Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following province/territory and capital city pairs is correctly matched according to the map of Canada?
Which of the following province/territory and capital city pairs is correctly matched according to the map of Canada?
- Manitoba - Toronto
- Quebec - Montreal
- Saskatchewan - Winnipeg
- Alberta - Edmonton (correct)
Based on the table of contents provided, which topic would likely include information about the formation of the Rocky Mountains?
Based on the table of contents provided, which topic would likely include information about the formation of the Rocky Mountains?
- Rock Cycle
- Climate Change
- Glaciation
- Landforms (correct)
If you were planning a trip to see the Northern Lights, which geographical region of Canada would give you the best chance of witnessing this phenomenon, based on the provided lowland region information?
If you were planning a trip to see the Northern Lights, which geographical region of Canada would give you the best chance of witnessing this phenomenon, based on the provided lowland region information?
- Hudson Bay
- Great Lakes- St. Lawrence River
- Arctic (correct)
- Interior Plains
A town is experiencing increased flooding due to melting glaciers. This situation best relates to which impact of climate change in Canada?
A town is experiencing increased flooding due to melting glaciers. This situation best relates to which impact of climate change in Canada?
What is true about the differences between alpine glaciers and ice sheets?
What is true about the differences between alpine glaciers and ice sheets?
Which of the following options is a valid action that governments can take to reduce climate change?
Which of the following options is a valid action that governments can take to reduce climate change?
How could the proximity to a large body of water affect the local climate?
How could the proximity to a large body of water affect the local climate?
Which of the following statements accurately describes the relationship between carbon sources and carbon sinks?
Which of the following statements accurately describes the relationship between carbon sources and carbon sinks?
Based on the information about plate tectonics, what geological process occurs at a divergent boundary?
Based on the information about plate tectonics, what geological process occurs at a divergent boundary?
Which of the following human activities is NOT a main contributor to climate change?
Which of the following human activities is NOT a main contributor to climate change?
Which of the following is a characteristic of the Appalachian Mountains?
Which of the following is a characteristic of the Appalachian Mountains?
What would be best described as continental climate?
What would be best described as continental climate?
How do glaciers alter landscapes?
How do glaciers alter landscapes?
Based on the information on Canada's climate, which factor explains why locations at higher elevations generally have colder temperatures?
Based on the information on Canada's climate, which factor explains why locations at higher elevations generally have colder temperatures?
If a region of Canada is experiencing more frequent droughts, which regional impact of climate change is this an example of?
If a region of Canada is experiencing more frequent droughts, which regional impact of climate change is this an example of?
Flashcards
What is the Earth's crust?
What is the Earth's crust?
The outermost solid layer of the Earth.
What is Oceanic Crust?
What is Oceanic Crust?
It is the top layer of Earth found under the ocean.
What is Continental Crust?
What is Continental Crust?
It is the top layer of Earth found on land.
What is the Earth's Core?
What is the Earth's Core?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the Earth's Mantle?
What is the Earth's Mantle?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a Divergent Boundary?
What is a Divergent Boundary?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a Convergent Boundary?
What is a Convergent Boundary?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Subduction?
What is Subduction?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How are mountains formed?
How are mountains formed?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are Interior Plains?
What are Interior Plains?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Great Lakes - St. Lawrence River?
What is Great Lakes - St. Lawrence River?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Hudson Bay?
What is Hudson Bay?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is weather?
What is weather?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is climate?
What is climate?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Climate Change?
What is Climate Change?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
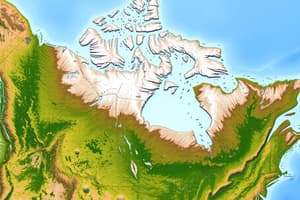
Map of Canada
- Canada shares international borders and has provincial/territorial borders
- The national capital is Ottawa
- Alberta's capital city is Edmonton
- British Columbia's capital city is Victoria
- Saskatchewan's capital city is Regina
- Manitoba's capital city is Winnipeg
- Quebec's capital city is Quebec City
- Ontario's capital city is Toronto
- New Brunswick's capital city is Fredericton
- Newfoundland and Labrador's capital city is St. John's
- Nova Scotia's capital city is Halifax
- Yukon's capital city is Whitehorse
- Northwest Territories's capital city is Yellowknife
- Nunavut's capital city is Iqaluit
- Prince Edward Island's capital city is Charlottetown
- Additional cities include Vancouver, Calgary, Saskatoon, Thunder Bay, Windsor, Hamilton, London, and Montreal.
Lakes
- Lakes in Canada include Lake Ontario, Lake Huron, Lake Erie, Lake Michigan, Lake Superior, Lake Winnipeg, Great Bear Lake, and Great Slave Lake
- Rivers in Canada include the Fraser River, Mackenzie River, Saskatchewan River, Saint Lawrence River and Ottawa River
Large Bodies of Water
- The Pacific, Atlantic, and Arctic Oceans border Canada
- Hudson Bay and the Gulf of St. Lawrence are also large bodies of water.
Landforms: Highland Regions
- Appalachian Mountains in Eastern Canada are old mountains with valleys, oceans, and forests, supporting forestry, farming, tourism, and fishing
- Innuitian Mountains on the northeast coast of Nunavut consist of young jagged mountains with valleys, little to no vegetation, valleys and oceans
- Western Cordillera includes Western Canada, BC, and the Yukon has three mountain ranges and supports industry: Coastal, Rocky, and Columbia.
Landforms: Lowland Regions
- Interior Plains in Alberta, Saskatchewan, Yukon Territory are flat with few trees and grasslands
- The Interior Plains characteristics support farming, along with oil and gas extraction
- Great Lakes-St. Lawrence River in Southern Ontario and Quebec has rolling hills, a large population, industries, and tourism
- Hudson Bay Lowlands along Manitoba and Ontario have water, swamps, and forests, some indigenous communities, and polar bear tourism
- The Arctic region in Northern Canada has no trees and minimal vegetation
Canadian Shield
- Occupying central Canada, the shield is the largest region with rocks, lakes, and trees
- These conditions are amenable to mining, tourism, forestry, and hydroelectricity
Earth Layers
- The Earth's crust is the outermost layer
- Oceanic crust is the Earth's top layer at the bottom of the ocean
- Continental crust is the Earth's top layer on land
- Core is the innermost layer, and it is solid
- Mantle is a layer below the crust filled with magma
- Tectonic plates are sections of the Earth’s crust
- The Earth's crust consists of 15-30 plates
Continental Drift: Tectonic Plates
- Divergent: Plates move apart and new areas of Earth's crust are created
- Convergent: Plates move towards each other
- Subduction: One plate slides underneath another, moves into Earth's interior, and is recycled
- Mountains form when two continental plates collide, folding and breaking massive layers of rock upwards
- Transform: Plates move parallel to each other
Climate Factors
- Latitude: The further from the equator, the colder it gets
- Ocean currents: Warm and cold currents affect air temperature as air passes over the ocean
- Wind/Air masses: Air masses take on characteristics of where they form (moist over water, dry over land, cold from the north, warm from the south)
- Elevation: The higher the elevation, the colder it gets
Climate: Relief
- Relief: Windward mountain sides receive more precipitation, while leeward sides receive less
Climate: Nearness to water
- Nearness to water: Large bodies of water heat and cool slower than air, moderating temperatures nearby
Climate Types
- Continental climate has a temperature range of over 25 degrees Celsius and less than 1000 mm of precipitation
- Maritime climate has a temperature range of less than 25 degrees Celsius and over 1000 mm of precipitation
- Mixed climate has characteristics of both continental and maritime climates
Climate Change: Overview
- Climate change: Long-term change in Earth's overall temperature with lasting ramifications
- Main cause: Human activities include fossil fuel burning, waste, agriculture, and deforestation
- Smog is made when fossil fuels are mixed with heat
- Animal waste emits methane and leads to deforestation
- A major event in climate change is the Industrial Revolution
- 400 billion tons of ice melts every year
- When shores cannot hold the water in the ice that melts, the area floods, and extreme weather results
Climate Change: Ocean Acidification
- Ocean acidification: Rising ocean temperature from increased CO2 levels
- Rising sea level, melting glaciers
Climate Change: Greenhouse effect
- The greenhouse effect: Greenhouse gasses trap heat near the surface
- Enhanced greenhouse effect results when extra greenhouse gases in the atmosphere trap too much of the Sun's energy
- Greenhouse gases: Carbon dioxide and methane
- Carbon sources release carbon dioxide into the atmosphere (e.g., carbon dioxide)
- Carbon sinks absorb more carbon from the atmosphere than they release (e.g., plants)
- Differnce: Carbon source releases more carbon dioxide while a carbon sink does the opposite
- More carbon dioxide results in in higher tempuratures
Climate Change: Indicators
- Rising temperatures Rsing sea levels Shrinking ice sheets Ocean warming
Climate Change: Impacts in Canada
- Rising temperatures
- Melting ice and permafrost
- Increased extreme weather events
- Rising sea levels
- Ecosystem changes
Climate Change: Regional Differences
- Northern Canada: Experiences fastest warming, impacting permafrost and sea ice
- Coastal Regions: Experience sea level rise and changes to marine ecosystems
- Prairie Provinces: Experience more frequent droughts
- Urban Areas: Experience intense rainfall and flood risks
Climate Change: Actions
- Individuals can adopt plant-based diets
- Goverments can implement bold climate policies
- COP15: the 15th Conference of the Parties to the UN Convention on Biological Diversity focuses on nature and biodiversity conservation
Glaciers
- A glacier is a huge mass of ice that moves slowly over land
- The two classifications are alpine glaciers and ice sheets
- The principal difference between them is that ice sheets are not limited to mountainous areas, unlike alpine glaciers
- Glaciers alter the landscape by erosion and deposition
- Glaciers form when more snow piles up, then melts, soon after falling, snow becomes denser, packed more tightly and more snow falls
- When glaciers move, they erode or remove the land beneath resulting in various landform features
- Glaciers give fertile soil and deposits of sand and gravel which can be used to create concrete and asphalt and freshwater
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.