Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is a primary function of simple cuboidal epithelia?
What is a primary function of simple cuboidal epithelia?
- Facilitating gas exchange
- Providing structural support
- Protection against abrasion
- Secretion and absorption (correct)
Which type of gland releases its secretions directly into the bloodstream?
Which type of gland releases its secretions directly into the bloodstream?
- Exocrine glands
- Endocrine glands (correct)
- Mucus glands
- Serous glands
What distinguishes multicellular exocrine glands from unicellular glands?
What distinguishes multicellular exocrine glands from unicellular glands?
- The ability to secrete hormones
- The number of ducts
- Presence of secretory vesicles
- Their structural complexity (correct)
Which type of secretion involves cells bursting and the destruction of gland cells?
Which type of secretion involves cells bursting and the destruction of gland cells?
Which gland is known for its mixed secretion, producing both serous and mucous substances?
Which gland is known for its mixed secretion, producing both serous and mucous substances?
Which type of exocrine gland is generally found in the ducts of sweat and mammary glands?
Which type of exocrine gland is generally found in the ducts of sweat and mammary glands?
Goblet cells are examples of which type of gland?
Goblet cells are examples of which type of gland?
What is a characteristic of merocrine secretion?
What is a characteristic of merocrine secretion?
Which type of gland has a single, continuous duct?
Which type of gland has a single, continuous duct?
Which gland is primarily responsible for producing oil to lubricate hair and skin?
Which gland is primarily responsible for producing oil to lubricate hair and skin?
What is a key characteristic of stratified cuboidal epithelia?
What is a key characteristic of stratified cuboidal epithelia?
Which type of gland is characterized by the release of secretions through ducts onto epithelial surfaces?
Which type of gland is characterized by the release of secretions through ducts onto epithelial surfaces?
What type of secretion is associated with mammary glands releasing portions of the cytoplasm?
What type of secretion is associated with mammary glands releasing portions of the cytoplasm?
What distinguishes merocrine glands from other types of exocrine glands?
What distinguishes merocrine glands from other types of exocrine glands?
What type of epithelium is primarily involved in the lining of internal passageways?
What type of epithelium is primarily involved in the lining of internal passageways?
Which gland type specifically does not use ducts for secretion?
Which gland type specifically does not use ducts for secretion?
What is the role of stem cells in relation to holocrine glands?
What is the role of stem cells in relation to holocrine glands?
Which of the following statements is true regarding mixed exocrine glands?
Which of the following statements is true regarding mixed exocrine glands?
What type of glandular tissue is goblet cells an example of?
What type of glandular tissue is goblet cells an example of?
Which type of exocrine secretion produces watery secretions?
Which type of exocrine secretion produces watery secretions?
What is the primary characteristic that differentiates simple glands from compound glands?
What is the primary characteristic that differentiates simple glands from compound glands?
Which secretion type involves the elimination of entire cells due to cellular rupture?
Which secretion type involves the elimination of entire cells due to cellular rupture?
In which type of gland would you primarily find goblet cells, and what is their function?
In which type of gland would you primarily find goblet cells, and what is their function?
What distinguishes serous glands from mucous glands?
What distinguishes serous glands from mucous glands?
Which of the following is a function associated with stratified cuboidal epithelia?
Which of the following is a function associated with stratified cuboidal epithelia?
Which gland is primarily associated with the production of a protein-rich fluid?
Which gland is primarily associated with the production of a protein-rich fluid?
What type of secretion is characterized by exocytosis of secretory vesicles?
What type of secretion is characterized by exocytosis of secretory vesicles?
Which of the following structures is classified as a multicellular gland?
Which of the following structures is classified as a multicellular gland?
Where in the body are endocrine glands primarily located?
Where in the body are endocrine glands primarily located?
What is the defining feature of mixed exocrine glands?
What is the defining feature of mixed exocrine glands?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Epithelial Tissue
- Epithelial tissue covers exposed surfaces, lines internal passageways, and forms glands.
- Epithelial tissue includes epithelia and glands.
- Epithelia are layers of cells covering internal or external surfaces.
- Glands are structures that produce fluid secretions.
Classification of Epithelia
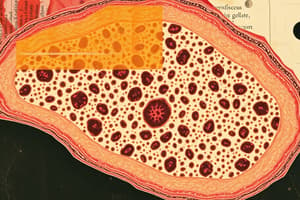
- Cuboidal epithelia are characterized by cube-shaped cells.
- Simple cuboidal epithelia are involved in secretion and absorption, found in glands and portions of kidney tubules.
- Stratified cuboidal epithelia are relatively rare, found in ducts of sweat glands and mammary glands.
Glandular Epithelia
- Glandular epithelia are a type of tissue that produces and releases substances in the body.
- Glands are collections of epithelial cells that produce secretions.
- Endocrine glands release hormones directly into the bloodstream (no ducts).
- Exocrine glands produce secretions that are discharged through ducts onto epithelial surfaces.
Gland Structure
- Unicellular glands are single-celled glands.
- Multicellular glands are composed of multiple cells.
- Goblet cells are unicellular exocrine glands located in epithelia of intestines that secrete mucin.
- Mucin mixes with water to form mucus.
Multicellular Exocrine Glands
- Multicellular exocrine glands are classified by the structure of their ducts and secretory units.
- Examples include sweat glands (sudoriferous), oil glands (sebaceous), and salivary glands.
- Salivary glands contain serous cells (protein-rich fluid) and mucous cells (mucins).
- Multicellular glands can be tubular.
- Simple glands have a single, continuous duct.
- Compound glands have branched ducts.
- Tubular glands have tubular secretory units with straight or coiled tubes.
Secretion Methods
- Merocrine secretion is released by secretory vesicles (exocytosis) (example: merocrine sweat glands).
- Apocrine secretion is released by shedding cytoplasm (example: mammary glands).
- Holocrine secretion is released by cells bursting, killing gland cells (example: sebaceous glands).
- Gland cells are replaced by stem cells.
Types of Exocrine Gland Secretions
- Serous glands produce watery secretions.
- Mucous glands secrete mucins.
- Mixed exocrine glands produce both serous and mucous secretions.
Epithelial Tissue and Glands
- Epithelial tissue covers surfaces and lines internal passageways.
- Epithelia are layers of cells covering internal or external surfaces.
- Glands are structures that produce fluid secretions.
Types of Epithelia
- Simple Cuboidal Epithelia: Secretion and absorption, found in glands and parts of kidney tubules.
- Stratified Cuboidal Epithelia: Relatively rare, found in ducts of sweat glands and mammary glands.
Glandular Epithelia
- Glands are collections of epithelial cells that produce secretions.
- Endocrine glands release hormones into the bloodstream without ducts.
- Exocrine glands release secretions through ducts onto epithelial surfaces.
Types of Glands
- Unicellular glands are single-celled glands.
- Goblet cells are unicellular exocrine glands that secrete mucin which mixes with water to form mucus.
- Multicellular glands are composed of many cells.
- Sweat glands are also known as sudoriferous glands.
- Oil glands are also known as sebaceous glands.
- Salivary glands contain serous cells that secrete protein-rich fluid and mucous cells that secrete mucins.
- Tubular glands have tubular secretory units with straight or coiled tubes.
- Simple glands have a single, continuous duct.
- Compound glands have branched ducts.
Types of Secretion
- Merocrine secretion: Released by secretory vesicles (exocytosis). Example: merocrine sweat glands.
- Apocrine secretion: Released by shedding cytoplasm. Example: mammary glands.
- Holocrine secretion: Released by cells bursting, killing gland cells. Gland cells are replaced by stem cells. Example: sebaceous glands.
Types of Secretions
- Serous glands: Secrete watery secretions.
- Mucous glands: Secrete mucins.
- Mixed exocrine glands: Secrete both serous and mucous.
Epithelial Tissues
- Epithelial tissues cover exposed surfaces, line internal passageways, and form glands.
- Epithelia are layers of cells covering internal or external surfaces.
- Glands are structures that produce fluid secretions.
Cuboidal Epithelia
- Simple cuboidal epithelia are involved in secretion and absorption and are found in glands and portions of kidney tubules.
- Stratified cuboidal epithelia are relatively rare and found in ducts of sweat glands and mammary glands.
Glandular Epithelia
- Glandular epithelia produce and release substances in the body.
- Glands are collections of epithelial cells that produce secretions.
Endocrine Glands
- Endocrine glands release hormones that enter the bloodstream.
- They lack ducts.
Exocrine Glands
- Exocrine glands produce exocrine secretions.
- They discharge secretions through ducts onto epithelial surfaces.
Gland Structure
- Unicellular glands are single-celled.
- Multicellular glands are composed of many cells.
Unicellular Glands
- Goblet cells are unicellular exocrine glands found in epithelia of intestines.
- They secrete mucin, which mixes with water to form mucus.
Multicellular Glands
- Multicellular exocrine glands are classified by the structure of their ducts and secretory units.
- Multicellular glands are tubular.
- Simple glands have a single, continuous duct.
- Compound glands have branched ducts.
- Tubular glands have tubular secretory units with straight or coiled tubes.
Examples of Multicellular Exocrine Glands
- Sweat glands (sudoriferous)
- Oil glands (sebaceous)
- Salivary glands (contain serous cells that secrete a protein-rich fluid, and mucous cells that secrete mucins)
Gland Secretion Methods
- Merocrine secretion: Released by secretory vesicles (exocytosis). Example: merocrine sweat glands.
- Apocrine secretion: Released by shedding cytoplasm. Example: mammary glands.
- Holocrine secretion: Released by cells bursting, killing gland cells. Gland cells replaced by stem cells. Example: sebaceous glands.
Types of Secretions
- Serous glands: Watery secretions.
- Mucous glands: Secrete mucins.
- Mixed exocrine glands: Both serous and mucous.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.