Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the most common cause of acromegaly?
What is the most common cause of acromegaly?
- Somatotropin adenoma (correct)
- Bronchial carcinoid
- Pancreatic islets tumors
- Hamartoma
Laron dwarfism is associated with mutations in the growth hormone receptor.
Laron dwarfism is associated with mutations in the growth hormone receptor.
True (A)
Name one method used in GH stimulation tests.
Name one method used in GH stimulation tests.
Glucagon-mediated GH stimulation
The condition characterized by excessive growth hormone secretion is called ______.
The condition characterized by excessive growth hormone secretion is called ______.
Match the types of tumors with their association in acromegaly:
Match the types of tumors with their association in acromegaly:
What is one of the causes of pituitary apoplexy?
What is one of the causes of pituitary apoplexy?
FSH and LH deficiencies can lead to muscle wasting and loss of libido.
FSH and LH deficiencies can lead to muscle wasting and loss of libido.
What is a clinical feature of pituitary apoplexy?
What is a clinical feature of pituitary apoplexy?
In diabetes insipidus, ADH levels may be masked by __________ insufficiency.
In diabetes insipidus, ADH levels may be masked by __________ insufficiency.
Match the symptoms with their respective conditions:
Match the symptoms with their respective conditions:
Which of the following is the most common cause of acquired hypopituitarism?
Which of the following is the most common cause of acquired hypopituitarism?
Hypotension is a clinical manifestation of ACTH deficiency.
Hypotension is a clinical manifestation of ACTH deficiency.
Name one infection that can lead to acquired hypopituitarism.
Name one infection that can lead to acquired hypopituitarism.
With acquired hypopituitarism, a deficiency in __________ can lead to fatigue, weight loss, and hypotension.
With acquired hypopituitarism, a deficiency in __________ can lead to fatigue, weight loss, and hypotension.
Match the following conditions with their respective descriptions:
Match the following conditions with their respective descriptions:
What is the typical age range for GH secreting adenoma patients?
What is the typical age range for GH secreting adenoma patients?
GH secreting adenomas are more common in males than females.
GH secreting adenomas are more common in males than females.
What is a major adverse effect of GH secreting adenomas?
What is a major adverse effect of GH secreting adenomas?
Acral enlargement in GH secreting adenomas refers to the enlargement of the ______ and ______ only.
Acral enlargement in GH secreting adenomas refers to the enlargement of the ______ and ______ only.
Match the following clinical features with their descriptions:
Match the following clinical features with their descriptions:
What is the primary role of IGF-1 in relation to GH?
What is the primary role of IGF-1 in relation to GH?
GH is secreted only during rapid eye movement (REM) sleep.
GH is secreted only during rapid eye movement (REM) sleep.
List one factor that inhibits GH secretion.
List one factor that inhibits GH secretion.
GH cannot be estimated directly due to its __________ nature.
GH cannot be estimated directly due to its __________ nature.
Match the following terms with their descriptions:
Match the following terms with their descriptions:
What is a precipitating factor for Sheehan's Syndrome?
What is a precipitating factor for Sheehan's Syndrome?
Sheehan's Syndrome is caused by an increase in blood flow to the pituitary gland.
Sheehan's Syndrome is caused by an increase in blood flow to the pituitary gland.
What treatment is typically administered via IV for patients with Sheehan's Syndrome?
What treatment is typically administered via IV for patients with Sheehan's Syndrome?
Sheehan's Syndrome can lead to ______ and hypoprolactinemia.
Sheehan's Syndrome can lead to ______ and hypoprolactinemia.
Match the following conditions with their descriptions:
Match the following conditions with their descriptions:
Which sign is associated with a Rathke's cleft cyst?
Which sign is associated with a Rathke's cleft cyst?
Transsphenoidal Hypophysectomy is typically the preferred surgical option for treating pituitary macroadenomas.
Transsphenoidal Hypophysectomy is typically the preferred surgical option for treating pituitary macroadenomas.
What is the success rate of surgical resection in patients with microadenomas?
What is the success rate of surgical resection in patients with microadenomas?
If GH levels are _______ after surgery, there is a good success rate for treatment.
If GH levels are _______ after surgery, there is a good success rate for treatment.
Match the conditions with their corresponding features:
Match the conditions with their corresponding features:
Which of the following actions is NOT associated with GH?
Which of the following actions is NOT associated with GH?
IGF-1 has an anti-lipolytic effect on lipids.
IGF-1 has an anti-lipolytic effect on lipids.
What mnemonic can help remember the actions of GH that are independent of IGF-1?
What mnemonic can help remember the actions of GH that are independent of IGF-1?
The major role of IGF-1 is skeletal and cartilage growth, regulated by ______.
The major role of IGF-1 is skeletal and cartilage growth, regulated by ______.
Match the following molecules with their primary effects:
Match the following molecules with their primary effects:
Which characteristic is NOT associated with Craniopharyngioma in children?
Which characteristic is NOT associated with Craniopharyngioma in children?
Rathke's Cleft Cyst typically appears as a unilocular sellar mass.
Rathke's Cleft Cyst typically appears as a unilocular sellar mass.
What imaging technique is considered the imaging of choice (IOC) for diagnosing acromegaly?
What imaging technique is considered the imaging of choice (IOC) for diagnosing acromegaly?
In Craniopharyngioma, the presence of ________ can result in central diabetes insipidus.
In Craniopharyngioma, the presence of ________ can result in central diabetes insipidus.
Match the following features with Craniopharyngioma or Rathke's Cleft Cyst:
Match the following features with Craniopharyngioma or Rathke's Cleft Cyst:
What is a common ophthalmic feature of GH-secreting adenoma?
What is a common ophthalmic feature of GH-secreting adenoma?
Elevated triglycerides is a metabolic manifestation associated with GH-secreting adenoma.
Elevated triglycerides is a metabolic manifestation associated with GH-secreting adenoma.
Name a cardiovascular condition that has an increased risk due to GH-secreting adenoma.
Name a cardiovascular condition that has an increased risk due to GH-secreting adenoma.
GH-secreting adenomas can cause _______ syndrome, which is characterized by obstructive sleep apnea.
GH-secreting adenomas can cause _______ syndrome, which is characterized by obstructive sleep apnea.
Match the following features with their corresponding presentation in GH-secreting adenoma:
Match the following features with their corresponding presentation in GH-secreting adenoma:
Which syndrome features precocious puberty and café-au-lait spots?
Which syndrome features precocious puberty and café-au-lait spots?
Functional tumors of macroadenomas include craniopharyngiomas.
Functional tumors of macroadenomas include craniopharyngiomas.
What is one of the imaging findings associated with GH-secreting adenomas?
What is one of the imaging findings associated with GH-secreting adenomas?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Growth Hormone Pathway
- Growth hormone receptor mutation (GHR) leads to elevated GH levels but impaired receptor function, resulting in low IGF-1 levels.
- Growth Hormone (GH) Stimulation Tests are used to measure GH levels and its response to different stimuli.
- Measuring IGF-1 levels is an indirect way to evaluate GH activity.
Acromegaly Causes
- Acromegaly is caused by excessive growth hormone secretion.
- Somatotropin adenoma is the most common cause of acromegaly, accounting for 98% of cases.
- Ectopic tumors, like those in the pancreatic islets (a classical finding) or the hypothalamus, can also lead to acromegaly.
- Other ectopic tumors include bronchial carcinoid, small cell lung cancer, and medullary carcinoma of the thyroid.
Acquired Hypopituitarism
- Loss of energy/loss of libido, bone and muscle wasting are common features of FSH/LH deficiency.
- Central obesity, hypertriglyceridemia, and endothelial dysfunction are common features of GH deficiency in adults.
- Diabetes Insipidus may be masked by other hormonal deficiencies.
- Hypocortisolemia is exacerbated by thyroxine in acquired hypopituitarism.
Pituitary Apoplexy
- Pituitary apoplexy is an acute condition caused by intra-pituitary hemorrhage.
- Clinical features include progressive headache, possible meningeal signs, ophthalmoplegia, decreased blood pressure, and hypoglycemia.
GH Secreting Adenoma
- GH secreting adenomas are macroadenomas affecting individuals between 35 - 50 years old.
- They are more common in males than females.
- Prolactinomas are microadenomas affecting individuals between 25 - 40 years old and are more common in females.
- Actions of GH secreting adenomas include increased GH levels, hypopituitarism and hyperprolactinemia (stack effect), and headache, visual impairment, and cavernous sinus thrombosis (mass effect).
- Organ manifestation includes acral enlargement (peripheral enlargement without affecting brain or internal organs), and classical coarse facies.
- Histology findings distinguish between a sparsely granulated adenoma (bad prognosis) and a densely granulated adenoma (good prognosis).
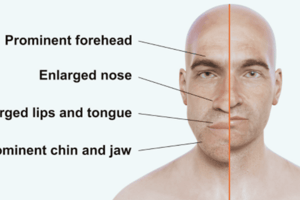
- Clinical Features include thick lips/nose, macroglossia, jaw malocclusion, prominent supraorbital ridge, frontal bossing, prognathism, and coarse facies.
Acquired Hypopituitarism - Causes
- Stalk effect (most common) causing both hypopituitarism and hyperprolactinemia.
- Sheehan's syndrome (most common).
- Viper bite (third most common).
- Secondary empty sella syndrome (fourth most common).
- Lymphocytic hypophysitis.
- Pituitary apoplexy.
- Infections: TB, Histoplasmosis, HIV, Toxoplasmosis
- Infiltration: Sarcoidosis, LCH (Langerhans' cell histiocytosis).
- Trauma/Surgery, Radiation (>18 Gy), Hemochromatosis.
Acquired Hypopituitarism - Presentation
- TSH deficiency (least prominent): Cold intolerance, bradycardia, constipation.
- ACTH deficiency (most prominent): Fatigue, asthenia, weight loss, loss of appetite, hypotension, postural hypotension, hypoglycemia, hyponatremia, no aldosterone effects, eosinophilia.
- Aldosterone deficiency (RAS deficiency): Salt craving, dehydration, hyperkalemia.
Endocrinology
- Investigations include MRI.
- Treatment involves 100 mg IV hydrocortisone and decompressive surgery.
Sheehan's Syndrome and Empty Sella Syndrome
- Sheehan's Syndrome is postpartum pituitary necrosis due to vascular insufficiency predisposing to pituitary apoplexy.
- Precipitating factors include postpartum hemorrhage (PPH), hypotension, and disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC).
- Pathophysiology involves increased pituitary gland size during pregnancy with increased demand for blood flow which is disrupted by precipitating factors. This leads to pituitary necrosis, hypopituitarism, and hypoprolactinemia.
Growth Hormone
- Growth hormone (GH) is secreted by somatotroph cells in the anterior pituitary gland.
- It contains 191 amino acids and is secreted during stages 2 and 4 of non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep.
GH Signaling Pathway
- GH signaling is mediated by the JAK-STAT pathway.
Estimation and Factors Affecting GH
- GH cannot be estimated directly due to its pulsatile nature.
- Indirect estimation involves measuring IGF-1 and IGFBP-3.
- Stimulators of GH secretion include hypoglycemia, GHRH, Ghrelin, acromegaly, and TRH administration.
- Inhibitors of GH secretion include somatostatin, aging, obesity, and hypocaloric state/malnutrition.
Direct and Indirect Actions of GH
- GH has a direct action on receptors and an indirect action mediated by Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1).
- Direct actions are on target tissues.
- Indirect actions are through stimulation of IGF-1 production in the liver, which acts on bones, muscles, and other tissues.
Factors that affect Growth in Obesity
- Growth is increased in obesity due to increased IGF-1 levels, even with low GH levels.
- This is partially due to increased insulin levels in obesity.
Classical Signs in Brain Lesions
- Ring enhancing lesion: Abscess.
- Notochordal remnant with clivus destruction: Chordoma.
- Calcification, bony hyperostosis, pneumosinus dilatations: Meningioma.
- Large lobulated suprasellar mass within 3rd ventricle causing obstructive hydrocephalus: Germinoma.
- Claw sign, posterior ledge sign, nodule inside, dot sign: Rathke's cleft cyst.
Surgical Resection
- After surgery, GH level is evaluated.
- An undetectable GH level indicates good success rate.
- A detectable GH level indicates low success rate, requiring medication to prevent relapse.
- MRI is performed after 3-6 months.
- Transsphenoidal Hypophysectomy is the preferred surgical approach.
- Gamma Knife Stereotactic radiotherapy is used when surgery is not feasible.
Medication
- Somatostatin Analogs target SST2 to SST5 receptors, including Octreotide, Lanreotide, and Pasireotide.
- Dopaminergic agonists like Bromocriptine and Cabergoline are used.
- GH Receptor Antagonist: Pegvisomant
- Microadenomas have an 80% success rate, while macroadenomas have a 50% success rate.
Actions of GH, IGF and GH Measurement
- GH and IGF-1 have similar actions on bone growth, epiphyseal growth, muscle anabolism, and protein anabolism.
- Non-similar actions include:
- Carbohydrate metabolism: GH is diabetogenic while IGF-1 is anti-diabetogenic.
- Lipid metabolism: GH is lipolytic while IGF-1 is anti-lipolytic.
- GH actions independent of IGF-1:
- BEAMS: Bone growth, epiphyseal growth, adipose tissue (lipolysis), muscle anabolism, salt and water retention.
Actions of IGF-1
- Wonder molecule: Genetic stability, stress resistance, telomere shortening.
- Effects: Thymus development, hematopoiesis, immune cell function, glomerular development, fetal growth, ovarian function, testicular function, neural development, amyloid-β clearance, anti-inflammatory, cardiovascular development, vasodilator, musculoskeletal development.
IGF-2
- Effects: Multiplication stimulation activity (MSA), diverse tissue, intrauterine growth development.
Somatostatin
- Effects not fully known.
Craniopharyngioma
- Characteristics:
- Childhood (5-15): 90% of cases, suprasellar + sellar location, M>F, Adamantinomatous appearance (usually solid), wet keratin nodule, calcification ++.
- Adults (50-74): 10% of cases, suprasellar location, M=F, Papillary appearance (solid), no calcification.
- MRI Findings: Vivid hyperintense T1 signal without contrast.
- CT Findings: Suprasellar mass with calcification.
- Central Diabetes Insipidus: Can be associated with Craniopharyngioma.
- Contrast Enhancement: Margins will only take contrast (claw sign).
Rathke's Cleft Cyst
- Characteristics: Unilocular sellar mass, typically seen in the 4th to 6th decade.
Management of Acromegaly
- Investigations:
- Screening: Elevated IGF-1 levels.
- Diagnostic: Oral glucose suppression test (75 gm Glucose) to check GH levels.
- Imaging: Gadolinium enhanced MRI.
- Pituitary Function Test: To check for other hormone dysfunction.
- Poor Prognosis: Associated with 24-hr GH >40 ng/ml.
Features of GH-secreting adenoma
- Ophthalmic features: Angle closure glaucoma.
- Nerve involvement: Carpal tunnel syndrome.
- Muscle: Myopathy (hypertrophy of type-1 and atrophy type-2).
- Cardiovascular: Increased risk of asymmetrical CVH, CAD, HF with preserved ejection fraction.
- Respiratory: Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS).
- Gastrointestinal: Non-malignant colonic polyposis.
- Skin: Seborrhea and hyperhydrosis, warm hands.
- Gonads: Oligomenorrhea.
Metabolic Manifestations
- Diabetes Mellitus (DM): Insulin resistance, acanthosis nigricans, hirsutism.
- Elevated triglycerides.
- Elevated Calcium: Hypercalcemia leading to stones.
- Elevated Phosphate: Hyperphosphatemia.
- Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalance: Salt and water retention (due to aldosterone), decreased sodium.
Features of High Activity and Poor Prognosis
- Diabetes Mellitus (DM): Insulin resistance.
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome (OSAS):
- Seborrhea.
- Arthritis.
Macroadenomas
- Functional Tumor:
- GH Secreting Adenoma: Acromegaly, prolactinoma.
- Non-Functional Tumor:
- Craniopharyngioma: (Bimodal age distribution), mass effect & stalk effect, apoplexy (bleeding), Rathke's cleft cyst.
Mc Cune Albright Syndrome
- Asymmetry of face: Polyostotic fibrous dysplasia (PDF).
- Features of Acromegaly: Classical features, precocious puberty, café-au-lait spots.
Imaging Findings:
- Heterogeneously enhancing GH secreting adenoma (all macroadenoma).
- Cystic component: Will not enhance.
Pituitary Gland Imaging:
- Pituitary gland enhanced (with contrast):
- Cystic part (without contrast): Not enhanced.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.