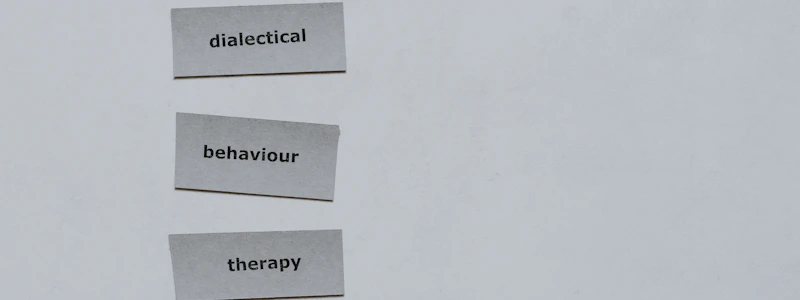
Podcast
Questions and Answers
Match the following psychological approaches with their definitions:
Match the following psychological approaches with their definitions:
Psychoanalytic theory = Unconscious mental processes shape our feelings, thoughts, and behaviors Behaviorism = The scientific study of observable behavior, where the mind is the target of study Humanistic perspective = The positive potential of human beings is assumed
Match the following individuals with their contributions to psychology:
Match the following individuals with their contributions to psychology:
Sigmund Freud = First clinical psychologist and developer of the psychoanalytic theory Ivan Pavlov = Contributor to the perspective of behaviorism Carl Rogers = Proponent of the humanistic perspective
Match the following psychological terms with their descriptions:
Match the following psychological terms with their descriptions:
Unconscious = Part of the mind that operates outside of conscious awareness Behaviorism = Scientific study of observable behavior Human flourishing = Concept associated with the humanistic perspective, referring to maximizing human potential
Match the following psychological theories with their key contributors:
Match the following psychological theories with their key contributors:
Match the following psychologists with the psychological perspectives they are associated with:
Match the following psychologists with the psychological perspectives they are associated with:
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Psychological Approaches and Definitions
- Psychodynamic Approach: Emphasizes the influence of the unconscious mind and childhood experiences on behavior.
- Behaviorism: Focuses on observable behavior and the role of environmental stimuli in shaping responses.
- Humanistic Psychology: Centers on individual potential and personal growth, promoting self-actualization.
- Cognitive Approach: Studies mental processes like perception, memory, and problem-solving.
Individuals and Their Contributions
- Sigmund Freud: Founder of psychoanalysis; introduced concepts of the unconscious, defense mechanisms, and psychosexual stages.
- B.F. Skinner: Promoted behaviorism; known for operant conditioning and reinforcement principles.
- Carl Rogers: Major figure in humanistic psychology; developed client-centered therapy and concept of unconditional positive regard.
- Albert Bandura: Best known for social learning theory and the concept of self-efficacy.
Psychological Terms and Descriptions
- Operant Conditioning: A learning process through rewards and punishments, shaping behavior over time.
- Cognitive Dissonance: The mental discomfort experienced when holding conflicting beliefs or values.
- Attachment Theory: Describes the dynamics of long-term relationships between humans, particularly between caregiver and child.
- Reinforcement: A stimulus that increases the likelihood of a behavior being repeated.
Psychological Theories and Key Contributors
- Psychoanalytic Theory: Developed by Sigmund Freud, focusing on the unconscious mind and early life experiences.
- Behaviorism Theory: Associated with B.F. Skinner, emphasizing environmental impact on behavior through conditioning.
- Cognitive Theory: Pioneered by Aaron Beck, concerning the role of thoughts in influencing emotions and behavior.
- Humanistic Theory: Associated with Carl Rogers and Abraham Maslow; focuses on personal growth and self-fulfillment.
Psychologists and Their Associated Perspectives
- Sigmund Freud: Psychodynamic perspective, emphasizing unconscious processes.
- B.F. Skinner: Behavioral perspective, focusing on conditioning and observable behavior.
- Carl Rogers: Humanistic perspective, highlighting individual potential and personal growth.
- Jean Piaget: Cognitive perspective, known for developmental stages in children's thinking.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.