Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary role of the pentose phosphate pathway?
What is the primary role of the pentose phosphate pathway?
- Production of NADPH for reductive biosynthesis (correct)
- Generation of ATP for energy production
- Synthesis of glucose from glycolysis
- Conversion of fatty acids into glucose
Which molecule is primarily generated during the oxidative non-reversible phase of the pentose phosphate pathway?
Which molecule is primarily generated during the oxidative non-reversible phase of the pentose phosphate pathway?
- D-ribose 5-phosphate
- Ribulose 5-phosphate
- NADPH (correct)
- Fructose 6-phosphate
In addition to NADPH, what is a significant product of the pentose phosphate pathway?
In addition to NADPH, what is a significant product of the pentose phosphate pathway?
- Fructose for glycolysis
- Glucose 1-phosphate
- Ribose for nucleotide synthesis (correct)
- Acetyl-CoA for fatty acid metabolism
Where does the pentose phosphate pathway occur within the cell?
Where does the pentose phosphate pathway occur within the cell?
What occurs during the initial steps of the oxidative non-reversible phase of the pentose phosphate pathway?
What occurs during the initial steps of the oxidative non-reversible phase of the pentose phosphate pathway?
What primarily regulates the entry of glucose into cells?
What primarily regulates the entry of glucose into cells?
What is a significant characteristic of glucokinase in the liver?
What is a significant characteristic of glucokinase in the liver?
Which of the following is NOT involved in the regulation of glycolysis?
Which of the following is NOT involved in the regulation of glycolysis?
Which step is the first irreversible reaction in glycolysis?
Which step is the first irreversible reaction in glycolysis?
What is the main role of hexokinase in glucose metabolism?
What is the main role of hexokinase in glucose metabolism?
How is glycolysis regulated at a molecular level?
How is glycolysis regulated at a molecular level?
What characteristic differentiates glucokinase from hexokinase?
What characteristic differentiates glucokinase from hexokinase?
Which of the following tissues is likely to have the highest concentration of glucose transporters?
Which of the following tissues is likely to have the highest concentration of glucose transporters?
Which enzyme involved in gluconeogenesis is located in the mitochondria?
Which enzyme involved in gluconeogenesis is located in the mitochondria?
What is a significant source of glycerol for gluconeogenesis?
What is a significant source of glycerol for gluconeogenesis?
What role do amino acids play in gluconeogenesis?
What role do amino acids play in gluconeogenesis?
Which of the following best describes the regulation of gluconeogenesis and glycolysis?
Which of the following best describes the regulation of gluconeogenesis and glycolysis?
What primarily determines the rate of glycolysis?
What primarily determines the rate of glycolysis?
Which precursors can be converted to glucose through gluconeogenesis?
Which precursors can be converted to glucose through gluconeogenesis?
Where is glucose 6-phosphatase located within the cell?
Where is glucose 6-phosphatase located within the cell?
Which process has temporal regulation to balance energy requirements?
Which process has temporal regulation to balance energy requirements?
What is produced as a result of the overall equation of the first phase of the pentose phosphate pathway?
What is produced as a result of the overall equation of the first phase of the pentose phosphate pathway?
Which enzyme is primarily responsible for transferring a 2-carbon fragment in the non-oxidative phase of the pentose phosphate pathway?
Which enzyme is primarily responsible for transferring a 2-carbon fragment in the non-oxidative phase of the pentose phosphate pathway?
What is the role of glutathione in red blood cells when exposed to superoxide radicals?
What is the role of glutathione in red blood cells when exposed to superoxide radicals?
Which factor inhibits glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase in the regulation of the pentose phosphate pathway?
Which factor inhibits glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase in the regulation of the pentose phosphate pathway?
What is the primary inducer for the synthesis of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase following a carbohydrate meal?
What is the primary inducer for the synthesis of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase following a carbohydrate meal?
What does glucose 6-phosphate convert into during the non-oxidative phase?
What does glucose 6-phosphate convert into during the non-oxidative phase?
Which statement correctly describes the role of glutathione peroxidase?
Which statement correctly describes the role of glutathione peroxidase?
During high levels of oxidative stress in red blood cells, which compound is critical in maintaining reduced conditions?
During high levels of oxidative stress in red blood cells, which compound is critical in maintaining reduced conditions?
What role does the liver play in blood sugar regulation?
What role does the liver play in blood sugar regulation?
Which enzyme is primarily regulated by energy charge in glycolysis?
Which enzyme is primarily regulated by energy charge in glycolysis?
What activates pyruvate kinase in the glycolytic pathway?
What activates pyruvate kinase in the glycolytic pathway?
Which of the following is NOT one of the three irreversible steps in glycolysis?
Which of the following is NOT one of the three irreversible steps in glycolysis?
What is the main source of pyruvate for gluconeogenesis during fasting?
What is the main source of pyruvate for gluconeogenesis during fasting?
Which process describes the synthesis of glucose from non-carbohydrate sources?
Which process describes the synthesis of glucose from non-carbohydrate sources?
Which reactions in gluconeogenesis bypass the irreversible steps of glycolysis?
Which reactions in gluconeogenesis bypass the irreversible steps of glycolysis?
In the context of glycolysis, what type of reaction are the irreversible steps associated with?
In the context of glycolysis, what type of reaction are the irreversible steps associated with?
What is the primary effect of glucagon and epinephrine on cAMP levels in cells?
What is the primary effect of glucagon and epinephrine on cAMP levels in cells?
Which isoform of hexokinase is associated with high catabolic activity in tumor cells?
Which isoform of hexokinase is associated with high catabolic activity in tumor cells?
Which glycolytic enzyme is known to have DNA-binding abilities and can act as a transcriptional regulator?
Which glycolytic enzyme is known to have DNA-binding abilities and can act as a transcriptional regulator?
What process does phosphoglucoisomerase (PGI) stimulate during cancer cell activity?
What process does phosphoglucoisomerase (PGI) stimulate during cancer cell activity?
What is the main source of ATP generation in muscle cells during heavy exercise once phosphocreatine is depleted?
What is the main source of ATP generation in muscle cells during heavy exercise once phosphocreatine is depleted?
How does the Cori Cycle contribute to energy management in skeletal muscle?
How does the Cori Cycle contribute to energy management in skeletal muscle?
Which of the following statements about cAMP is true?
Which of the following statements about cAMP is true?
What happens to lactate produced in muscles during intense exercise?
What happens to lactate produced in muscles during intense exercise?
Flashcards
Pentose phosphate pathway
Pentose phosphate pathway
Also known as the Hexose Monophosphate Shunt or Phosphogluconate Pathway. It's an alternative way to oxidize glucose without directly using or making ATP.
Pentose phosphate pathway phases
Pentose phosphate pathway phases
The pentose phosphate pathway is divided into two stages, one that's reversible and one that's not.
Oxidative non-reversible phase
Oxidative non-reversible phase
This phase of the pentose phosphate pathway produces NADPH and it's not reversible.
Importance of NADPH
Importance of NADPH
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pentose phosphate pathway connection to glycolysis
Pentose phosphate pathway connection to glycolysis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gluconeogenesis
Gluconeogenesis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Amino Acids as Gluconeogenesis Precursors
Amino Acids as Gluconeogenesis Precursors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glycerol in Gluconeogenesis
Glycerol in Gluconeogenesis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glucose 6-Phosphatase
Glucose 6-Phosphatase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pyruvate Carboxylase
Pyruvate Carboxylase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Phosphoenolpyruvate Carboxykinase
Phosphoenolpyruvate Carboxykinase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Reciprocal Regulation of Glycolysis and Gluconeogenesis
Reciprocal Regulation of Glycolysis and Gluconeogenesis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Liver as the Gluconeogenesis Center
Liver as the Gluconeogenesis Center
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the first irreversible step in glycolysis?
What is the first irreversible step in glycolysis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is glucokinase, and how does it differ from hexokinase?
What is glucokinase, and how does it differ from hexokinase?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Why isn't glucokinase inhibited by glucose-6-phosphate?
Why isn't glucokinase inhibited by glucose-6-phosphate?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What determines the rate of glucose entry into a cell?
What determines the rate of glucose entry into a cell?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are GLUTs?
What are GLUTs?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does the liver store glucose efficiently?
How does the liver store glucose efficiently?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1)?
What is phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1)?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How is phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1) regulated?
How is phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1) regulated?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What hormones control cAMP levels?
What hormones control cAMP levels?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does cAMP affect F2,6BP?
How does cAMP affect F2,6BP?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What's the role of hexokinase in yeast cells?
What's the role of hexokinase in yeast cells?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How many isoforms of hexokinase are found in mammals?
How many isoforms of hexokinase are found in mammals?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What additional roles do some glycolytic enzymes have?
What additional roles do some glycolytic enzymes have?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What's the connection between PGI and cancer?
What's the connection between PGI and cancer?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the Cori Cycle and when is it active?
What is the Cori Cycle and when is it active?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the significance of the Cori Cycle?
What is the significance of the Cori Cycle?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the committed step of glycolysis?
What is the committed step of glycolysis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does citrate affect glycolysis?
How does citrate affect glycolysis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the role of glucagon?
What is the role of glucagon?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is gluconeogenesis?
What is gluconeogenesis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the three irreversible steps in glycolysis?
What are the three irreversible steps in glycolysis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a reversible reaction?
What is a reversible reaction?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is glycolysis?
What is glycolysis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How is pyruvate kinase regulated?
How is pyruvate kinase regulated?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pentose Phosphate Pathway (PPP)
Pentose Phosphate Pathway (PPP)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oxidative Irreversible Phase
Oxidative Irreversible Phase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Non-Oxidative Reversible Phase
Non-Oxidative Reversible Phase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Transketolase
Transketolase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Transaldolase
Transaldolase
Signup and view all the flashcards
PPP in Red Blood Cells
PPP in Red Blood Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rate Limiting Reaction
Rate Limiting Reaction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase
Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
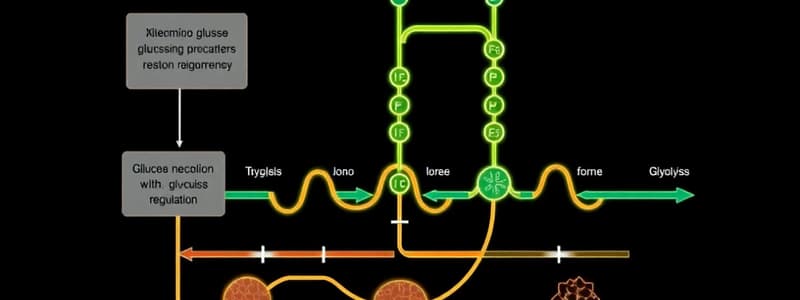
Glucose Metabolism Overview
- Glucose metabolism is a complex process involving several interconnected pathways including glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, the Cori cycle, pentose phosphate pathways, and glycogen metabolism.
- The regulation of these pathways are essential for maintaining blood glucose levels and energy balance.
Regulation of Glycolysis
- Flux through a metabolic pathway can be regulated in several ways, including substrate availability, enzyme concentration, allosteric regulation, and covalent modification.
- The first irreversible reaction in glycolysis is catalyzed by hexokinase, which is linked to glucose uptake and locks glucose in the cell.
- Hexokinase has many isozymes, most inhibited by glucose-6-phosphate (product inhibition).
- Glucokinase is an isozyme in the liver, with a higher Km and not inhibited by glucose-6-phosphate. This allows the liver to modulate blood sugar.
- PFK-1 (Phosphofructokinase-1) is a committed step in glycolysis, regulated by energy charge(ATP, AMP ratio) and citrate (feedback inhibition).
- Pyruvate kinase, the third irreversible step, is activated by F1,6bP (feed-forward activation).
Glucose Entry into Cells
- Tissues have unique functions and isozymes of glucose transporter, GLUT.
- Muscle glucose uptake is insulin dependent.
- Liver has a higher concentration of glucose.
Regulation of Glucose Uptake
- Rate of glucose uptake is limited by the number of glucose transporters on the cell surface and the transporters' affinity for glucose.
- Insulin activates glucose uptake by activating the recruitment of glucose transporters (GLUT4) to the cell membrane.
Regulation of Gluconeogenesis
- Gluconeogenesis is the synthesis of glucose from pyruvate or other noncarbohydrate sources (e.g., lactate, amino acids, glycerol).
- It occurs mainly in the liver and to a lesser extent in the kidney and small intestine.
- Three glycolysis reactions are essentially irreversible: hexokinase (or glucokinase), phosphofructokinase, and pyruvate kinase. These steps must be bypassed during gluconeogenesis, using different enzymes. The bypass reactions involve simple hydrolysis reactions.
- Gluconeogenesis and glycolysis are reciprocally regulated, and one pathway is relatively inactive while the other is highly active in a given cell.
- The rate of gluconeogenesis is determined by the concentration of precursors of glucose.
- Specific enzymes are localized in the cytosol or mitochondria, which is critical for regulation.
Precursors for Gluconeogenesis
- Any metabolite converted to pyruvate or oxaloacetate can be a glucose precursor.
- Major gluconeogenic precursors in mammals are lactate, some amino acids (especially alanine), and glycerol.
Cori Cycle
- The Cori cycle operates during exercise, with muscle utilizing phosphocreatine for ATP. When phosphocreatine is depleted, ATP is provided from glycolysis and glucose uptake from the blood.
- Lactate produced from pyruvate passes via the blood to the liver where it's converted to glucose.
- The glucose travels back to the muscle to fuel glycolysis. The cycle allows the body to accommodate large fluctuations in energy needs.
Pentose Phosphate Pathway
- The pentose phosphate pathway is an alternative route for glucose oxidation without needing ATP, taking place entirely in the cytoplasm.
- Important in producing NADPH for reductive synthesis, for example, of fatty acids, cholesterol, and steroid hormones.
- It also produces ribose-5-phosphate for nucleotide synthesis.
Regulation of Pentose Phosphate Pathway
- Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (rate limiting reaction) is controlled by allosteric regulation (feedback inhibition by NADPH) and inducible enzyme synthesis.
Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Deficiency
- Mutations in G6PD cause a deficiency, inhibiting NADPH production.
- Impaired detoxification of H2O2, lipid peroxidation, erythrocyte membrane breakdown, and hemolytic anemia can result.
Glycogen Metabolism
- Glycogen is broken down and synthesized, with glucose-6-phosphate as a central intermediate between these processes.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.