Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary cause of acromegaly?
What is the primary cause of acromegaly?
- An overactive thyroid gland
- A deficiency of GH
- A genetic predisposition
- A benign tumor in the pituitary gland (correct)
What is the typical age at diagnosis of acromegaly?
What is the typical age at diagnosis of acromegaly?
- 10-15 years old
- 60-65 years old
- 40-45 years old (correct)
- 20-25 years old
What is the primary treatment option for acromegaly?
What is the primary treatment option for acromegaly?
- Surgery (correct)
- Radiation therapy
- Drug therapy
- Combination therapy
Which of the following is NOT a common symptom of acromegaly?
Which of the following is NOT a common symptom of acromegaly?
What is the primary diagnostic test for acromegaly?
What is the primary diagnostic test for acromegaly?
What is the main drug used for treating acromegaly when surgery is not effective?
What is the main drug used for treating acromegaly when surgery is not effective?
Why is it important to monitor GH levels in a pulsatile fashion?
Why is it important to monitor GH levels in a pulsatile fashion?
Which of the following is NOT a potential long-term complication of acromegaly, even after treatment?
Which of the following is NOT a potential long-term complication of acromegaly, even after treatment?
What is the role of IGF-1 in acromegaly?
What is the role of IGF-1 in acromegaly?
How often are GH levels measured to guide drug dosing in patients undergoing treatment with somatostatin analogs?
How often are GH levels measured to guide drug dosing in patients undergoing treatment with somatostatin analogs?
What hormone is suppressed by the use of dopamine agonists in acromegaly treatment?
What hormone is suppressed by the use of dopamine agonists in acromegaly treatment?
What is the typical response of GH levels to an oral glucose tolerance test?
What is the typical response of GH levels to an oral glucose tolerance test?
What is one of the long-term health risks associated with acromegaly?
What is one of the long-term health risks associated with acromegaly?
Which of the following is a symptom that may persist even after surgery for acromegaly?
Which of the following is a symptom that may persist even after surgery for acromegaly?
What is the role of pegvisomant (Somavert) in the treatment of acromegaly?
What is the role of pegvisomant (Somavert) in the treatment of acromegaly?
Why might someone with acromegaly experience sleep apnea?
Why might someone with acromegaly experience sleep apnea?
What type of imaging study is typically used to diagnose pituitary adenomas in acromegaly?
What type of imaging study is typically used to diagnose pituitary adenomas in acromegaly?
What is a potential complication of acromegaly related to vision?
What is a potential complication of acromegaly related to vision?
What is the primary goal of treatment for acromegaly?
What is the primary goal of treatment for acromegaly?
Why is it important for acromegaly patients to undergo a complete eye examination, including visual fields?
Why is it important for acromegaly patients to undergo a complete eye examination, including visual fields?
Flashcards
Acromegaly
Acromegaly
A rare condition caused by excess growth hormone (GH) leading to abnormal growth of bones and tissues.
Prevalence of Acromegaly
Prevalence of Acromegaly
Approximately 3 cases per million people are diagnosed annually in the U.S.
Pituitary Adenoma
Pituitary Adenoma
A benign tumor in the pituitary gland that often causes acromegaly by secreting excess GH.
Clinical Manifestations
Clinical Manifestations
Signup and view all the flashcards
IGF-1 Testing
IGF-1 Testing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT)
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Symptoms of Acromegaly
Symptoms of Acromegaly
Signup and view all the flashcards
Life Expectancy Impact
Life Expectancy Impact
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diabetes and Acromegaly
Diabetes and Acromegaly
Signup and view all the flashcards
Common Conditions Associated
Common Conditions Associated
Signup and view all the flashcards
GH Levels
GH Levels
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hypophysectomy
Hypophysectomy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Octreotide
Octreotide
Signup and view all the flashcards
IGF-1 Levels
IGF-1 Levels
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dopamine Agonists
Dopamine Agonists
Signup and view all the flashcards
Psychosocial Effects
Psychosocial Effects
Signup and view all the flashcards
Adjuvant Therapy
Adjuvant Therapy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Support Groups
Support Groups
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Acromegaly Overview
- Acromegaly is a rare condition, with approximately 3 cases per 1 million people diagnosed annually in the US.
- It affects both genders equally, with a mean age at diagnosis of 40-45 years.
- The cause is often a benign pituitary adenoma producing excess growth hormone (GH).
Pathophysiology and Clinical Manifestations
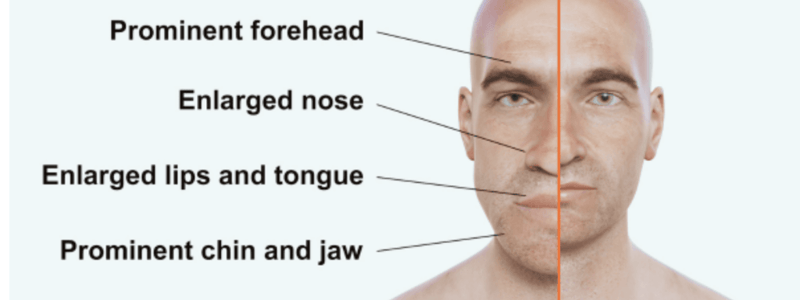
- Excess GH leads to soft tissue and bone overgrowth, particularly in the hands, feet, and face.
- Epiphyseal closure prevents lengthening of arms and legs.
- Manifestations develop slowly over years, potentially going unnoticed.
- Physical changes include thickening and enlargement of facial, foot, and head bones and tissues.
- Patients may experience proximal muscle weakness, joint pain (varying in severity), carpal tunnel syndrome, and peripheral neuropathy.
- Tongue enlargement impacts speech and dental health; deepened voice from vocal cord hypertrophy is also seen.
- Sleep apnea is possible due to upper airway narrowing.
- Skin thickening, oiliness, and acne are common.
- Vision changes can occur due to optic nerve pressure from a pituitary adenoma. Headaches are frequent.
- GH antagonizes insulin, leading to glucose intolerance and possible diabetes symptoms (increased thirst and urination).
Prognosis and Diagnostic Studies
- Reduced life expectancy (5-10 years) due to increased risk of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and colorectal cancer.
- Joint pain and deformities may persist even with successful treatment.
- Diagnosis involves assessing plasma insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) levels and GH response to an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT).
- IGF-1 reflects GH's peripheral actions, rising with GH levels though IGF-1 levels are more consistent than GH levels.
- During an OGTT, normal GH levels fall, while GH levels in acromegaly do not fall and may even rise.
- Imaging (MRI or CT scan) can detect pituitary adenomas.
- Complete eye exams, including visual field testing, are needed to assess possible optic nerve pressure.
Treatment and Interprofessional Care
- Treatment aims to restore normal GH levels through surgery, radiation, medication, or a combination.
- Surgery (hypophysectomy) is often the initial choice, especially for smaller tumors, to reduce GH levels immediately and reduce IGF-1 levels within weeks.
- Adjuvant therapies (radiation or medication) may be needed for larger tumors or higher GH levels.
- Medication options include somatostatin analogs (e.g., octreotide), dopamine agonists (e.g., bromocriptine), or GH antagonists (e.g., pegvisomant).
- Octreotide is administered subcutaneously thrice weekly; long-acting analogs (octreotide LAR, pasireotide, lanreotide) are given intravenously every four weeks.
- GH antagonists directly block the liver's IGF-1 production.
- Serial photos can support patient recovery.
- Psychosocial concerns (body image, sexuality, depression) and physical issues (fatigue, sleep disturbance) may persist, requiring patient support and/or referral to a support group.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.