrosis and NC arthrosis w/sag. According to the Drago, Oloff and Jacobs Classification, in which stage does this patient fall within?
A 63-year-old female presents with left big toe joint pain, smoker, and left 1st MTPJ has 15° of motion loaded and unloaded. Radiographs show 1st MTPJ Arthosis and the patient presents with Structural Rigidus. According to the Drago, Oloff and Jacobs Classification, in which stage does this patient fall within?
A 63-year-old female presents with left big toe joint pain, smoker, and left 1st MTPJ has 15° of motion loaded and unloaded. Radiographs show 1st MTPJ Arthosis and the patient presents with Structural Rigidus. According to the Drago, Oloff and Jacobs Classification, in which stage does this patient fall within?
According to one slide, the most common complication associated with the Keller Procedure is ________ ________.
According to one slide, the most common complication associated with the Keller Procedure is ________ ________.
Which of the following is NOT a known cause of Subsidence (Sinking of the implant into the metaphyseal bone)?
Which of the following is NOT a known cause of Subsidence (Sinking of the implant into the metaphyseal bone)?
The valenti procedure indicates low functional requirements for patients similar to the Keller procedure.
The valenti procedure indicates low functional requirements for patients similar to the Keller procedure.
What is the main property a Synthetic Cartilage Graft helps mimic?
What is the main property a Synthetic Cartilage Graft helps mimic?
Which of the following is NOT considered an indication for Cheilectomy?
Which of the following is NOT considered an indication for Cheilectomy?
Normal motion during propulsion at the first MTPJ switches from rolling to ________ after the initial 20-30 degrees.
Normal motion during propulsion at the first MTPJ switches from rolling to ________ after the initial 20-30 degrees.
When performing orthotic casting, which joint is the user supposed to being with?
When performing orthotic casting, which joint is the user supposed to being with?
What is the benefit of Osteomed Encompass?
What is the benefit of Osteomed Encompass?
The integra Movement Great Toe uses a cement material.
The integra Movement Great Toe uses a cement material.
Which type of joint is the 1st MTPJ?
Which type of joint is the 1st MTPJ?
Normal 1st MTPJ ROM is 45-55 degrees.
Normal 1st MTPJ ROM is 45-55 degrees.
Which of the following is NOT a requirement for normal 1st MTPJ ROM?
Which of the following is NOT a requirement for normal 1st MTPJ ROM?
Elevation of the first metatarsal is also known as metatarsus primus ______.
Elevation of the first metatarsal is also known as metatarsus primus ______.
Why is the term 'hallux limitus' employed?
Why is the term 'hallux limitus' employed?
Functional hallux limitus presents decreased hallux dorsiflexion regardless of whether the forefoot is loaded or unloaded.
Functional hallux limitus presents decreased hallux dorsiflexion regardless of whether the forefoot is loaded or unloaded.
Which of the following biomechanical factors contributes to Hallux Rigidus?
Which of the following biomechanical factors contributes to Hallux Rigidus?
List three common findings associated with Hallux Rigidus.
List three common findings associated with Hallux Rigidus.
Which radiographic finding is characteristic of Hallux Rigidus?
Which radiographic finding is characteristic of Hallux Rigidus?
In the Drago, Oloff, & Jacobs Classification, Stage 1 is known as Joint Deterioration.
In the Drago, Oloff, & Jacobs Classification, Stage 1 is known as Joint Deterioration.
According to the Drago, Oloff, & Jacobs Classification, which stage typically presents with limited dorsiflexion with weightbearing but normal ROM with non-weight-bearing?
According to the Drago, Oloff, & Jacobs Classification, which stage typically presents with limited dorsiflexion with weightbearing but normal ROM with non-weight-bearing?
In Stage 2: Adaptation of the Drago, Oloff, & Jacobs Classification, ______ of the first metatarsal head is observed.
In Stage 2: Adaptation of the Drago, Oloff, & Jacobs Classification, ______ of the first metatarsal head is observed.
According to the Drago, Oloff, & Jacobs Classification, what is the treatment for Stage 1: Functional Limitus?
According to the Drago, Oloff, & Jacobs Classification, what is the treatment for Stage 1: Functional Limitus?
A treatment goal of an orthotic for hallux rigidus is to decrease ROM of a painful 1st MTPJ to mimic fusion.
A treatment goal of an orthotic for hallux rigidus is to decrease ROM of a painful 1st MTPJ to mimic fusion.
Which of the following surgical treatments is classified as a joint-destructive procedure?
Which of the following surgical treatments is classified as a joint-destructive procedure?
Removal of osteophytes from the metatarsal head and proximal phalanx, known as a ______, can be the primary procedure in surgical treatment.
Removal of osteophytes from the metatarsal head and proximal phalanx, known as a ______, can be the primary procedure in surgical treatment.
Which of the following is most useful with long 1st metatarsals and mild elevatus?
Which of the following is most useful with long 1st metatarsals and mild elevatus?
Chondroplasty is commonly performed in isolation to address Hallux Rigidus.
Chondroplasty is commonly performed in isolation to address Hallux Rigidus.
A 'V' cut in the sagittal plane removing the majority of the MTPJ describes what procedure?
A 'V' cut in the sagittal plane removing the majority of the MTPJ describes what procedure?
Why do patients develop central metatarsalgia with Keller procedures?
Why do patients develop central metatarsalgia with Keller procedures?
Which of the following is the 'gold standard' for hallux rigidus surgical treatment?
Which of the following is the 'gold standard' for hallux rigidus surgical treatment?
Patients typically like double fusions (1st MTPJ and 1st TMTJ).
Patients typically like double fusions (1st MTPJ and 1st TMTJ).
A Lapidus procedure is indicated to address which structural problem?
A Lapidus procedure is indicated to address which structural problem?
In orthotic casting, plantarflexing the first ray to remove supinatus/forefoot varus is ______ to first ray function.
In orthotic casting, plantarflexing the first ray to remove supinatus/forefoot varus is ______ to first ray function.
A reverse Morton's extension aims to achieve what?
A reverse Morton's extension aims to achieve what?
Match each Drago, Oloff, & Jacobs Classification stage with its description:
Match each Drago, Oloff, & Jacobs Classification stage with its description:
Which statement is most accurate regarding orthotics and hallux rigidus?
Which statement is most accurate regarding orthotics and hallux rigidus?
A first ray that is too plantarflexed can create hallux IPJ pain or arthrosis.
A first ray that is too plantarflexed can create hallux IPJ pain or arthrosis.
Which statement is consistent with a Stage 4 hallux rigidus?
Which statement is consistent with a Stage 4 hallux rigidus?
In the context of hallux rigidus surgical treatment, why is positioning critical for proper function post operatively?
In the context of hallux rigidus surgical treatment, why is positioning critical for proper function post operatively?
What is the primary goal of arthrodiastasis in treating hallux rigidus?
What is the primary goal of arthrodiastasis in treating hallux rigidus?
When performing the orthotic casting, it is important to start with the ______ joint in neutral position.
When performing the orthotic casting, it is important to start with the ______ joint in neutral position.
A Morton's extension aims to plantarflex the hallux.
A Morton's extension aims to plantarflex the hallux.
What is a major concern regarding 1st MTPJ implant arthroplasty?
What is a major concern regarding 1st MTPJ implant arthroplasty?
Valenti considers the V cut in the sagittal plane a joint salvage procedure.
Valenti considers the V cut in the sagittal plane a joint salvage procedure.
A patient presents with mild hallux limitus and a slightly elevated 1st metatarsal. What surgical procedure might be considered?
A patient presents with mild hallux limitus and a slightly elevated 1st metatarsal. What surgical procedure might be considered?
Aside from structural considerations, what else should be considered when performing a Keller?
Aside from structural considerations, what else should be considered when performing a Keller?
Which surgical treatment addresses cartilage erosions, but is rarely done in isolation?
Which surgical treatment addresses cartilage erosions, but is rarely done in isolation?
Hallux limitus and rigidus are progressive disorders of the first ______ joints.
Hallux limitus and rigidus are progressive disorders of the first ______ joints.
Explain how positioning is critical for 1st MTPJ fusion.
Explain how positioning is critical for 1st MTPJ fusion.
After reviewing X-rays, you decide with the patient to do a decompression option as opposed to a joint destructive option. All of the options fall under which surgical treatment?
After reviewing X-rays, you decide with the patient to do a decompression option as opposed to a joint destructive option. All of the options fall under which surgical treatment?
Which of the following is NOT a common finding in patients with Hallux Rigidus?
Which of the following is NOT a common finding in patients with Hallux Rigidus?
A Morton's extension is used to plantarflex the hallux and decreases the range of motion (ROM) of the 1st MTPJ.
A Morton's extension is used to plantarflex the hallux and decreases the range of motion (ROM) of the 1st MTPJ.
According to the Drago, Oloff, & Jacobs Classification, which stage of hallux rigidus involves obliteration of the joint space, exuberant dorsal osteophytes, and less than 10 degrees of ROM?
According to the Drago, Oloff, & Jacobs Classification, which stage of hallux rigidus involves obliteration of the joint space, exuberant dorsal osteophytes, and less than 10 degrees of ROM?
In the context of orthotic casting for hallux rigidus, plantarflexing the first ray to remove supinatus/forefoot varus is considered ______ to first ray function.
In the context of orthotic casting for hallux rigidus, plantarflexing the first ray to remove supinatus/forefoot varus is considered ______ to first ray function.
Match the surgical procedures with their primary characteristics:
Match the surgical procedures with their primary characteristics:
What type of joint is the first metatarsophalangeal joint (MTPJ)?
What type of joint is the first metatarsophalangeal joint (MTPJ)?
Normal ROM of the 1st MTPJ is in the range of 85-95°.
Normal ROM of the 1st MTPJ is in the range of 85-95°.
Which motion predominantly occurs during the first 20-30° of hallux dorsiflexion?
Which motion predominantly occurs during the first 20-30° of hallux dorsiflexion?
Hallux limitus is characterized by a complete absence of motion in the first MTP joint.
Hallux limitus is characterized by a complete absence of motion in the first MTP joint.
Elevation of the first metatarsal (metatarsus primus elevatus) in hallux rigidus causes the proximal phalanx of the hallux to do what?
Elevation of the first metatarsal (metatarsus primus elevatus) in hallux rigidus causes the proximal phalanx of the hallux to do what?
Which of the following best differentiates functional hallux limitus from structural hallux rigidus?
Which of the following best differentiates functional hallux limitus from structural hallux rigidus?
In structural hallux rigidus, decreased hallux dorsiflexion is only present when the forefoot is loaded.
In structural hallux rigidus, decreased hallux dorsiflexion is only present when the forefoot is loaded.
Which of the following is considered a functional (biomechanical) etiology of hallux rigidus?
Which of the following is considered a functional (biomechanical) etiology of hallux rigidus?
What radiographic finding indicative of hallux rigidus presents as a bony growth on the dorsal aspect of the metatarsal head?
What radiographic finding indicative of hallux rigidus presents as a bony growth on the dorsal aspect of the metatarsal head?
According to the Drago, Oloff, & Jacobs Classification, Stage I hallux limitus is characterized by limited dorsiflexion with weightbearing but normal ______ with non-weight-bearing.
According to the Drago, Oloff, & Jacobs Classification, Stage I hallux limitus is characterized by limited dorsiflexion with weightbearing but normal ______ with non-weight-bearing.
Match the Drago, Oloff, & Jacobs Classification stages with their descriptions:
Match the Drago, Oloff, & Jacobs Classification stages with their descriptions:
Which of the following is a characteristic radiographic finding in Stage 2 (Adaptation) of the Drago, Oloff, & Jacobs Classification for hallux rigidus?
Which of the following is a characteristic radiographic finding in Stage 2 (Adaptation) of the Drago, Oloff, & Jacobs Classification for hallux rigidus?
In stage 4 (Ankylosis) of the Drago, Oloff, & Jacobs classification, joint-salvage procedures are typically the recommended treatment.
In stage 4 (Ankylosis) of the Drago, Oloff, & Jacobs classification, joint-salvage procedures are typically the recommended treatment.
According to the treatment algorithm suggested, which of the following procedures is typically recommended for addressing peripheral osteophytosis in hallux rigidus?
According to the treatment algorithm suggested, which of the following procedures is typically recommended for addressing peripheral osteophytosis in hallux rigidus?
What surgical procedure involves joint clean up, and removal of osteophytes from the metatarsal head and proximal phalanx?
What surgical procedure involves joint clean up, and removal of osteophytes from the metatarsal head and proximal phalanx?
Which of the following statements is true regarding cheilectomy?
Which of the following statements is true regarding cheilectomy?
During orthotic casting, plantar-flexing the first ray to remove supinatus/forefoot varus is recommended.
During orthotic casting, plantar-flexing the first ray to remove supinatus/forefoot varus is recommended.
What is the main goal of using a reverse Morton's extension in orthotic management?
What is the main goal of using a reverse Morton's extension in orthotic management?
What is the primary effect of a Morton’s extension on the hallux?
What is the primary effect of a Morton’s extension on the hallux?
A Youngswick osteotomy involves an Austin osteotomy and an extra parallel cut ______.
A Youngswick osteotomy involves an Austin osteotomy and an extra parallel cut ______.
Kessel & Bonney osteotomies are contraindicated in adolescents.
Kessel & Bonney osteotomies are contraindicated in adolescents.
What surgical procedure involves external fixation with a mini-rail to stretch periarticular soft-tissue structure for hallux rigidus?
What surgical procedure involves external fixation with a mini-rail to stretch periarticular soft-tissue structure for hallux rigidus?
Why is chondroplasty rarely performed in isolation for hallux rigidus?
Why is chondroplasty rarely performed in isolation for hallux rigidus?
What is the biggest risk associated with a Valenti procedure?
What is the biggest risk associated with a Valenti procedure?
A Keller procedure involves resection of the base of the ______ phalanx.
A Keller procedure involves resection of the base of the ______ phalanx.
A common complication of a Keller procedure is central metatarsalgia.
A common complication of a Keller procedure is central metatarsalgia.
Which of these is NOT a common concern with 1st MTPJ implant arthroplasty:
Which of these is NOT a common concern with 1st MTPJ implant arthroplasty:
What is a common complication with synthetic cartilage grafts?
What is a common complication with synthetic cartilage grafts?
What is often considered the 'gold standard' for hallux rigidus surgical treatment?
What is often considered the 'gold standard' for hallux rigidus surgical treatment?
Patients DO like double fusions (1st MTPJ and 1st TMTJ)
Patients DO like double fusions (1st MTPJ and 1st TMTJ)
Case #1: A 71-year-old female presents for treatment of her right foot pain. 1st MTPJ has no ROM with forefoot loaded and 40 degrees when unloaded. What stage of hallux rigidus is the patient most likely in?
Case #1: A 71-year-old female presents for treatment of her right foot pain. 1st MTPJ has no ROM with forefoot loaded and 40 degrees when unloaded. What stage of hallux rigidus is the patient most likely in?
Case #1: A 71-year-old female presents for treatment of her right foot pain. 1st MTPJ has no ROM with forefoot loaded and 40 degrees when unloaded. What conservative treatment options could be prescribed?
Case #1: A 71-year-old female presents for treatment of her right foot pain. 1st MTPJ has no ROM with forefoot loaded and 40 degrees when unloaded. What conservative treatment options could be prescribed?
Case #2: A 66-year-old female presents for treatment of her right big toe joint pain. The patients first MTPJ has no ROM with forefoot loaded/50° when unloaded. What orthotics should be prescribed?
Case #2: A 66-year-old female presents for treatment of her right big toe joint pain. The patients first MTPJ has no ROM with forefoot loaded/50° when unloaded. What orthotics should be prescribed?
Case #3: A 63-year-old female presents for treatment of her left big toe joint pain. The patient is a smoker with a 15-degree ROM of her left first MTPJ loaded and unloaded, and there is pain with the ROM and some crepitus. What pathology is most likely present?
Case #3: A 63-year-old female presents for treatment of her left big toe joint pain. The patient is a smoker with a 15-degree ROM of her left first MTPJ loaded and unloaded, and there is pain with the ROM and some crepitus. What pathology is most likely present?
Case #4: A 29-year-old female presents for treatment of her right big toe joint pain. She states that she had a prior big toe joint surgery. The patient is found to be mal-positioned with Short 1st metatarsal and complains of pain throughout the rotation and 2nd metatarsal pain. What pathology is most likely present?
Case #4: A 29-year-old female presents for treatment of her right big toe joint pain. She states that she had a prior big toe joint surgery. The patient is found to be mal-positioned with Short 1st metatarsal and complains of pain throughout the rotation and 2nd metatarsal pain. What pathology is most likely present?
What is the best course of action to take if the cartilage won't last long rubbing on metal?
What is the best course of action to take if the cartilage won't last long rubbing on metal?
A patient with Hallux Valgus will be a common situation?
A patient with Hallux Valgus will be a common situation?
What is not considered as a challenge for patients under case#4?
What is not considered as a challenge for patients under case#4?
Which factor will determine appropriate treatment option and strategy
Which factor will determine appropriate treatment option and strategy
What is a recommended conservative treatment choice to begin with
What is a recommended conservative treatment choice to begin with
Which of the following is NOT typically a learning objective related to hallux rigidus?
Which of the following is NOT typically a learning objective related to hallux rigidus?
Hallux limitus is characterized by complete range of motion (ROM) at the first metatarsophalangeal joint (MTPJ).
Hallux limitus is characterized by complete range of motion (ROM) at the first metatarsophalangeal joint (MTPJ).
What type of joint is the first MTPJ?
What type of joint is the first MTPJ?
In the normal first MTPJ range of motion, the ginglymus joint facilitates a ______ joint.
In the normal first MTPJ range of motion, the ginglymus joint facilitates a ______ joint.
During normal propulsion, first ray plantarflexion changes the motion of the first MTPJ to a rolling motion.
During normal propulsion, first ray plantarflexion changes the motion of the first MTPJ to a rolling motion.
What is the approximate degree of normal range of motion (ROM) at the first MTPJ?
What is the approximate degree of normal range of motion (ROM) at the first MTPJ?
Which of the following aids is associated with the shape of the first metatarsal head?
Which of the following aids is associated with the shape of the first metatarsal head?
Normal first MTPJ range of motion requires an absent intact plantar aponeurosis (Windlass).
Normal first MTPJ range of motion requires an absent intact plantar aponeurosis (Windlass).
In hallux rigidus, elevation of the first metatarsal can lead to what?
In hallux rigidus, elevation of the first metatarsal can lead to what?
What term is sometimes used when some movement is still available in the first MTP joint, as opposed to complete rigidity?
What term is sometimes used when some movement is still available in the first MTP joint, as opposed to complete rigidity?
Hallux limitus is always structural and never functional.
Hallux limitus is always structural and never functional.
Which of the following is characteristic of structural hallux rigidus?
Which of the following is characteristic of structural hallux rigidus?
Which of the following is a common biomechanical etiology of hallux rigidus?
Which of the following is a common biomechanical etiology of hallux rigidus?
Metatarsus primus elevatus is best described as a ______ etiology related to Hallux Rigidus.
Metatarsus primus elevatus is best described as a ______ etiology related to Hallux Rigidus.
Hallux Rigidus can sometimes be caused iatrogenically due to a previous surgery.
Hallux Rigidus can sometimes be caused iatrogenically due to a previous surgery.
Which of the following is a common clinical finding associated with hallux rigidus?
Which of the following is a common clinical finding associated with hallux rigidus?
What radiographic finding provides indication of Hallux Rigidus?
What radiographic finding provides indication of Hallux Rigidus?
According to the Drago, Oloff, & Jacobs Classification, Stage I hallux limitus exhibits severe flattening of the metatarsal head.
According to the Drago, Oloff, & Jacobs Classification, Stage I hallux limitus exhibits severe flattening of the metatarsal head.
Which of the Drago, Oloff, & Jacobs Classification stages is characterized by obliteration of joint space?
Which of the Drago, Oloff, & Jacobs Classification stages is characterized by obliteration of joint space?
According to the Drago, Oloff, & Jacobs Classification, a Joint- ______ procedure is indicated in a Stage 1: Functional Limitus.
According to the Drago, Oloff, & Jacobs Classification, a Joint- ______ procedure is indicated in a Stage 1: Functional Limitus.
What is the primary difference between stage 2 and stage 3 of the Drago, Oloff, & Jacobs Classification?
What is the primary difference between stage 2 and stage 3 of the Drago, Oloff, & Jacobs Classification?
Severe flattening of the first metatarsal head is a characteristic of hallux rigidus in Stage 3: Deterioration of the Drago, Oloff, & Jacobs Classification.
Severe flattening of the first metatarsal head is a characteristic of hallux rigidus in Stage 3: Deterioration of the Drago, Oloff, & Jacobs Classification.
In the treatment algorithm for hallux rigidus, which stage typically indicates the need for a joint-destructive procedure?
In the treatment algorithm for hallux rigidus, which stage typically indicates the need for a joint-destructive procedure?
Which of the following is a goal of orthotic management for hallux rigidus?
Which of the following is a goal of orthotic management for hallux rigidus?
A Morton's extension is used to plantarflex the hallux
A Morton's extension is used to plantarflex the hallux
Plantarflexing the first ray to remove supinatus/forefoot varus is ______ to first ray function.
Plantarflexing the first ray to remove supinatus/forefoot varus is ______ to first ray function.
What type of orthotic modification allows the first ray to plantarflex more?
What type of orthotic modification allows the first ray to plantarflex more?
Which of the following is a joint salvage procedure for hallux rigidus?
Which of the following is a joint salvage procedure for hallux rigidus?
Which of the following is not related to Cheilectomy?
Which of the following is not related to Cheilectomy?
A cheilectomy increases joint movement, creating greater movement of an arthritic joint, which results in less pain.
A cheilectomy increases joint movement, creating greater movement of an arthritic joint, which results in less pain.
A Youngswick osteotomy is most useful with which presentation?
A Youngswick osteotomy is most useful with which presentation?
A Kessel & Bonney procedure is used for what procedure?
A Kessel & Bonney procedure is used for what procedure?
Arthrodiastasis stretches periaritucular structures using what implant?
Arthrodiastasis stretches periaritucular structures using what implant?
Chondroplasty should be done in isolation
Chondroplasty should be done in isolation
The Valenti procedure is similar to which of the following joint destructive options?
The Valenti procedure is similar to which of the following joint destructive options?
The Keller procedure includes ______ of the base of the proximal phalanx.
The Keller procedure includes ______ of the base of the proximal phalanx.
A 1st MTPJ Implant Arthroplasty addresses the biomechanical pathology that caused the rigidus by utilizing what feature on the implant?
A 1st MTPJ Implant Arthroplasty addresses the biomechanical pathology that caused the rigidus by utilizing what feature on the implant?
1st MTPJ Fusion is considered a temporary treatment option for hallux rigidus.
1st MTPJ Fusion is considered a temporary treatment option for hallux rigidus.
Which of the following is a potential complication of malpositioning in 1st MTPJ arthrodesis?
Which of the following is a potential complication of malpositioning in 1st MTPJ arthrodesis?
A Lapidus procedure realigns a structurally pathologic 1st ______.
A Lapidus procedure realigns a structurally pathologic 1st ______.
What is the average amount of motion a normal MTP1 should have unloaded?
What is the average amount of motion a normal MTP1 should have unloaded?
During an orthotic casting, why is important to plantarflex 1st ray?
During an orthotic casting, why is important to plantarflex 1st ray?
Ankle equinus is a possible pathology to see in MTP1 arthrosis .
Ankle equinus is a possible pathology to see in MTP1 arthrosis .
Which property does the 1st synthetic cartilage implant aim to mimic?
Which property does the 1st synthetic cartilage implant aim to mimic?
The best treatment is usually a [BLANK] to the 1st MTP joint
The best treatment is usually a [BLANK] to the 1st MTP joint
Which of the following classifications is used to categorize hallux rigidus?
Which of the following classifications is used to categorize hallux rigidus?
In functional hallux limitus, hallux dorsiflexion is decreased regardless of whether the forefoot is loaded or unloaded.
In functional hallux limitus, hallux dorsiflexion is decreased regardless of whether the forefoot is loaded or unloaded.
What is the normal range of motion (ROM) in degrees for the first metatarsophalangeal joint?
What is the normal range of motion (ROM) in degrees for the first metatarsophalangeal joint?
Elevation of the first metatarsal, also known as metatarsus primus ______, can cause the proximal phalanx of the hallux to sublux plantarly.
Elevation of the first metatarsal, also known as metatarsus primus ______, can cause the proximal phalanx of the hallux to sublux plantarly.
Which of these surgical treatments for hallux rigidus involves removing osteophytes from the metatarsal head and proximal phalanx, potentially increasing joint movement, but may also increase pain if the joint is already deteriorated?
Which of these surgical treatments for hallux rigidus involves removing osteophytes from the metatarsal head and proximal phalanx, potentially increasing joint movement, but may also increase pain if the joint is already deteriorated?
In the context of normal first MTPJ biomechanics during gait, which statement MOST accurately delineates the interplay between rolling and sliding motions during hallux dorsiflexion?
In the context of normal first MTPJ biomechanics during gait, which statement MOST accurately delineates the interplay between rolling and sliding motions during hallux dorsiflexion?
According to biomechanical etiologies of hallux rigidus, which of the following scenarios represents the MOST complex interaction of contributing factors, integrating both structural and functional components?
According to biomechanical etiologies of hallux rigidus, which of the following scenarios represents the MOST complex interaction of contributing factors, integrating both structural and functional components?
When assessing radiographic findings of hallux rigidus, what is the MOST discerning characteristic that differentiates between stages of the condition, indicating progression from adaptation to joint deterioration?
When assessing radiographic findings of hallux rigidus, what is the MOST discerning characteristic that differentiates between stages of the condition, indicating progression from adaptation to joint deterioration?
In the context of hallux rigidus development, which statement BEST describes the complex biomechanical consequences stemming primarily from excessive pronation during the propulsive phase of gait?
In the context of hallux rigidus development, which statement BEST describes the complex biomechanical consequences stemming primarily from excessive pronation during the propulsive phase of gait?
According to the Drago, Oloff, and Jacobs classification, which feature signifies the transition from Stage II (Adaptation) to Stage III (Deterioration) in hallux rigidus?
According to the Drago, Oloff, and Jacobs classification, which feature signifies the transition from Stage II (Adaptation) to Stage III (Deterioration) in hallux rigidus?
When contemplating surgical strategies for a high-demand athlete presenting with early-stage hallux rigidus and a congruent joint, what is the MOST critical factor in determining whether to proceed with a joint-sparing versus joint-sacrificing procedure?
When contemplating surgical strategies for a high-demand athlete presenting with early-stage hallux rigidus and a congruent joint, what is the MOST critical factor in determining whether to proceed with a joint-sparing versus joint-sacrificing procedure?
In the context of surgical management for hallux rigidus, which statement underlines a core principle behind performing a decompression osteotomy?
In the context of surgical management for hallux rigidus, which statement underlines a core principle behind performing a decompression osteotomy?
In an intraoperative cheilectomy, which technical execution poses the greatest risk of iatrogenic destabilization of the first MTP joint, potentially exacerbating progression of hallux rigidus?
In an intraoperative cheilectomy, which technical execution poses the greatest risk of iatrogenic destabilization of the first MTP joint, potentially exacerbating progression of hallux rigidus?
When evaluating a patient for a Youngswick osteotomy, which of the following represents the MOST critical radiographic inclusion criteria to optimize outcomes?
When evaluating a patient for a Youngswick osteotomy, which of the following represents the MOST critical radiographic inclusion criteria to optimize outcomes?
In the decision-making process for surgical intervention with hallux rigidus, which represents the MOST significant limitation of a Kessel & Bonney procedure?
In the decision-making process for surgical intervention with hallux rigidus, which represents the MOST significant limitation of a Kessel & Bonney procedure?
Considering the physiological rationale of arthrodiastasis, which statement accurately describes how cartilage healing is promoted?
Considering the physiological rationale of arthrodiastasis, which statement accurately describes how cartilage healing is promoted?
What is the primary biomechanical rationale behind the avoidance of chondroplasty as a standalone surgical procedure?
What is the primary biomechanical rationale behind the avoidance of chondroplasty as a standalone surgical procedure?
With respect to joint destructive procedures for hallux rigidus, which surgical intervention MOST severely compromises the biomechanical integrity of the first ray, leading to predictable sequelae?
With respect to joint destructive procedures for hallux rigidus, which surgical intervention MOST severely compromises the biomechanical integrity of the first ray, leading to predictable sequelae?
How do synthetic cartilage grafts attempt to facilitate improved joint function?
How do synthetic cartilage grafts attempt to facilitate improved joint function?
When performing a first MTPJ fusion, what is the MOST detrimental technical error that could potentially lead to significant post-operative morbidity and functional deficits?
When performing a first MTPJ fusion, what is the MOST detrimental technical error that could potentially lead to significant post-operative morbidity and functional deficits?
In the treatment of hallux rigidus, what represents the MOST significant technical challenge in a Lapidus procedure?
In the treatment of hallux rigidus, what represents the MOST significant technical challenge in a Lapidus procedure?
Considering the initial non-surgical management for the 71-year-old female patient with late-stage hallux rigidus (Case #1), which addition represents the most biomechanically sound approach in addressing her collective pathologies?
Considering the initial non-surgical management for the 71-year-old female patient with late-stage hallux rigidus (Case #1), which addition represents the most biomechanically sound approach in addressing her collective pathologies?
In the 66-year-old female with hallux limitus following a previous bunion surgery (Case #2), what clinical and radiographic findings most strongly support a diagnosis of functional limitus?
In the 66-year-old female with hallux limitus following a previous bunion surgery (Case #2), what clinical and radiographic findings most strongly support a diagnosis of functional limitus?
Given the clinical presentation of the 63-year-old smoker with 15° of motion at the first MTPJ (Case #3), what represents the critical consideration when determining appropriate treatment?
Given the clinical presentation of the 63-year-old smoker with 15° of motion at the first MTPJ (Case #3), what represents the critical consideration when determining appropriate treatment?
When planning the revision strategy of a 29-year-old female with a mal-positioned implant, lytic changes, and considering bone stock and age (Case #4), what represents the MOST definitive surgical approach?
When planning the revision strategy of a 29-year-old female with a mal-positioned implant, lytic changes, and considering bone stock and age (Case #4), what represents the MOST definitive surgical approach?
Which revisional surgery is the best course of action for the elderly patient in Case #5 who presents status post surgeries presenting with a hallux extensus with a pain score?
Which revisional surgery is the best course of action for the elderly patient in Case #5 who presents status post surgeries presenting with a hallux extensus with a pain score?
The MTPJ joint’s main function involves transitioning from rolling to ____ as the first ray begins to plantarflex and provide adequate toe-off.
The MTPJ joint’s main function involves transitioning from rolling to ____ as the first ray begins to plantarflex and provide adequate toe-off.
What is the main role for the sesamoids?
What is the main role for the sesamoids?
If pain is present at end range of the MTPJ and small dorsal exostosis begins to arise, then what degree of hallux limitus is occurring?
If pain is present at end range of the MTPJ and small dorsal exostosis begins to arise, then what degree of hallux limitus is occurring?
The following criteria encompass the treatment considerations for functional vs structural hallux limitus. Which example would best be treated using custom orthotics?
The following criteria encompass the treatment considerations for functional vs structural hallux limitus. Which example would best be treated using custom orthotics?
If a pronated foot causes dorsiflexion then an orthotic needs to ___ the first metatarsal?
If a pronated foot causes dorsiflexion then an orthotic needs to ___ the first metatarsal?
Keller Arthroplasty is a salvage procedure of the first MTP joint, what is the biggest complication?
Keller Arthroplasty is a salvage procedure of the first MTP joint, what is the biggest complication?
As a doctor, what is the reasoning why we use arthrodiastasis to clean up the MTP Joint?
As a doctor, what is the reasoning why we use arthrodiastasis to clean up the MTP Joint?
Synthetic cartilage grafts attempt to mimic the modulus elasticity of actual cartilage. A common complication is ____?
Synthetic cartilage grafts attempt to mimic the modulus elasticity of actual cartilage. A common complication is ____?
What is a contraindication of a Cheilectomy?
What is a contraindication of a Cheilectomy?
After a Cheilectomy, drilling the subchondral bone is a must, what does the doctor hope that stimulation will promote?
After a Cheilectomy, drilling the subchondral bone is a must, what does the doctor hope that stimulation will promote?
There are a lot of surgical options for hallux rigidus, what is regarded as the most successful?
There are a lot of surgical options for hallux rigidus, what is regarded as the most successful?
According to the Drago, Oloff and Jacobs classification, what symptoms would a late stages patient exude?
According to the Drago, Oloff and Jacobs classification, what symptoms would a late stages patient exude?
If a 75-year-old female presents with stage 4 findings what procedure should the Doctor consider?
If a 75-year-old female presents with stage 4 findings what procedure should the Doctor consider?
The first ray and big toe move in a certain motion during a normal gait cycle. During the neutral position if the STJ is locked is the forefoot varus?
The first ray and big toe move in a certain motion during a normal gait cycle. During the neutral position if the STJ is locked is the forefoot varus?
What amount of dorsiflexion is required after MTPJ fusion for proper function?
What amount of dorsiflexion is required after MTPJ fusion for proper function?
Why is it important to know whether a surgeon should choose an arthroplasty or arthrodesis?
Why is it important to know whether a surgeon should choose an arthroplasty or arthrodesis?
Does a patient with functional hallux limitus have pain with ROM?
Does a patient with functional hallux limitus have pain with ROM?
With end ROM or long periods of weight bearing a hallux rigidus patient may experience some pain. When using a Mortons extension, why is that used at that point for the hallux rigidus joint?
With end ROM or long periods of weight bearing a hallux rigidus patient may experience some pain. When using a Mortons extension, why is that used at that point for the hallux rigidus joint?
What issues are we most likely to face from a surgical procedure with uncertain details?
What issues are we most likely to face from a surgical procedure with uncertain details?
How to you correct an elevated first metatarsal?
How to you correct an elevated first metatarsal?
What aspect of the Youngswick osteotomy MOST significantly mitigates the risk of iatrogenic complications directly linked to sagittal plane malalignment of the first metatarsal?
What aspect of the Youngswick osteotomy MOST significantly mitigates the risk of iatrogenic complications directly linked to sagittal plane malalignment of the first metatarsal?
Considering the complexities of arthrodiastasis, what is the MOST critical parameter to monitor throughout the entire treatment duration in order to maximize chondrogenic potential while concurrently averting irreversible joint subluxation or avascular necrosis?
Considering the complexities of arthrodiastasis, what is the MOST critical parameter to monitor throughout the entire treatment duration in order to maximize chondrogenic potential while concurrently averting irreversible joint subluxation or avascular necrosis?
In order to precisely titrate the degree of plantarflexion achieved during a first MTPJ arthrodesis for end-stage hallux rigidus, what adjunctive assessment technique MOST effectively optimizes subsequent gait biomechanics and attenuates the potential for secondary complications arising from sagittal plane malalignment?
In order to precisely titrate the degree of plantarflexion achieved during a first MTPJ arthrodesis for end-stage hallux rigidus, what adjunctive assessment technique MOST effectively optimizes subsequent gait biomechanics and attenuates the potential for secondary complications arising from sagittal plane malalignment?
When considering the utilization of interpositional arthroplasty for hallux rigidus, what is the MOST accurate and complete description of a universally recognized shortcoming inherent to numerous implant designs that directly contributes to implant subsidence and subsequent adjacent joint degeneration?
When considering the utilization of interpositional arthroplasty for hallux rigidus, what is the MOST accurate and complete description of a universally recognized shortcoming inherent to numerous implant designs that directly contributes to implant subsidence and subsequent adjacent joint degeneration?
A patient presents with hallux rigidus attributed to a pathologically long first metatarsal in relation to the second, showing concomitant structural pronation of the foot. From a biomechanical perspective, which surgical approach would most comprehensively address the underlying pathomechanics while concurrently optimizing first MTPJ kinetics?
A patient presents with hallux rigidus attributed to a pathologically long first metatarsal in relation to the second, showing concomitant structural pronation of the foot. From a biomechanical perspective, which surgical approach would most comprehensively address the underlying pathomechanics while concurrently optimizing first MTPJ kinetics?
In orthotic fabrication for functional hallux limitus, what biomechanical rationale underlies the strategic implementation of a reverse Morton's extension, assuming a hypermobile first ray complicated by a flexible forefoot valgus?
In orthotic fabrication for functional hallux limitus, what biomechanical rationale underlies the strategic implementation of a reverse Morton's extension, assuming a hypermobile first ray complicated by a flexible forefoot valgus?
When contemplating first MTPJ implant arthroplasty for hallux rigidus, what pre-operative imaging modality would MOST definitively influence the surgeon's decision-making process regarding implant selection, anatomical restoration, and potential for future revision?
When contemplating first MTPJ implant arthroplasty for hallux rigidus, what pre-operative imaging modality would MOST definitively influence the surgeon's decision-making process regarding implant selection, anatomical restoration, and potential for future revision?
Which intervention provides the MOST favorable biomechanical trade-off between motion preservation and prevention of altered gait mechanics in a high-performance athlete presenting with hallux rigidus?
Which intervention provides the MOST favorable biomechanical trade-off between motion preservation and prevention of altered gait mechanics in a high-performance athlete presenting with hallux rigidus?
A 63-year-old moderately active smoker presents with stage 3 hallux rigidus characterized by structural rigidus, MTPJ arthrosis, and crepitus throughout range of motion. Which initial treatment option should MOST importantly be considered, factoring in the patient’s smoking history?
A 63-year-old moderately active smoker presents with stage 3 hallux rigidus characterized by structural rigidus, MTPJ arthrosis, and crepitus throughout range of motion. Which initial treatment option should MOST importantly be considered, factoring in the patient’s smoking history?
In the context of first MTPJ range of motion (ROM), what biomechanical event necessitates the transition from roll to slide mechanics after the first 20-30° of hallux dorsiflexion during gait?
In the context of first MTPJ range of motion (ROM), what biomechanical event necessitates the transition from roll to slide mechanics after the first 20-30° of hallux dorsiflexion during gait?
Concerning the management of end-stage hallux rigidus with a Keller resection arthroplasty, what intraoperative step is MOST critical to ensure long-term first ray stability and prevent detrimental proximal migration of the hallux, mitigating potential transfer lesions in the adjacent metatarsals?
Concerning the management of end-stage hallux rigidus with a Keller resection arthroplasty, what intraoperative step is MOST critical to ensure long-term first ray stability and prevent detrimental proximal migration of the hallux, mitigating potential transfer lesions in the adjacent metatarsals?
What BEST describes the biomechanical impact of the Lapidus procedure when utilized in the context of hallux rigidus concurrent with underlying structural instability?
What BEST describes the biomechanical impact of the Lapidus procedure when utilized in the context of hallux rigidus concurrent with underlying structural instability?
Within the spectrum of joint-sparing interventions for hallux rigidus, under which specific condition might arthrodiastasis be MOST strongly considered as a potentially viable intervention?
Within the spectrum of joint-sparing interventions for hallux rigidus, under which specific condition might arthrodiastasis be MOST strongly considered as a potentially viable intervention?
When evaluating a patient with hallux rigidus, which clinical sign would MOST strongly contraindicate an isolated cheilectomy as a viable long-term solution?
When evaluating a patient with hallux rigidus, which clinical sign would MOST strongly contraindicate an isolated cheilectomy as a viable long-term solution?
When performing orthotic casting for functional hallux limitus, what hands-on manuver is MOST crucial to optimize first ray function during the casting process?
When performing orthotic casting for functional hallux limitus, what hands-on manuver is MOST crucial to optimize first ray function during the casting process?
Assuming adequate decompression during a planned cheilectomy for hallux rigidus, what intraoperative assessment MOST reliably confirms the achieved potential for augmented range of motion?
Assuming adequate decompression during a planned cheilectomy for hallux rigidus, what intraoperative assessment MOST reliably confirms the achieved potential for augmented range of motion?
In instances of hallux rigidus stemming from metatarsus primus elevatus, which surgical measure offers the MOST biomechanically sound approach to re-establish first ray purchase during gait propulsion, whilst simultaneously rectifying sagittal plane malalignment?
In instances of hallux rigidus stemming from metatarsus primus elevatus, which surgical measure offers the MOST biomechanically sound approach to re-establish first ray purchase during gait propulsion, whilst simultaneously rectifying sagittal plane malalignment?
Considering the functional anatomy of the first ray, what primary pathomechanical effect is induced by an excessively rigid plantar fascia, irrespective of the presence or absence of hallux limitus?
Considering the functional anatomy of the first ray, what primary pathomechanical effect is induced by an excessively rigid plantar fascia, irrespective of the presence or absence of hallux limitus?
In cases of hallux rigidus, what statement accurately describes the role of the peroneus longus tendon in preventing development of hallux rigidus?
In cases of hallux rigidus, what statement accurately describes the role of the peroneus longus tendon in preventing development of hallux rigidus?
What best characterizes the biomechanical sequence within the first metatarsophalangeal joint (MTPJ) during normal dorsiflexion?
What best characterizes the biomechanical sequence within the first metatarsophalangeal joint (MTPJ) during normal dorsiflexion?
What key operative steps are required to perform a Youngswick osteotomy for hallux limitus, emphasizing the need to maintain intrinsic stability and prevent iatrogenic complications?
What key operative steps are required to perform a Youngswick osteotomy for hallux limitus, emphasizing the need to maintain intrinsic stability and prevent iatrogenic complications?
Match each surgical measure for hallux rigidus with its primary biomechanical goal:
Match each surgical measure for hallux rigidus with its primary biomechanical goal:
After a cheilectomy, drilling the subchondral bone stimulates bleeding to promote what event?
After a cheilectomy, drilling the subchondral bone stimulates bleeding to promote what event?
What direction, in relation to the weight bearing surface, should a surgeon aim to plantarflex the first ray to enhance weight-bearing and reduce first MTP joint load?
What direction, in relation to the weight bearing surface, should a surgeon aim to plantarflex the first ray to enhance weight-bearing and reduce first MTP joint load?
With MTPJ fusion, indicate the correct amount of dorsiflexion required in degrees.
With MTPJ fusion, indicate the correct amount of dorsiflexion required in degrees.
Following cheilectomy for hallux rigidus, what specific treatment stimulates fibrocartilage production?
Following cheilectomy for hallux rigidus, what specific treatment stimulates fibrocartilage production?
A hallux rigidus patient diagnosed with a long first metatarsal in relation to the second exhibits signs of functional hallux limitus. What is the MOST effective offloading strategy?
A hallux rigidus patient diagnosed with a long first metatarsal in relation to the second exhibits signs of functional hallux limitus. What is the MOST effective offloading strategy?
Which statement accurately delineates the biomechanical differences within the first metatarsophalangeal joint (MTPJ) during normal dorsiflexion?
Which statement accurately delineates the biomechanical differences within the first metatarsophalangeal joint (MTPJ) during normal dorsiflexion?
Regarding the goal associated with cheilectomies for joint clean up, what statement holds TRUE?
Regarding the goal associated with cheilectomies for joint clean up, what statement holds TRUE?
For the Youngswick osteotomy, characterized by a decompression osteotomy and an Austin osteotomy with an extra parallel cut dorsally, which of the following scenarios is primarily indicated for this osteotomy?
For the Youngswick osteotomy, characterized by a decompression osteotomy and an Austin osteotomy with an extra parallel cut dorsally, which of the following scenarios is primarily indicated for this osteotomy?
According to the literature, what is the result of reverse Mortons extension in realtion to first ray mechanics?
According to the literature, what is the result of reverse Mortons extension in realtion to first ray mechanics?
What is not a known cause of Subsidence (Sinking of the implant into the metaphyseal bone)?
What is not a known cause of Subsidence (Sinking of the implant into the metaphyseal bone)?
For a patient diagnosed with hallux rigidus because of pronation leading to the dorsiflexion of the first metatarsal. How would you create a foot orthotic to reduce the halllucal symptoms?
For a patient diagnosed with hallux rigidus because of pronation leading to the dorsiflexion of the first metatarsal. How would you create a foot orthotic to reduce the halllucal symptoms?
When it comes to MTPJ fusion, the positioning is what to ensure proper alignment?
When it comes to MTPJ fusion, the positioning is what to ensure proper alignment?
As the primary procedure, when is Chondroplasty MOST likely to be successful?
As the primary procedure, when is Chondroplasty MOST likely to be successful?
According to the normal anatomy of 1st ray with the windlass mechanism during gait, the hallux is restricted more, with less dorsiflexion with excess plantarflexion.
According to the normal anatomy of 1st ray with the windlass mechanism during gait, the hallux is restricted more, with less dorsiflexion with excess plantarflexion.
When selecting between metallic hemi-implants for first MTPJ arthroplasty, which is the MOST pertinent advantage of a dorsal elevation design?
When selecting between metallic hemi-implants for first MTPJ arthroplasty, which is the MOST pertinent advantage of a dorsal elevation design?
In the context of interpositional arthroplasty for hallux rigidus, a significant limitation of synthetic cartilage implant designs is what?
In the context of interpositional arthroplasty for hallux rigidus, a significant limitation of synthetic cartilage implant designs is what?
In the context of surgical planning for hallux rigidus, what represents the MOST critical biomechanical consideration when determining the degree of plantarflexion during a first metatarsophalangeal joint (MTPJ) arthrodesis to minimize the risk of adjacent joint degeneration and optimize long-term gait mechanics?
In the context of surgical planning for hallux rigidus, what represents the MOST critical biomechanical consideration when determining the degree of plantarflexion during a first metatarsophalangeal joint (MTPJ) arthrodesis to minimize the risk of adjacent joint degeneration and optimize long-term gait mechanics?
In the case of a 29-year-old female with hallux rigidus secondary to a mal-positioned implant and bone loss, which surgical option balances the need for bone grafting, structural stability, and functional restoration?
In the case of a 29-year-old female with hallux rigidus secondary to a mal-positioned implant and bone loss, which surgical option balances the need for bone grafting, structural stability, and functional restoration?
For an 80-year-old patient, previously treated with multiple surgeries, now presenting with pain and hallux extensus with limited range of motion, what is the MOST appropriate strategy?
For an 80-year-old patient, previously treated with multiple surgeries, now presenting with pain and hallux extensus with limited range of motion, what is the MOST appropriate strategy?
In stage III hallux rigidus, which surgical intervention is most appropriate according to the text?
In stage III hallux rigidus, which surgical intervention is most appropriate according to the text?
When performing orthotic casting for hallux limitus, achieving adequate plantarflexion of the first ray requires meticulous attention to concurrent biomechanical variables; what specific combination of joint manipulations is critical to ensure optimal first ray plantarflexion and accurate capture of forefoot-to-rearfoot relationship during the casting process?
When performing orthotic casting for hallux limitus, achieving adequate plantarflexion of the first ray requires meticulous attention to concurrent biomechanical variables; what specific combination of joint manipulations is critical to ensure optimal first ray plantarflexion and accurate capture of forefoot-to-rearfoot relationship during the casting process?
Flashcards
Hallux Rigidus
Hallux Rigidus
A progressive disorder of the first MTP joint with diminished ROM and degenerative alterations.
Normal 1st MTPJ ROM
Normal 1st MTPJ ROM
Rolling motion for initial dorsiflexion, transitioning to sliding motion after first ray plantarflexion.
Functional Hallux Limitus
Functional Hallux Limitus
Decreased hallux dorsiflexion occurs only when the forefoot is loaded.
Structural Hallux Rigidus
Structural Hallux Rigidus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Metatarsus Primus Elevatus
Metatarsus Primus Elevatus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Functional Etiologies of Hallux Rigidus
Functional Etiologies of Hallux Rigidus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Structural Etiologies of Hallux Rigidus
Structural Etiologies of Hallux Rigidus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hallux Rigidus
Hallux Rigidus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Drago, Oloff, & Jacobs Stage I
Drago, Oloff, & Jacobs Stage I
Signup and view all the flashcards
Drago, Oloff, & Jacobs Stage II
Drago, Oloff, & Jacobs Stage II
Signup and view all the flashcards
Drago, Oloff, & Jacobs Stage III
Drago, Oloff, & Jacobs Stage III
Signup and view all the flashcards
Drago, Oloff, & Jacobs Stage IV
Drago, Oloff, & Jacobs Stage IV
Signup and view all the flashcards
Orthotic Management
Orthotic Management
Signup and view all the flashcards
Reverse Morton's Extension
Reverse Morton's Extension
Signup and view all the flashcards
Morton's Extension
Morton's Extension
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cheilectomy
Cheilectomy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Youngswick Osteotomy
Youngswick Osteotomy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kessel & Bonney
Kessel & Bonney
Signup and view all the flashcards
Arthrodiastasis
Arthrodiastasis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chondroplasty
Chondroplasty
Signup and view all the flashcards
Valenti Procedure
Valenti Procedure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Keller Procedure
Keller Procedure
Signup and view all the flashcards
1st MTPJ Fusion
1st MTPJ Fusion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lapidus Procedure
Lapidus Procedure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ginglymoarthrodial Joint
Ginglymoarthrodial Joint
Signup and view all the flashcards
1st Metatarsal Head Shape
1st Metatarsal Head Shape
Signup and view all the flashcards
Orthotic Casting
Orthotic Casting
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chondroplasty Implication
Chondroplasty Implication
Signup and view all the flashcards
1st MTPJ Implant Arthroplasty
1st MTPJ Implant Arthroplasty
Signup and view all the flashcards
Synthetic Cartilage Grafts: Subsidence
Synthetic Cartilage Grafts: Subsidence
Signup and view all the flashcards
1st MTPJ Rolling Motion
1st MTPJ Rolling Motion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Metatarsus primus elevatus consequence
Metatarsus primus elevatus consequence
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hallux Limitus
Hallux Limitus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Reverse Morton's Extension Action
Reverse Morton's Extension Action
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cheilectomy procedure
Cheilectomy procedure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lapidus
Lapidus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hallux Rigidus: Osteophytes
Hallux Rigidus: Osteophytes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Drago, Oloff & Jacobs Classification
Drago, Oloff & Jacobs Classification
Signup and view all the flashcards
Arthrodial Joint
Arthrodial Joint
Signup and view all the flashcards
Normal 1st MTPJ ROM Range
Normal 1st MTPJ ROM Range
Signup and view all the flashcards
Subchondral Drilling
Subchondral Drilling
Signup and view all the flashcards
Orthotic modification: Plantarflex 1st Met
Orthotic modification: Plantarflex 1st Met
Signup and view all the flashcards
Youngswick Distal Osteotomy
Youngswick Distal Osteotomy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kessel & Bonney indication
Kessel & Bonney indication
Signup and view all the flashcards
Post-Keller Metatarsalgia
Post-Keller Metatarsalgia
Signup and view all the flashcards
MTPJ Fusion Complication
MTPJ Fusion Complication
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lapidus Procedure Goal
Lapidus Procedure Goal
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ginglymus Joint
Ginglymus Joint
Signup and view all the flashcards
Normal ROM of 1st MTPJ
Normal ROM of 1st MTPJ
Signup and view all the flashcards
Requirements for Normal 1st MTPJ ROM
Requirements for Normal 1st MTPJ ROM
Signup and view all the flashcards
Compression
Compression
Signup and view all the flashcards
Orthotic Management Goals
Orthotic Management Goals
Signup and view all the flashcards
Critical step in orthotic casting
Critical step in orthotic casting
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cheilectomy definition
Cheilectomy definition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- Case Based Medicine: Hallux Limitus, Hallux Rigidus Presentation by Jarrod Smith, DPM, FACFAS, Assistant Professor at Des Moines University College of Podiatric Medicine and Surgery
Learning Objectives
- Understand typical first ray anatomy and function
- Have knowledge of the etiologies and radiographic findings of hallux rigidus
- Understand the role pronation plays in hallux rigidus
- Know the Drago, Oloff & Jacobs classification of hallux rigidus
- Understand surgical treatment options for hallux rigidus
- Know about postoperative management of hallux rigidus procedures
Normal First MTPJ ROM
- The first MTPJ is a ginglymoarthrodial joint
- Ginglymus joints are hinge joints
- The first 20-30 degrees of hallux dorsiflexion is a rolling motion
- Arthrodial joints are sliding joints
- First ray plantarflexion changes the motion to a sliding motion for the remainder of propulsion
- Compression occurs at the end range of motion
- Normal ROM is 65-75 degrees
- The first metatarsal head is cam-shaped which aids in rolling, sliding, and compression
Normal First MTPJ ROM Requirements
- First ray plantarflexion is needed
- STJ supination is required
- Normal parabola involves the second metatarsal being longer than the first
- Normal intrinsic/extrinsic muscle function is needed
- Normal sesamoid function
- Intact proximal phalangeal base (Windlass) is required
- Intact plantar aponeurosis (Windlass) is required
Hallux Rigidus
- Hallux Rigidus is a progressive disorder of the first MTP joint
- Characterized by diminished ROM and degenerative alterations of the joint
- Elevation of the first metatarsal (metatarsus primus elevatus) causes the proximal phalanx of the hallux to sublux plantarly, causing (hallux equinus/flexus)
- Because some movement is generally available the term hallux limitus is used
- Only 25-30 degrees are possible without first ray plantarflexion
Functional vs Structural Hallux Limitus
- Functional hallux limitus is flexible
- Decreased hallux dorsiflexion only when the forefoot is loaded
- Responds well to orthotic management
- Structural hallux rigidus is fixed
- Decreased hallux dorsiflexion with the forefoot loaded and unloaded
- Orthotics have limited utility
Hallux Rigidus Etiology
- Functional biomechanical etiologies include
- Dorsiflexion of the first metatarsal
- Pronation
- First ray hypermobility
- Weak peroneus longus
- Structural etiologies include
- Metatarsus primus elevatus
- Long first metatarsal/short second metatarsal
- Long hallux proximal phalanx
- Iatrogenic causes include previous surgery
- Trauma and arthritides (gout, RA)
Hallux Rigidus Common Findings
- Pain in the joint
- Limited motion at the first MTPJ
- Dorsal bump on the first metatarsal head
- Dorsal bunion
- Hypermobility of the hallux IPJ
- Plantar callus at the IPJ
- Metatarsus primus elevatus
- Metatarsalgia leading to lateral dumping
Hallux Rigidus Radiographic Findings
- Dorsal osteophytic formation
- First metatarsal head (flag sign) and/or base of the proximal phalanx
- Metatarsus primus elevatus
- First MTP joint space narrowing
- Flattening of the first metatarsal head
- Subchondral sclerosis
- Pronatory changes in the foot
Drago, Oloff, & Jacobs Classification
- Stage I: Functional Limitus includes
- Limited dorsiflexion with weightbearing but normal ROM with non-weight-bearing
- Little/no degenerative changes
- Biomechanical derangement (pronation)
- First ray insufficiency
- Metatarsus primus elevatus
- Hallux equinus
- Hyperextension of the hallux IPJ
- Treatment typically involves a joint-salvage procedure
- Stage 2: Adaptation presents as
- Flattening of the first metatarsal head
- Osteochondral defect
- Cartilage fibrillation/erosion
- Pain on end ROM
- Limited passive ROM
- Small dorsal exostosis
- Subchondral sclerosis
- Periarticular lipping of the first metatarsal head, proximal phalanx, & sesamoids
- Treatment is joint-salvage procedure
- Stage 3: Deterioration has
- Severe flattening of the first metatarsal head
- Dorsal osteophytosis
- Asymmetric joint space narrowing
- Degeneration of articular cartilage
- Crepitus
- Subchondral cystic formation
- Pain on full ROM
- Treated with Joint-Salvage or Joint-Destructive procedure
- Stage 4: Ankylosis includes
- Obliteration of joint space
- Exuberant dorsal osteophytosis w/ loose bodies
- < 10° ROM
- Degeneration of articular cartilage
- Deformity/Malalignment
- Total ankylosis
- Treated with Joint-Destructive procedure
Hallux Rigidus Treatment Options
- Conservative treatment
- Functional Treatment
- Orthotic management, Physical therapy, Plantarflexion strengthening, Joint mobilization
- Adjunct Treatment has limited utility without functional treatment
- NSAIDs, Injections
- Orthotic casting involves:
- Starting with subtalar joint in neutral position
- Locking the midtarsal joint by applying a dorsiflexory force to the 4th/5th met heads
- Holding the STJ in neutral with the midtarsal joint locked with one hand & plantarflex the first ray with the other
- Plantarflexing the first ray, removing supinatus/forefoot varus which is critical to first ray function
- Goals of orthotic treatment:
- Increase ROM of the first MTPJ by correcting the biomechanics
- Plantarflex the first metatarsal by raising the arch and increasing metatarsal declination to reverse Morton's extension
- Decrease ROM of a painful first MTPJ = mimicking a fusion by dorsiflexing the hallux using a morton's extension
- Reverse Morton's Extension allows the first ray to plantarflex more if able, and increases ROM of the first MTPJ
- Morton's Extension: Dorsiflexes the hallux and decreases ROM of the 1st MTPJ
Hallux Rigidus Surgical Treatment Options
- Surgical treatment may involve:
- Joint salvage procedures
- Cheilectomy
- Decompression osteotomy
- Youngswick - distal metatarsal osteotomy
- Kessel & Bonney- phalangeal osteotomy
- Arthrodiastasis
- Chondroplasty which is rarely used in isolation
- Joint clean up procedure involves removal of osteophytosis from the metatarsal head and proximal phalanx
- Can be coupled with chondroplasty if a chondral defect is present
- Drilling of subchondral bone stimulates bleeding which may lead to fibrocartilaginous ingrowth
- Increases joint movement which increases movement of an arthritic joint which may increase pain if the joint is deteriorated
- This should be presented to patients as a “stop gap" procedure, but if it ends up being definitive treatment, then that's great
- Needing to progress to a fusion shouldn't be shocking
- Youngswick, is a type of decompression osteotomy
- Austin osteotomy with an extra parallel cut dorsally
- Allows for shortening and plantarflexion
- Most useful with long 1st metatarsals (same length as 2nd or longer) and mild elevatus
- Kessel & Bonney osteotomy is a type of decompression osteotomy which:
- Changes the posture of the hallux
- Is indicated for adolescents early on then indications expanded to adults
- May make revision fusion more difficult due to prominent plantar phalangeal base
- Arthrodiastasis involves external fixation with a mini-rail
- Stretches periarticular soft-tissue structure, and gives cartilage a “rest”
- Hypothesized that cartilage is nourished via disuse osteopenia of the subchondral plate
- Chondroplasty addresses cartilage erosions that are often present, but it is rarely done in isolation biomechanical cause is not addressed
Hallux Rigidus, Destructive Procedures
- Resection arthroplasty
- Valenti
- Keller
- Interpositional implant arthroplasty
- Hemi-implants
- Silastic implants
- Cartiva
- Total joint replacement
- First MTPJ arthrodesis
- Lapidus
- Valenti involves a V cut in the sagittal plan removing the majority of the MTPJ
- Some may consider this a joint salvage procedure, although this may be disagreed with
- Revision to a fusion would be very difficult
- The indications are the same as a Keller, and indicated for patients with low functional requirements
- Keller involves resection of the base of the proximal phalanx
- Considering what normal 1st MTPJ ROM requires
- Only indicated in patients with low functional requirements
- Most common complication is central metatarsalgia. The question is why?
- Should not be said in rotation unless the patient is non-ambulatory
First MTPJ Implant Arthroplasty
- Requires bone resection for implantation
- Sub second metatarsalgia is a very common complication
- Large discrepancy in the modulus of elasticity of cartilage vs cobalt chromium
- Fails to address the biomechanical pathology that caused the rigidus
- Makes revision to a fusion more difficult
Synthetic Cartilage Graft
- Is the first implant to mimic the modulus of elasticity of cartilage
- Subsidence is a very common complication where the implant sinks into the metaphyseal bone, and happens quite rapidly
Specific Revision System
- There are revision systems designed to address failures of destructive procedures
First MTPJ Fusion
- Is the "gold standard" for hallux rigidus surgical treatment
- Definitive
- Positioning is critical for proper function post-operatively
- Too dorsiflexed leads to hallux malleus
- Too plantarflexed equals hallux IPJ pain/arthrosis
- A joint is painful when it moves, so it can't hurt if it doesn't move, however malposition will create other problems
Lapidus
- Realigns a structurally pathologic first metatarsal
- Shortens the first ray thus “decompresses” the joint
- Need a very clean first MTPJ
- Patients do NOT like double fusions (1st MTPJ and 1st TMTJ)
Case 1
- Involves a 71-year-old female presents for treatment of her right foot pain
- Her past medical history includes obesity
- Examination shows:
- Her pulses are palpable, and sensorium is intact
- First MTPJ has no ROM with forefoot loaded and/or 40° when unloaded
- The first MTPJ is painful at the dorsal aspect on palpation
- Reveals mild crepitus and pain on palpation of the midfoot with mild edema
- Pathology includes 1st MTPJ arthrosis, NC arthrosis w/ sag, and equinus
- The stage is late stage 3
- Treatment options include OTC orthotics to start, a stretching regimen, next step to custom orthotics, 1st MTPJ and/or NC fusion
Case 2
- Involves a 66-year-old female who presents for treatment of her right big toe joint pain
- Her past medical history includes prior bunion surgery on the right 2 years ago
- The Podiatrist who performed the original surgery is recommending fusion, and she is here for a 2nd opinion
- Examination shows:
- Pulses are palpable and sensorium is intact
- The 1st MTPJ has no ROM with forefoot loaded and exhibits 50° when unloaded
- The joint is painful at the dorsal aspect on palpation and there is no crepitus
- Pathology includes functional limitus and NC sag, and the stage is 2
- Treatment options include OTC orthotics or next step custom orthotics
Case 3
- Involves a 63-year-old female who presents for treatment of her left big toe joint pain
- Her past medical history includes smoking about half a pack a day for 20 years
- Otherwise, she is unremarkable
- Examination shows:
- Pulses are palpable and sensorium is intact
- Left 1st MTPJ has 15° of motion loaded and unloaded
- The joint is painful throughout ROM w/ crepitus
- Pathology includes 1st MTPJ arthrosis and structural rigidus
- The stage is 3
Case 4
- Involves a 29-year-old female presenting for treatment of her right big toe joint pain
- Her past medical history includes prior big toe joint surgery but she is not exactly sure what was performed
- Otherwise, she is unremarkable
- Examination:
- Pulses are palpable and sensorium is intact
- Right 1st MTPJ has 20° of motion loaded and unloaded
- The joint is painful throughout ROM and there is sub 2nd metatarsal pain
- Has a mal-positioned implant with concerning lytic changes under the implant
- Short 1st metatarsal
- Indicating poor patient selection
- Challenges involve bone loss, erosion of the plantar phalanx, and the cartilage will not last long rubbing on metal after implant
Case 5
- Involves a 78-year-old female who presents for treatment of her left big toe joint pain
- Her past medical history includes obesity, otherwise unremarkable
- Examination:
- Pulses are palpable and sensorium is intact
- Left 1st MTPJ has 25° of motion loaded and unloaded
- The joint is painful throughout ROM at the sesamoids
- Sub 2nd metatarsal pain
- Pathology includes structural rigidus, metatarsus primus elevatus, sesamoidal arthrosis, and HAV
- The stage is 2
- The patient originally sought a 2nd opinion and was treated elsewhere, but this presentation was the follow up
- The patient is now an 80-year-old female presenting for treatment of her left big toe joint pain
- Her past medical history includes Hx of left foot surgery x 2, and obesity
- Otherwise, unremarkable
- Examination:
- Pulses are palpable and sensorium is intact
- Left 1st MTPJ has 5° of motion with hallux extensus
- Sub 2nd metatarsal pain
- She had a prior fusion and further bone work was performed
Copyright notice
- This presentation may contain copyrighted material used for educational purposes under the guidelines of Fair Use and the TEACH Act.
- It is intended only for use by students enrolled in this course. Reproduction or distribution is prohibited, which is a violation of the DMU Integrity Code and may also violate federal copyright protection laws.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.