Podcast
Questions and Answers
Acromegaly is caused by a pituitary adenoma producing excess growth hormone.
Acromegaly is caused by a pituitary adenoma producing excess growth hormone.
True (A)
Enlarged pituitary fossa is a result of the reduction in the size of the adenoma.
Enlarged pituitary fossa is a result of the reduction in the size of the adenoma.
False (B)
Tufting of the terminal phalanges in acromegaly gives a ‘shield’ appearance.
Tufting of the terminal phalanges in acromegaly gives a ‘shield’ appearance.
False (B)
Cardiac hypertrophy occurs early in the progression of acromegaly.
Cardiac hypertrophy occurs early in the progression of acromegaly.
Acromegaly typically results in decreased joint spaces, particularly in the MCP joints.
Acromegaly typically results in decreased joint spaces, particularly in the MCP joints.
Widened bone width in acromegaly occurs with alterations in cortical thickness.
Widened bone width in acromegaly occurs with alterations in cortical thickness.
Flashcards
What is Acromegaly?
What is Acromegaly?
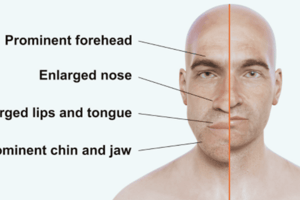
A condition caused by a tumor in the pituitary gland that produces excess growth hormone.
What are the skeletal changes in the skull of someone with Acromegaly?
What are the skeletal changes in the skull of someone with Acromegaly?
Thickening of the skull vault, enlarged paranasal sinuses, mastoids, and pituitary fossa.
Describe the skeletal changes in the thorax and spine of someone with Acromegaly.
Describe the skeletal changes in the thorax and spine of someone with Acromegaly.
Increased sagittal diameter of the chest with kyphosis, and increased AP and transverse diameters of the vertebral bodies.
What are the skeletal feature changes in the appendicular skeleton of someone with Acromegaly?
What are the skeletal feature changes in the appendicular skeleton of someone with Acromegaly?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a common finding in the foot of someone with Acromegaly?
What is a common finding in the foot of someone with Acromegaly?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does Acromegaly affect organs besides the skeleton?
How does Acromegaly affect organs besides the skeleton?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Acromegaly
- Caused by a pituitary adenoma, producing excessive growth hormone.
- Primarily manifested in the musculoskeletal system.
Skull Manifestations
- Thickened skull vault.
- Enlarged paranasal sinuses and mastoids.
- Enlarged pituitary fossa due to the adenoma.
- Prognathism (protruding mandible).
Thorax and Spine Manifestations
- Increased sagittal diameter of the chest, with kyphosis.
- Increased anterior-posterior (AP) and transverse diameters of vertebral bodies, with posterior scalloping.
Appendicular Skeleton Manifestations
- Increased bone width, but unchanged cortical thickness.
- Tufting of terminal phalanges, resembling an "arrowhead" shape.
- Prominent muscle attachments.
- Widened joint spaces (especially metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joints) due to cartilage hypertrophy.
- Premature osteoarthritis.
- Increased heel-pad thickness (>21.5 mm in women, >23 mm in men).
- Generalized osteoporosis.
Extraskeletal Manifestations
- Cardiac hypertrophy (early) and dilated cardiomyopathy (late).
- Visceromegaly — affecting organs like liver, spleen, kidneys, prostate, thyroid, and salivary glands.
- Tracheal cartilage calcification.
- Increased risk of diabetes.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.