Podcast
Questions and Answers
A client with acromegaly exhibits which of the following clinical manifestations?
A client with acromegaly exhibits which of the following clinical manifestations?
- Weight loss and increased appetite
- Overgrowth of the forehead and jaw (correct)
- Decreased hand and feet size
- Decreased joint pain
In a growth hormone suppression test, what indicates the suppression of growth hormone (GH) after administering glucose?
In a growth hormone suppression test, what indicates the suppression of growth hormone (GH) after administering glucose?
- No change in GH levels.
- Increase in GH levels.
- Decrease in GH levels. (correct)
- GH levels are not affected by glucose.
A nurse is caring for a patient after a hypophysectomy. Which postoperative instruction is most important to prevent complications?
A nurse is caring for a patient after a hypophysectomy. Which postoperative instruction is most important to prevent complications?
- Administering stool softeners.
- Instruct the client to avoid blowing their nose (correct)
- Instruct the client to bend at the waist when picking items up.
- Encourage frequent tooth brushing
A client with diabetes insipidus (DI) is prescribed desmopressin. What therapeutic effect should the nurse monitor for?
A client with diabetes insipidus (DI) is prescribed desmopressin. What therapeutic effect should the nurse monitor for?
A patient is diagnosed with SIADH. Which of the following findings would the nurse expect?
A patient is diagnosed with SIADH. Which of the following findings would the nurse expect?
A nurse is caring for a patient with SIADH. What is the priority nursing intervention?
A nurse is caring for a patient with SIADH. What is the priority nursing intervention?
A patient with hyperthyroidism is prescribed methimazole. The nurse knows to monitor for:
A patient with hyperthyroidism is prescribed methimazole. The nurse knows to monitor for:
A nurse is planning care for a patient undergoing radioactive iodine therapy for hyperthyroidism. What is an important precaution to include?
A nurse is planning care for a patient undergoing radioactive iodine therapy for hyperthyroidism. What is an important precaution to include?
Following a thyroidectomy, a patient reports tingling around the mouth and muscle twitching. Which electrolyte imbalance should the nurse suspect?
Following a thyroidectomy, a patient reports tingling around the mouth and muscle twitching. Which electrolyte imbalance should the nurse suspect?
What signs and symptoms indicate a thyroid storm?
What signs and symptoms indicate a thyroid storm?
What is the primary goal when providing nursing care for a patient with hypothyroidism?
What is the primary goal when providing nursing care for a patient with hypothyroidism?
A patient with hypothyroidism is prescribed levothyroxine. What instruction should the nurse emphasize?
A patient with hypothyroidism is prescribed levothyroxine. What instruction should the nurse emphasize?
A patient is brought to the ED unconscious, bradycardic, and hypoglycemic. What condition is most likely?
A patient is brought to the ED unconscious, bradycardic, and hypoglycemic. What condition is most likely?
Which assessment finding is most indicative of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)?
Which assessment finding is most indicative of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)?
A patient in DKA has a blood glucose level of 500 mg/dL and is receiving IV insulin. When the blood glucose reaches 250 mg/dL, what change in the IV solution should the nurse anticipate?
A patient in DKA has a blood glucose level of 500 mg/dL and is receiving IV insulin. When the blood glucose reaches 250 mg/dL, what change in the IV solution should the nurse anticipate?
A patient with hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state (HHS) is being treated with IV fluids and insulin. What should the nurse monitor most closely?
A patient with hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state (HHS) is being treated with IV fluids and insulin. What should the nurse monitor most closely?
Which dietary modification is most appropriate for a patient with hypertension?
Which dietary modification is most appropriate for a patient with hypertension?
Which of the following assessment findings is a common clinical manifestation of hypertension?
Which of the following assessment findings is a common clinical manifestation of hypertension?
The nurse is caring for a client with heart failure who reports sudden weight gain, shortness of breath, and swelling in the ankles. What is the nurse's priority action?
The nurse is caring for a client with heart failure who reports sudden weight gain, shortness of breath, and swelling in the ankles. What is the nurse's priority action?
A patient with heart failure has an ejection fraction of 35%. What does this indicate about the heart's function?
A patient with heart failure has an ejection fraction of 35%. What does this indicate about the heart's function?
Which of the following laboratory results is most useful in determining level of heart failure?
Which of the following laboratory results is most useful in determining level of heart failure?
A patient with heart failure is prescribed furosemide. What electrolyte imbalance is the patient at risk for developing?
A patient with heart failure is prescribed furosemide. What electrolyte imbalance is the patient at risk for developing?
A patient is taking digoxin for heart failure. Which signs and symptoms should the nurse monitor for to detect digoxin toxicity?
A patient is taking digoxin for heart failure. Which signs and symptoms should the nurse monitor for to detect digoxin toxicity?
What is the primary treatment for heparin toxicity?
What is the primary treatment for heparin toxicity?
A patient with peripheral artery disease (PAD) reports leg pain that worsens with elevation and is relieved by lowering the leg. What is the most likely cause of this pain?
A patient with peripheral artery disease (PAD) reports leg pain that worsens with elevation and is relieved by lowering the leg. What is the most likely cause of this pain?
Which of the following interventions is most important for a patient following arterial revascularization surgery?
Which of the following interventions is most important for a patient following arterial revascularization surgery?
A patient reports leg pain, tingling, numbness, and swelling. Which condition should the nurse suspect?
A patient reports leg pain, tingling, numbness, and swelling. Which condition should the nurse suspect?
A nurse is assessing a patient with venous insufficiency. Which of the following findings is expected?
A nurse is assessing a patient with venous insufficiency. Which of the following findings is expected?
Which intervention is most important when caring for a patient with a pulmonary embolism?
Which intervention is most important when caring for a patient with a pulmonary embolism?
What type of shock is most likely to result from a severe hemorrhage?
What type of shock is most likely to result from a severe hemorrhage?
A patient reports severe abdominal pain and is diagnosed with an abdominal aortic aneurysm. What is the appropriate initial nursing intervention?
A patient reports severe abdominal pain and is diagnosed with an abdominal aortic aneurysm. What is the appropriate initial nursing intervention?
A patient is in the oliguric phase of acute kidney injury (AKI). What assessment finding is most concerning?
A patient is in the oliguric phase of acute kidney injury (AKI). What assessment finding is most concerning?
A patient in AKI has a low specific gravity. Why does this occur?
A patient in AKI has a low specific gravity. Why does this occur?
Which class of antibiotics is most concerning for patients with kidney problems?
Which class of antibiotics is most concerning for patients with kidney problems?
A patient in hyperkalemia can be given which medication?
A patient in hyperkalemia can be given which medication?
A patient is experiencing dialysis disequilibrium syndrome. What are signs and symptoms of this condition?
A patient is experiencing dialysis disequilibrium syndrome. What are signs and symptoms of this condition?
A nurse should give which education instructions about the prevention of urinary tract infections UTIs?
A nurse should give which education instructions about the prevention of urinary tract infections UTIs?
A nurse is caring for a patient with GERD. What instruction should be given to promote health?
A nurse is caring for a patient with GERD. What instruction should be given to promote health?
A patient states 'When I swallow it's so painful!' Which symptom is most representative of this patient?
A patient states 'When I swallow it's so painful!' Which symptom is most representative of this patient?
Which complication should the nurse monitor after esophageal surgery?
Which complication should the nurse monitor after esophageal surgery?
Which medication ends in -PRAZOLE to combat GERD symptoms?
Which medication ends in -PRAZOLE to combat GERD symptoms?
What is the best dietary recommendation to give a patient with Celiac disease?
What is the best dietary recommendation to give a patient with Celiac disease?
How is Irritable Bowel Syndrome diagnosed?
How is Irritable Bowel Syndrome diagnosed?
Which manifestation indicated a patient is having an acute inflammatory bowel disease
Which manifestation indicated a patient is having an acute inflammatory bowel disease
A patient takes Sulfasalazine for gastro conditions. Which should the nurse include in instructions?
A patient takes Sulfasalazine for gastro conditions. Which should the nurse include in instructions?
Which of the following indicated obstruction of the bile duct? Choose all that apply.
Which of the following indicated obstruction of the bile duct? Choose all that apply.
Flashcards
Cushing's Disease
Cushing's Disease
Too much ACTH leads to this disease.
Gigantism
Gigantism
Too much GH in children leads to this condition.
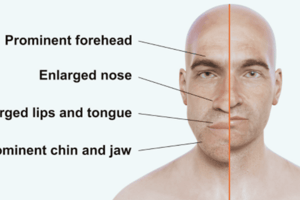
Acromegaly
Acromegaly
Too much GH in adults causes this condition.
Little GH
Little GH
A condition of dwarfism is caused by this.
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diabetes Insipidus (DI)
Diabetes Insipidus (DI)
Low ADH is found in this disorder.
Signup and view all the flashcards
SIADH
SIADH
Too much ADH is known as this disorder.
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acromegaly
Acromegaly
Overgrowth of forehead, jaw, feet, hands, heart, and liver caused by too much GH in adults
Signup and view all the flashcards
Suppress GH
Suppress GH
Glucose is supposed to do this to GH.
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dopamine agonists
Dopamine agonists
Bromocriptine and cabergoline are these.
Signup and view all the flashcards
Somatostatin analogs
Somatostatin analogs
Octreotide and lanreotide are these.
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hypophysectomy
Hypophysectomy
This procedure removes the pituitary gland.
Signup and view all the flashcards
Semi to high Fowler's
Semi to high Fowler's
Postoperative position after hypophysectomy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Desmopressin
Desmopressin
Synthetic ADH medication
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diabetes insipidus
Diabetes insipidus
Excessive urination and thirst are typical of this disorder.
Signup and view all the flashcards
SIADH
SIADH
Too much ADH, water retention causing low sodium and blood osmolarity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Head injuries, meningitis
Head injuries, meningitis
Common risk factors for SIADH
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dark urine, nausea
Dark urine, nausea
Expected findings in SIADH
Signup and view all the flashcards
Restrict fluids
Restrict fluids
First priority in SIADH nursing care
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tetracycline/demeclocycline
Tetracycline/demeclocycline
Medication to stimulate urine flow, not good for kidneys
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vasopressin antagonist
Vasopressin antagonist
This medication causes water loss without sodium loss
Signup and view all the flashcards
TSH increases
TSH increases
This happens when T3 and T4 levels drop.
Signup and view all the flashcards
Calcitonin
Calcitonin
This hormone decreases calcium in the blood.
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hyperthyroidism results
Hyperthyroidism results
Too much T3 and T4 released
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thionamides
Thionamides
Medications that inhibit thyroid hormone production
Signup and view all the flashcards
Beta blockers
Beta blockers
Used to decrease hyperthyroidism symptoms.
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thyroid Storm
Thyroid Storm
Released apon taking too much thyroid hormone
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism
Low T3 and T4 in the blood with decrased metabolic rate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Levothyroxine
Levothyroxine
This medication increases effects of warfarin and digoxin.
Signup and view all the flashcards
Myxedema coma
Myxedema coma
Condition caused by life threatening hypothyroidism
Signup and view all the flashcards
DKA
DKA
Caused by not following insulin regimen, infection, or increased cortisol
Signup and view all the flashcards
HHS
HHS
Complication of diabetes with blood glucose that's greater than 600
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hypertension
Hypertension
Averages above 140 over 90 in blood pressure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Congested Heart Failure
Congested Heart Failure
When the heart cannot properly fill with blood that the body needs.
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ejection fraction
Ejection fraction
Measures how much blood is left in the ventricle wth each heart beat
Signup and view all the flashcards
No smoking or alcohol
No smoking or alcohol
Lifestyle changes for congestive heart failure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Loop and Thiazide diuretics
Loop and Thiazide diuretics
Used to reduce the fluid build up in the body while inhibit the reabsorption of Na and fluids
Signup and view all the flashcards
COX
COX
An enzyme that protects the lining of the Gl and ensure there is blood flow
Signup and view all the flashcards
Prokinetic medication
Prokinetic medication
Causes and increase in upper GI motility increasing peristalsis.
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glasgow Coma Scale
Glasgow Coma Scale
Determines LOC in patients with head injury.
Signup and view all the flashcards
Second and third space
Second and third space
Lumbar needle is place to get CSF between
Signup and view all the flashcardsStudy Notes
Disorders
- Excess ACTH causes Cushing's Disease.
- Excess GH manifests as gigantism in children and acromegaly in adults.
- Insufficient GH leads to dwarfism.
- Low ADH is found in Diabetes Insipidus (DI) and results in excessive urination.
- Excess ADH is called SIADH, which stops urination.
Acromegaly
- Overgrowth affects the forehead, jaw, feet, hands, heart, and liver due to excessive GH in adults.
- Risk factors include age and benign tumors.
- Findings include thick lips, joint pain, hyperglycemia, lower jaw protrusion, and a bulging forehead.
Growth Hormone Suppression Test
- Glucose should suppress GH.
- Obtain baseline GH and glucose levels, administer glucose, and monitor follow-up levels 10, 60, and 120 minutes post-administration.
- Restrict consumption to only water, 6 to 8 hours after the test.
Medications for Acromegaly
- Bromocriptine mesylate and cabergoline are dopamine agonists that inhibit GH release; providers should be notified if dizziness or nasal drainage occurs.
- Octreotide and lanreotide are somatostatin analogs that inhibit GH release.
Hypophysectomy
- This procedure involves removing the pituitary gland through a transnasal or orinasal approach.
- Preoperatively avoid teeth brushing, nose blowing, and waist bending to minimize increased Intracranial Pressure (ICP).
- Postoperatively, the patient should be placed in a semi- to high-Fowler's position, neurological status should be assessed frequently, and watery drainage from the mustache dressing should be observed. Encourage mouth-breathing and discourage coughing.
Client Education Post-Hypophysectomy
- Lifelong hormone replacement therapy is required.
- Avoid activities that increase ICP.
- Rinse mouth frequently, report nose dripping, and consume a high-fiber diet.
Diabetes Insipidus (DI)
- ADH deficiency prevents kidney's urine concentrating, resulting in diluted urine excretion, excessive thirst, and electrolyte imbalance. Neurogenic DI is caused by brain damage; nephrogenic DI by direct kidney damage.
- Expected findings include polyuria, polydipsia, and polyphagia.
- Physical assessment reveals tachycardia, hypotension, poor skin turgor, weak peripheral pulses, weight loss, and a dry mucous membrane.
- Lab tests show urine specific gravity below 1.005, urine osmolality under 275, and blood osmolality above 300 with elevated Na and K.
- Care involves monitoring vital signs, urine output, weight, prescribed diet, IV therapy for hydration, and fall precautions.
- Desmopressin, a synthetic ADH, can be given intranasally, orally, or parenterally to help the kidney conserve urine. Vasopressin, used in neurogenic DI, may cause vasoconstriction, requiring Cardiac Artery Disease (CAD) management.
Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone (SIADH)
- Excess ADH leads to water retention with hyponatremia and decreased blood osmolarity.
- Risk factors include head injuries, meningitis, and medications that cause excess ADH release.
- Findings include headache, weakness, anorexia, muscle cramping, weight gain without edema, personality changes, dark yellow urine, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
- Physical assessment may reveal Cheyne-Stokes respirations indicating a crisis; seizures, coma, and potential death may result from low sodium levels. Tachycardia, bounding pulse, edema, distended neck veins, hypertension, and pulmonary or peripheral edema may also occur.
- Lab tests reveal increased urine levels and decreased blood osmolality levels.
- Care emphasizes fluid restriction and diluted feedings; monitor vital signs, BP, tachycardia, hypothermia, lung sounds for pulmonary edema, and Na levels, implementing seizure precautions as needed.
- Tetracycline or demeclocycline may stimulate urine flow but are not suitable with kidney problem; they can cause diarrhea or yeast infection. Vasopressin antagonists cause water loss without Na loss, requiring monitoring of Na, glucose, intake, output, and bowel patterns. Hypertonic solutions like 3% NaCl reduce edema and elevate Na levels, useful for dyspnea due to pulmonary edema.
Water Intoxication
- Overconsumption of water can cause cerebral or pulmonary edema, death, or shortness of breath (SOB).
Hyperthyroidism
- When T3 and T4 levels decrease, the body releases TSH to increase them. T4 affects metabolism, energy production, the breakdown of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates.
- Calcitonin decreases calcium levels in the blood.
- Excessive T3 and T4 release describes hyperthyroidism.
- Common causes include Graves' disease, thyroiditis, toxic nodular goiter, and iodine-induced conditions.
- Findings include weakness, fatigue, heat intolerance, weight loss, diarrhea, and exophthalmos (bulging eyes).
- Lab tests show increased blood TSH in Graves' disease and elevated free T4 and T3 in the blood. A thyroid scan identifies thyroid size, needing pregnancy and iodide use checks.
- Nursing involves reducing room temperature, reporting temperature increases, and providing cold showers or sponge baths.
- Thionamides like methimazole and propylthiouracil inhibit thyroid hormone production, used to treat Graves’ disease over radioactive iodine therapy; hypothyroidism should be monitored for.
- Medications should be taken with meals and not stopped abruptly. Methimazole must be stopped if pregnancy occurs.
- Beta-blockers like metoprolol, propanol, and atenolol decrease hyperthyroidism symptoms, requiring monitoring of blood pressure, heart rate, and orthostatic changes.
Iodine Solutions
- Lugol's solution, with 5% elemental iodine and 10% potassium iodide solution, inhibits thyroid hormone release.
- Iodine should be taken 1 hour after antithyroid medications, mixed with juice or liquids, and taken with food; notify the provider for fever, sore throat, metallic taste, or mouth ulcers.
Radioactive Iodine Ablation Therapy
- A single dose of radioactive iodine destroys hormone-producing cells; lifelong replacement may be needed.
- Avoid in pregnant patients and monitor for hypothyroidism signs such as edema, cold intolerance, bradycardia, weight gain, and depression.
- Therapy effects may take 6 to 8 weeks, and patients should stay away from infants and pregnant individuals. Use separate toilet for 2 weeks, flush 3 times after use, take a laxative, and avoid sharing cups.
Thyroidectomy
- This is partial or total thyroid gland removal for cancer or if radiation therapy fails.
- Methimazole or propylthiouracil is given 4 to 6 weeks pre-surgery, followed by iodine 10 to 14 days before the procedure.
- Post-procedure, support the head with neck pillows, promote deep breathing, and ensure oral or tracheal care. Tracheostomy supplies should be available due to potential edema and hemorrhage; check for hypocalcemia via Chvostek's and Trousseau's signs and prepare IV calcium gluconate and calcium chloride. Monitor for hypothyroidism signs and report fever or chest palpitations.
Thyroid Storm
- Large amounts of thyroid hormone release with stress, infection, or trauma, leading to hyperthermia, hypertension, delirium, abdominal pain, chest pain, and dyspnea; cool blankets, thionamides, sodium iodide, and propanol are used.
Airway Obstruction
- Can result from hemorrhage, tracheal collapse, or edema; manage with high Fowler's position, neck swelling reduction, and humidified air.
Hypothyroidism
- Condition where diminished T3 and T4 decrease metabolic rate; autoimmune thyroiditis, medication, and thyroid gland damage or removal, are the most common causes.
- Secondary hypothyroidism arises from tumors decreasing thyroid release. Lithium, amiodarone, thalidomide, rifampin, phenobarbital, phenytoin, and carbamazepine can decrease thyroid hormone release, and radiation therapy can also cause hypothyroidism.
- Expected findings includes fatigue, lethargy, cold intolerance, pallor, weight gain, bradycardia, hypotension, slow speech, hair loss, and swelling of face, tongue, hands, and feet.
- Nurses should monitor for bradycardia and hypotension alongside weight gain, and use antiembolism socks and monitor respiratory status, provide a low-calorie diet, and stool softeners.
- Carefully use barbiturates and sedatives to avoid worsening respiratory depression.
- Levothyroxine increases warfarin effects and the need for insulin and digoxin. It should be used cautiously with CAD patients since it forces the heart to work harder, and chest pain and palpitations should be monitored. Antacids, calcium, and iron can affect its absorption. Take on an empty stomach 30 to 60 minutes before breakfast.
Myxedema Coma
- This is a life-threatening condition from hypothyroidism, leading to respiratory failure, hypotension, hypothermia, hypoglycemia, bradycardia, and coma.
- Administer fluids, manage airway, monitor ABGs and temperature, and administer levothyroxine and glucose.
Complications of Diabetes Mellitus
- DKA results from not following insulin regimen, infection, or increased cortisol, glucagon, or epinephrine release. The patient exhibits the 3 P's: polydipsia, polyuria, and polyphagia, with weight loss because the body is in a catabolic state. Lack of glucose to the brain results to neurological dysfunction. Other symptoms include blurred vision, headache, and weakness.
- Ketones are found in the blood, causing acidosis, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and fruity breath. Ketones may also be present in the urine. Polyuria can lead to orthostatic hypotension from excessive fluid depletion. DKA presents with blood glucose greater than 300. Sodium will be low due to excessive urination and potassium may be normal or low initially, then deplete with treatment. Respirations will be Kussmaul due to metabolic acidosis.
HHS
- Characterized by glucose levels over 600, caused by poorly managed diabetes, fluid intake, or stress. Symptoms include the 3 P's, orthostatic hypotension from fluid loss, altered mental status, and blurred vision. Sodium is low, while Potassium may be high initially. BUN and creatinine may be elevated, but ketones are not found in urine or blood. Blood osmolarity is high due to elevated glucose and electrolytes. Metabolic acidosis is not present, but bicarbonate levels may be normal or high.
Nursing Care for DKA and HHS
- Monitor vital signs every 15 minutes, then every 4 hours for dehydration or infection. Rehydrate with 6L to 10L of IV fluids in 24 hours. Start with 0.9% NaCl initially, switching to 0.45% NaCl for high sodium related to dehydration. Hypotonic solutions like 0.45% NaCl can replenish lost body fluids.
- When glucose reaches 250, add IV dextrose 5% to prevent hypoglycemia and cerebral edema. Administer insulin at 0.1 to 0.15 unit/kg IV bolus, followed by continuous IV infusion at 0.1 unit/kg/hr, IV administration is faster than subcutaneous absorption.
Hypertension (HTN)
- Blood pressure averages above 140/90, confirmed after two tests. Risk management involves a low-sodium diet, exercise, weight management, smoking cessation, and reduced alcohol intake.
- African Americans and Hispanics are disproportionately affected. Primary hypertension has no identifiable cause, while secondary hypertension does. Hypertension and cardiac output are inversely related.
- Geriatric considerations include increased plaque, elastin, and collagen buildup in blood vessels, impairing vasodilation and kidney function causing Systolic Hypertension.
- Clinical symptoms include retinal changes like hemorrhage, exudate, and papilledema. Increased BUN and creatinine can manifest as nocturia.
- Check BP at least twice and consider home or ambulatory BP monitoring. Masked hypertension shows HTN outside the hospital setting, white-coat syndrome shows high BP in the hospital. Rest and void coffee or alcohol intake for 30 minutes.
- Untreated hypertension can lead to heart failure and CKD. Calcium Channel Blocker's (CCB's) amlodipine decreases calcium release, administer on an empty stomach and monitor for edema, constipation, and irregular heartbeat.
Congestive Heart Failure (CHF)
- This is when the heart cannot pump enough blood to meet metabolic needs. Dysfunction includes systolic failure which prevents adequate contraction, and diastolic failure which prevents ventricle filling. Managed with meds and lifestyle changes, prevalent in African American and Hispanic communities, risk increases with age.
- Other disorders include hypertension, cardiomyopathy, valvular disorders, or kidney disorders.
- Atherosclerosis and ischemia deprive oxygen, reducing contractility and promoting muscle necrosis. Systemic and pulmonary hypertension requires the heart to work harder.
CHF Pathophysiology
- Systolic heart failure triggers baroreceptors. Renin to angiotensin I conversion occurs in the kidneys, converted by ACE to angiotensin II, causing aldosterone increase which affects Na and fluid retention vasoconstriction.
- ANP and BNP promote diuresis. Ventricular remodeling enlarges the heart.
Left-Sided Heart Failure Manifestations
- Inability to pump through the aorta causes blood to flow backward into the lungs, impairing gas exchange and leading to pulmonary interstitial edema.
- Symptoms include dyspnea, cough, crackles, and low SpO2 with possible S3 gallop. The patient may feel orthopnea, so the patient wants to be in upright positions to feel comfortable. May also cause dry cough with pink frothy sputum. Basilar crackles indicate the development of left sided heart failure and fluid backup.
Right-Sided Heart Failure Manifestations
- Inability to draw blood to the heart causes jugular vein distention (JVD) and hydrostatic pressure, leading to edema, hepatomegaly, and ascites.
- Congestive heart failure begins with left-sided failure, extending to right-sided failure with edema, hepatomegaly, ascites, and JVD.
- Increased atrial pressure causes pulmonary edema; patients experience low O2 saturation, shortness of breath, and tachypnea. In severe cases, there may be skin coolness, clamminess, and suffocation.
- Ejection fraction, normally 55% to 65%, measures blood volume left in the ventricle. Reduction correlates with systolic heart failure. Preserved ejection fraction, around 50%, correlates with diastolic heart failure. Reduced score is 40-49%. BNP levels aid heart failure evaluation.
Medical Management
- Reduce alcohol and smoking.
- Lifestyle changes needed are weight reduction with healthy eating habits and reduced sodium.
Pharmacologic Therapy for Heart Failure
- Reduce fluid buildup with loop diuretics like furosemide and thiazide diuretics like metolazone or hydrochlorothiazide that block Na reabsorption.
- Both loop and thiazide may cause hyperkalemia and orthostatic hypotension.
- Aldosterone antagonists include spironolactone blocks Reabsorption of fluids and potassium retention, monitor K Make sure to monitor for elevated creatinine since this indicates kidney damage.
- ACE inhibitors like lisinopril lower blood pressure, monitor for cough, dizziness, and hyperkalemia. For cough, administer ARBs like valsartan or losartan.
- Sacubitril-valsartan (ARNIs) are expensive, better than ACE and ARBs for HF treatment.
- Beta-blockers like labetalol to counteract SNS, can cause dizziness, hypotension, depression, and bronchoconstriction, administer Beta blockers with caution for asthma, COPD, bronchitis, and diabetes patients.
- Hydralazine isosorbide nitrate for patients with systolic BP over 90.
- Digitalis/ Digoxin may cause cardiac effects, it is crucial to monitor Kidney and potassium levels, improves diuresis by increasing blood flow to the kidneys. Digoxin toxicity causes visual disturbances, confusion, and bradycardia.
Other Heart Failure Medications
- Dopamine used in cases of left ventricle heart failure.
- Milrinone vasodilates severe heart failure cases.
- Caution patients with Hypotension should not receive Vasodilators like nitroglycerin and nitroprusside to bring relief symptoms.
Heparin Toxicity
- Protamine to treat IV Heparin toxicity 20mg/min or 50mg in 10 mins do not exceed from 10mg every 2 hours since it shows risk of protamine toxicity
- Bleeding, increased HR, decreased BP, bruising, petechiae, hematoma, and black and tarry stool aPTT is 1.5 to 2 X of base line.
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)
-
Narrowing of blood vessels in the lower extremities.Thickening of blood vessel or plaque build up Atherosclerosis(harding of the arterial walls) Diet with diabetes, hyperlipidemia sedentary
-
Pain and numbness in legs/feet, Pain elevation, lowed (ruber) or extreme redness, Thicked tow nail
-
Arteriography injection look out for bleeding, Exercise tolerance, Plethysmography and MRA Contrast decrease Blood Flow
-
Rebuild Circulation, Heat use and insulated socks, low caffeine and Nicotine in-between Avoid, Positioning Balloon angio
-
Plate Anticoagulant like aspirin, clopidogrel
-
Laser area plaque monitor Bleeidng
-
Athereetomy scraping plaque monitor bleeding for 2.6 hours
-
Revascularization for loosing Limp make sure to compare pulses and dopper shift
Compartment Syndrome
- tissue block blood glow Monitor by 6Ps assessment
Peripheral Venous Disorders
Blood caused by lack of blood glow cause by VTE
- Venous weak caused obesity/prutitis ,dark ankle ,socks avoid thight clothe or elevate
- Trilemberg/scerlothesis
- Vte clot or lack of glow/ PE chest or SOB encourage movement
Dysrhythmia Treatments
- Bradycardia is treated with atropine, then dopamine or epinephrine.
- Electrical management can use pacemeaker
- Afib uses Amiodarone, adenosine, and Cardiversion
- VTACH no pulse uses amiodarone , lidaccinne and Defibrillation
Heart Attack
- Check troopin after 10 days or monitor myglobin for cardia
- Heart use MONA morphine, O2, Nitrites, and Asprin
Stroke
- Watch for Slurred Speech (monitor)Dizzness and Fall
- Check 2 Times
Pacemaker
- Electrically Stimulate Temporary
- Trans Attach, Painful , After medication
- Epicadirectly is Heart Used with open Surgery
- Permanent or ICDS internic that cirectly Sends electricity area
- Place it in the Pectoral last long
- Fixed Rates
- Demand rate is low
- Check the heart rate or signs
- Report Hicuups signs of Pressures
Cardiac intervention
- Removes Plaque
- AngionBalloon use = Strent bare
Stroke
- FAST check
- Unilateral Neglert one side you dont feel
- 123 check Lox and Aways
Shock
- Cordogenic is the heart and not pumping blood caused by a lot of factos
- Hypo decrease fluid in ICF / obstrutive hard is to get thier
- Distributing is vasodilating . Education health life style and wear seait belts
Aneuresom
- Arteries Balooning two Saccular one side effect entire artery Abd pain with feeling bruti is aneurysms thoratic sevr pain cough brweath
Acurd kideny
- Rifle/ risking of kidney loss or ESKD is severty use of AKD
- Pre Kidney kidney is actual dammage of afterkidney absturtuion of Kidneys or spesis can also be BPH -Oliguria /Electrolyte diuresis back to normal kid will not let Kid work
- Give med for hyper k - Sodium bicarbonate to kaxylate and k glucontate
- Can see burn and creatine protein is brocken down
- Nephrosis
Urinary track
- lower/pelvis pelvis turn to septic
- Female short uti statis dbt inipidus
Pyelonephritis
- Uric/untreatued or 2 year and in uti,headache or naucea vomit 1 Anitbos are 2 L of glucono. glomerur nephitis respitory lead to glomerur neaphis
Peritoneal dialess
utri to kidney faitl
Opiod
- Analgestaics are good
Hep C
- Hiv blood stick Liver b
Aloc
- Decrese ammoun in the body/Diuirees / beta is for paracen
Scerlosis
- Live scar issue channel make over lap and junodice Tioxin and acloho
Cilitica
- Immmue respinise food leads diatrrha/stem /atigue wheret
Ostomise
- lleom /in ileuem liquid stoom / colo up liquid/trans verse solid ,decinding near /s normal is pin nk /odor fixhe/gacars No high after stoimies
Pendcitus
- Inflammed in quadrant
Bown d
- Gl to food caugh to pouch
Clorehtis
Anemia /sufula must check allergic rxn Monitor CBC
- Preditons
- Sahrp/ murhyi Celoium intaltionlder / bilirubin
Extraperial
- shock.
Celiac Disease
- This is caused because it is Animmune response to eatting gluten, Symptoms arediarhhea steatorrhea fatigue avoid Bareley and rye or wheretm
Mlonitre food and bleendind eat dfor rffood
Ostomies
- This for ilem and in has liquid to stop chromoes or ulcerated colits and then place if the patient.
Can have Ascending/transerse/ decineing
- No high fibre
Can be pialkn or balck and bbulish .
Meterproide
- Prometiv mecs
- Tumor
- Upper body protends /tests sea and psA ca detext
- Appnciits Quad
- c. angro checkkid and allerkies/
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.