Podcast
Questions and Answers
What geographical feature helped isolate Britain and Ireland from mainland Europe?
What geographical feature helped isolate Britain and Ireland from mainland Europe?
How did the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 C.E. influence Europe?
How did the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 C.E. influence Europe?
What impact did major rivers have on the regions of Europe?
What impact did major rivers have on the regions of Europe?
What was a significant climatic condition affecting agricultural practices in Southern Europe?
What was a significant climatic condition affecting agricultural practices in Southern Europe?
Signup and view all the answers
What characterized the political landscape of Western Europe by 500 C.E.?
What characterized the political landscape of Western Europe by 500 C.E.?
Signup and view all the answers
What was a consequence of Europe's geographical diversity on agriculture?
What was a consequence of Europe's geographical diversity on agriculture?
Signup and view all the answers
What cultural effect did the fragmentation of power in Western Europe have in later centuries?
What cultural effect did the fragmentation of power in Western Europe have in later centuries?
Signup and view all the answers
Which mountain range contributed to the cultural divisions in Europe?
Which mountain range contributed to the cultural divisions in Europe?
Signup and view all the answers
What was one significant economic consequence of the Black Death in medieval Europe?
What was one significant economic consequence of the Black Death in medieval Europe?
Signup and view all the answers
How did the Black Death impact the feudal system in Europe?
How did the Black Death impact the feudal system in Europe?
Signup and view all the answers
What role did the Catholic Church play in shaping medieval European society?
What role did the Catholic Church play in shaping medieval European society?
Signup and view all the answers
What was a direct effect of the Crusades on European economy?
What was a direct effect of the Crusades on European economy?
Signup and view all the answers
Which document established the principle that the king’s power could be limited by law?
Which document established the principle that the king’s power could be limited by law?
Signup and view all the answers
How did geography influence trade in medieval Europe?
How did geography influence trade in medieval Europe?
Signup and view all the answers
What was a significant result of the social changes following the Black Death?
What was a significant result of the social changes following the Black Death?
Signup and view all the answers
What was the role of independent territories in medieval Europe?
What was the role of independent territories in medieval Europe?
Signup and view all the answers
What was the significance of Clovis' conversion to Christianity in 481 C.E.?
What was the significance of Clovis' conversion to Christianity in 481 C.E.?
Signup and view all the answers
Which battle was crucial in halting Muslim expansion in Western Europe?
Which battle was crucial in halting Muslim expansion in Western Europe?
Signup and view all the answers
What role did Charlemagne play in the Carolingian Renaissance?
What role did Charlemagne play in the Carolingian Renaissance?
Signup and view all the answers
What was the primary consequence of the Viking raids across Europe?
What was the primary consequence of the Viking raids across Europe?
Signup and view all the answers
Who was responsible for founding the Holy Roman Empire in 962 C.E.?
Who was responsible for founding the Holy Roman Empire in 962 C.E.?
Signup and view all the answers
Which event is a direct result of the Church's influence in governance during the medieval period?
Which event is a direct result of the Church's influence in governance during the medieval period?
Signup and view all the answers
What was a key characteristic of feudalism that emerged after Charlemagne's reign?
What was a key characteristic of feudalism that emerged after Charlemagne's reign?
Signup and view all the answers
How did the relationship between Pope Gregory VII and Henry IV symbolize Church influence?
How did the relationship between Pope Gregory VII and Henry IV symbolize Church influence?
Signup and view all the answers
What was one result of St. Patrick's missionary work during the 400s C.E.?
What was one result of St. Patrick's missionary work during the 400s C.E.?
Signup and view all the answers
What marked the end of the power transition from kings to officials in Frankish governance?
What marked the end of the power transition from kings to officials in Frankish governance?
Signup and view all the answers
What was the purpose of the Concordat of Worms in 1122 C.E.?
What was the purpose of the Concordat of Worms in 1122 C.E.?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following statements is true about Charlemagne's military campaigns?
Which of the following statements is true about Charlemagne's military campaigns?
Signup and view all the answers
Which issue characterized the struggle for power between the Church and monarchy?
Which issue characterized the struggle for power between the Church and monarchy?
Signup and view all the answers
What characterized the feudal system as a dominant social structure in Europe?
What characterized the feudal system as a dominant social structure in Europe?
Signup and view all the answers
What role did the construction of castles play during the feudal period?
What role did the construction of castles play during the feudal period?
Signup and view all the answers
How was the relationship between lords and vassals formalized?
How was the relationship between lords and vassals formalized?
Signup and view all the answers
What were the main categories of peasants in feudal society?
What were the main categories of peasants in feudal society?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following cities emerged as a key trading hub by 1200 C.E.?
Which of the following cities emerged as a key trading hub by 1200 C.E.?
Signup and view all the answers
What economic change occurred due to the feudal system by 1100 C.E.?
What economic change occurred due to the feudal system by 1100 C.E.?
Signup and view all the answers
What significant change did merchant families in Florence contribute to?
What significant change did merchant families in Florence contribute to?
Signup and view all the answers
What role did guilds play in medieval society?
What role did guilds play in medieval society?
Signup and view all the answers
What was one outcome of William the Conqueror's victory in the Battle of Hastings?
What was one outcome of William the Conqueror's victory in the Battle of Hastings?
Signup and view all the answers
What legal principle did Henry II introduce to strengthen royal authority?
What legal principle did Henry II introduce to strengthen royal authority?
Signup and view all the answers
What prompted the creation of the Magna Carta?
What prompted the creation of the Magna Carta?
Signup and view all the answers
What was a significant factor in the rise of local governance during the later Middle Ages?
What was a significant factor in the rise of local governance during the later Middle Ages?
Signup and view all the answers
What agricultural system was characteristic of the manor structure?
What agricultural system was characteristic of the manor structure?
Signup and view all the answers
What technological advancement improved the effectiveness of knights in battle?
What technological advancement improved the effectiveness of knights in battle?
Signup and view all the answers
What significant event occurred in 1215 that limited royal power in England?
What significant event occurred in 1215 that limited royal power in England?
Signup and view all the answers
Which French monarch is known for significantly expanding the power of the monarchy during his reign from 1180 to 1223?
Which French monarch is known for significantly expanding the power of the monarchy during his reign from 1180 to 1223?
Signup and view all the answers
What was one of the major outcomes after the Mongol invasion of Kievan Rus in 1240?
What was one of the major outcomes after the Mongol invasion of Kievan Rus in 1240?
Signup and view all the answers
Which Pope issued a call for the First Crusade in 1095?
Which Pope issued a call for the First Crusade in 1095?
Signup and view all the answers
What impact did the establishment of ghettos have on Jewish communities in medieval Europe?
What impact did the establishment of ghettos have on Jewish communities in medieval Europe?
Signup and view all the answers
What was one of the primary effects of the Crusades on European society?
What was one of the primary effects of the Crusades on European society?
Signup and view all the answers
Which country emerged as a notable refuge for Jewish communities during the 12th century?
Which country emerged as a notable refuge for Jewish communities during the 12th century?
Signup and view all the answers
What new intellectual movement emerged during the Middle Ages that sought to reconcile faith with reason?
What new intellectual movement emerged during the Middle Ages that sought to reconcile faith with reason?
Signup and view all the answers
Which religious order was founded in 1098 C.E. and aimed for a return to a simpler monastic life?
Which religious order was founded in 1098 C.E. and aimed for a return to a simpler monastic life?
Signup and view all the answers
What major event led to the demographic shift of the Jewish population in Europe during the 1100s?
What major event led to the demographic shift of the Jewish population in Europe during the 1100s?
Signup and view all the answers
What climatic conditions contributed to the famine of the 1300s in northern Europe?
What climatic conditions contributed to the famine of the 1300s in northern Europe?
Signup and view all the answers
What was a consequence of the Inquisition established in 1233 C.E.?
What was a consequence of the Inquisition established in 1233 C.E.?
Signup and view all the answers
What notable cultural impact did the Crusades have on Europe?
What notable cultural impact did the Crusades have on Europe?
Signup and view all the answers
How did the bubonic plague primarily spread to Europe in the 14th century?
How did the bubonic plague primarily spread to Europe in the 14th century?
Signup and view all the answers
What was the primary goal of the First Crusade?
What was the primary goal of the First Crusade?
Signup and view all the answers
What was one major effect of the Black Death on European labor dynamics?
What was one major effect of the Black Death on European labor dynamics?
Signup and view all the answers
Which king is credited with the significant rise of Moscow and the title of czar?
Which king is credited with the significant rise of Moscow and the title of czar?
Signup and view all the answers
Which significant event marked the division of the Catholic Church during the Late Middle Ages?
Which significant event marked the division of the Catholic Church during the Late Middle Ages?
Signup and view all the answers
Which regions faced significant cultural exchanges as a result of the Crusades?
Which regions faced significant cultural exchanges as a result of the Crusades?
Signup and view all the answers
What role did Joan of Arc play in the Hundred Years' War?
What role did Joan of Arc play in the Hundred Years' War?
Signup and view all the answers
What was one consequence of the economic shifts caused by the outbreak of the plague?
What was one consequence of the economic shifts caused by the outbreak of the plague?
Signup and view all the answers
What was one consequence of increased trade routes during the Middle Ages?
What was one consequence of increased trade routes during the Middle Ages?
Signup and view all the answers
How did the Catholic Church influence medieval governance?
How did the Catholic Church influence medieval governance?
Signup and view all the answers
What was a cultural result of the Jewish migration to Eastern Europe during the 12th century?
What was a cultural result of the Jewish migration to Eastern Europe during the 12th century?
Signup and view all the answers
How did Joan of Arc challenge gender norms of her time?
How did Joan of Arc challenge gender norms of her time?
Signup and view all the answers
What was one factor driving the expulsion of Jews from various European countries?
What was one factor driving the expulsion of Jews from various European countries?
Signup and view all the answers
Which war was characterized by territorial disputes and lasting over a century?
Which war was characterized by territorial disputes and lasting over a century?
Signup and view all the answers
What was a result of the labor shortages caused by the plague?
What was a result of the labor shortages caused by the plague?
Signup and view all the answers
Study Notes
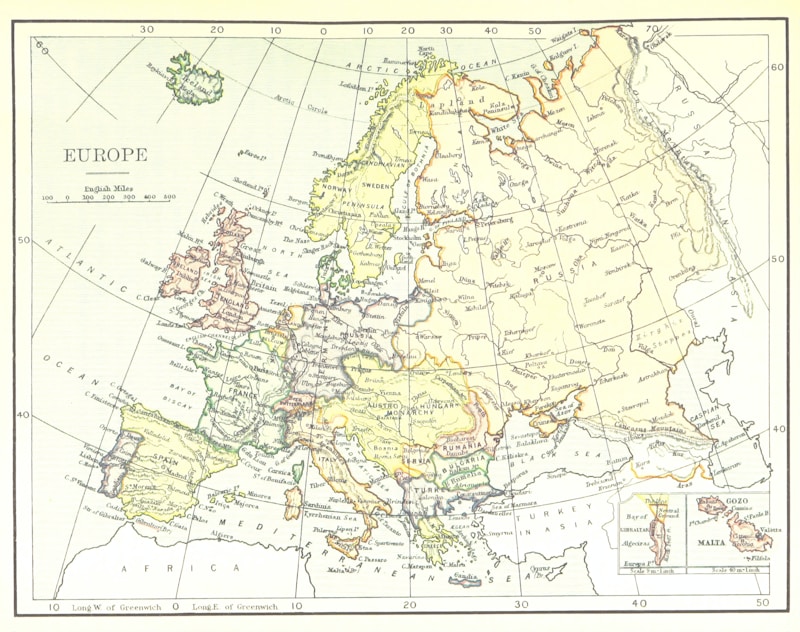
Geography of Europe and its Influence
- Europe's location near coastlines and major rivers was crucial for trade and cultural exchange.
- The Roman Empire's vast domain profoundly shaped Europe's political landscape.
- The fall of Rome triggered changes influenced by physical geography, such as the rise of mountain-separated cultures.
- The English Channel acted as a barrier between Britain and mainland Europe, influencing distinct cultural development.
- Climate variations across Europe influenced agricultural practices, resulting in different farming techniques and crop yields.
Germanic Kingdoms & the Franks
- By 500 CE, Western Europe was fragmented into Germanic kingdoms with diverse cultures.
- Germanic tribes near Rome adopted Roman customs, while those further away retained indigenous traditions.
- The Franks, settling in present-day France and western Germany, became the most powerful Germanic group.
- Clovis, the first Frankish king, converted to Christianity, uniting his people.
- The 'mayors of the palace' gained power, signifying governance shifts from kings.
- Charles Martel received papal support against Islamic expansion, halting its westward spread at the Battle of Tours.
- Charles Martel's son, Pepin, established a precedent for papal influence in politics.
- Charlemagne, crowned in 800 CE, consolidated these trends into a vast Frankish empire.
Charlemagne's Empire and Aftermath
- Charlemagne's reign brought about the Carolingian Renaissance, marked by a resurgence in learning and culture.
- Charlemagne established schools and libraries, fostering education and cultural revival.
- His empire had localized governance, using counts as regional officials.
- Following Charlemagne's death, the empire fragmented, leading to waves of invasions.
Waves of Invaders (800s-900s CE)
- Muslims raided France and Italy.
- Vikings, or Norsemen, raided across Europe, exploiting their seafaring skills.
- Viking raids fostered cultural exchange and the creation of trade routes.
- The invasions contributed to the emergence of feudalism as a system of local power and protection.
Rise of the Holy Roman Empire
- Otto of Saxony, becoming king of Germany in 936 CE and emperor in 962 CE, launched the Holy Roman Empire.
- The Holy Roman Empire encompassed much of modern Germany and northern Italy, but was plagued by conflicts between German and Italian territories.
- The Church played a significant role in legitimizing Otto's rule.
The Church's Role: Expansion and Authority
- Following the fall of the Western Roman Empire, missionary efforts led to the spread of Christianity throughout Europe.
- St. Patrick's missionary work in Ireland and Pope Gregory I's dispatch of monks to Britain were key to this expansion.
- Monasteries became centers of learning.
- The Church's influence extended to nearly every aspect of daily life.
- The power conflicts and evolving roles of the Church and secular rulers shaped medieval politics.
- Pope Gregory VII’s actions (excommunicating Henry IV) showcase the Church's power over secular rulers.
- The Concordat of Worms in 1122 CE defined a compromise in the relationship between religious and governmental power.
The Feudal Order
- Feudalism emerged from Charles Martel's land-granting system to nobles, setting the stage for a hierarchical class structure.
- The system was formalized by oaths of loyalty between lords and vassals, creating mutual obligations.
- Knights, trained warriors serving vassals, were a significant part of the military.
- Castles became symbols of noble power and protection.
Life in Medieval Manors
- Manors were self-sufficient agricultural estates.
- Stewards managed the resources and agricultural processes of the manor.
- Peasants, categorized as freemen or serfs, were integral to the manor's operation.
- Serfs' rights and obligations varied.
Growth of Towns and Trade
- Medieval Europe saw a revival in trade and urban growth after 1100 CE.
- Peasants produced surplus goods beyond subsistence needs.
- Italian cities like Venice, Pisa, and Genoa became prominent trading centers in the Mediterranean.
- Demand for Asian goods fostered the growth of trade and banking systems.
The Rise of a Middle Class
- Increased trade and urbanization fostered a new middle class of merchants, bankers, and artisans.
- These individuals gained wealth and influence, sometimes influencing local governance.
Role of Guilds
- Guilds, associations of craftsmen and merchants, regulated quality and trade.
- Apprenticeships led to journeyman status and eventual master status within guilds.
Governance and Royal Power in England
- Anglo-Saxon kingdoms were unified under Alfred the Great.
- William the Conqueror's (Normandy) victory at the Battle of Hastings led to Norman rule and land redistribution.
- Henry II strengthened royal authority, enacting common law and emphasizing the principle of habeas corpus.
- King John's reign (1199-1216) led to the signing of Magna Carta, which limited royal power and asserted freemen's rights.
- Magna Carta influenced the development of Parliament.
The Monarchy in France and Eastern Europe
- The Kingdom of France emerged after the division of the Frankish Empire.
- The Capetian dynasty expanded French royal power.
- The Estates-General (France) emerged, representing different social classes.
- Kievan Rus, formed by Slavs, thrived on trade and adopted Eastern Orthodox Christianity.
- The Mongol invasion of 1240 led to its decline, with the rise of Moscow under Ivan III.
The Crusades
- Pope Urban II called for a crusade to reclaim Jerusalem and the Holy Land from Muslim control.
- The Crusades increased contact between Europe and other cultures.
- The Crusades had significant economic and social ramifications.
Developments in Education
- Universities emerged in Bologna and Paris (1150 CE), focusing on subjects like grammar, logic, and theology.
- Scholasticism, a method of learning, aimed to reconcile faith with reason.
Rise of Universities and Scholasticism
- Early universities emphasized grammar, logic, and theology.
- Scholasticism blended faith and reason, influencing philosophical thought.
The Role of Religion in Medieval Life
- The Catholic Church was a dominant force, shaping nearly every aspect of daily life.
- Church rituals were central to medieval spirituality.
- New religious orders and reform movements emerged.
Challenges and Conflicts in Medieval Society
- The Inquisition, established to combat heresy, utilized severe punishments for dissenters.
- Anti-Semitism increased, affecting Jewish communities who faced restrictions and expulsion.
- The famine of the 14th century (crop failures and disease) impacted populations.
The Bubonic Plague (Black Death)
- The bubonic plague decimated populations across Europe.
- The plague caused labor shortages and economic disruption.
- Survivors gained increased bargaining power in the labor market.
Socio-Political Changes (Late Middle Ages)
- The Late Middle Ages saw religious disputes, political conflicts, and reform movements.
Joan of Arc
- Joan of Arc inspired French resistance during the Hundred Years' War.
- She was a significant figure in French history.
- Her leadership challenged societal gender norms.
- Joan's fate and legacy are tied to French nationalism and Catholicism.
Discussion Questions (Summary)
- Geography influenced trade, cultural exchange, and territory formation.
- Feudalism impacted decentralization and local power over kingdoms.
- Magna Carta contributed to establishing limited royal power in England.
- Crusades impacted trade, cultural exchange, and religious conflict.
- The Church played a central role in social and political life.
- The Black Death caused social and economic upheaval.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
Explore the geographical influences on Europe and how they shaped the rise of Germanic kingdoms, including the Franks. This quiz covers key concepts such as trade routes, cultural exchanges, and the political landscape after the fall of the Roman Empire. Test your knowledge of historical geography and cultural development in Europe.