Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which type of epithelial tissue is primarily responsible for secretion?
Which type of epithelial tissue is primarily responsible for secretion?
- Glandular epithelium (correct)
- Basement membrane epithelium
- Connective epithelium
- Covering epithelium
What characteristic distinguishes the basal surface of epithelial cells?
What characteristic distinguishes the basal surface of epithelial cells?
- Has a rich blood supply
- Is anchored to the basement membrane (correct)
- Contains microvilli
- Is exposed to external surfaces
Which of the following is NOT a general characteristic of epithelial tissue?
Which of the following is NOT a general characteristic of epithelial tissue?
- Polarity
- Rapid healing
- Presence of vascular tissue (correct)
- Avascularity
What term describes a single layer of epithelial cells?
What term describes a single layer of epithelial cells?
Which of the following describes the shape of squamous epithelial cells?
Which of the following describes the shape of squamous epithelial cells?
What is a key function of the microvilli that may line the apical surface of epithelial cells?
What is a key function of the microvilli that may line the apical surface of epithelial cells?
What term describes multiple layers of epithelial cells?
What term describes multiple layers of epithelial cells?
Which epithelial tissue type is typically involved in lining organs and cavities?
Which epithelial tissue type is typically involved in lining organs and cavities?
What feature of epithelial cells contributes to their rapid healing capability?
What feature of epithelial cells contributes to their rapid healing capability?
What characteristic indicates the presence of nerves in epithelial tissue?
What characteristic indicates the presence of nerves in epithelial tissue?
What type of epithelium is characterized by dead cells packed with keratin protein?
What type of epithelium is characterized by dead cells packed with keratin protein?
Which type of epithelium is found lining the upper respiratory passages and includes mucus-secreting cells?
Which type of epithelium is found lining the upper respiratory passages and includes mucus-secreting cells?
What is a key feature of nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium?
What is a key feature of nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium?
Which type of cells can be found in the lining of the digestive tract that secrete mucus?
Which type of cells can be found in the lining of the digestive tract that secrete mucus?
Transitional epithelium can be found lining which of the following organs?
Transitional epithelium can be found lining which of the following organs?
Which cell feature enhances the surface area of epithelial cells in some locations?
Which cell feature enhances the surface area of epithelial cells in some locations?
What characterizes pseudostratified columnar epithelium as opposed to other functions?
What characterizes pseudostratified columnar epithelium as opposed to other functions?
What type of epithelial cells would you expect in the lining of kidney tubules?
What type of epithelial cells would you expect in the lining of kidney tubules?
In which of the following locations would you find keratinized stratified squamous epithelium?
In which of the following locations would you find keratinized stratified squamous epithelium?
Which characteristic does NOT belong to simple columnar epithelium?
Which characteristic does NOT belong to simple columnar epithelium?
What is the primary function of the basement membrane?
What is the primary function of the basement membrane?
Which of the following correctly describes the layers of the basement membrane?
Which of the following correctly describes the layers of the basement membrane?
Which type of fiber is primarily responsible for the strength of connective tissue?
Which type of fiber is primarily responsible for the strength of connective tissue?
What is the gel-like material that constitutes the extracellular matrix primarily composed of?
What is the gel-like material that constitutes the extracellular matrix primarily composed of?
What role do glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) play in the extracellular matrix?
What role do glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) play in the extracellular matrix?
Which connective tissue element helps in cell adhesion within the extracellular matrix?
Which connective tissue element helps in cell adhesion within the extracellular matrix?
Which of the following statements is NOT true about the basement membrane?
Which of the following statements is NOT true about the basement membrane?
What characterizes the reticular fibers compared to collagen fibers?
What characterizes the reticular fibers compared to collagen fibers?
The extracellular matrix contains all of the following components EXCEPT:
The extracellular matrix contains all of the following components EXCEPT:
Which cell type is responsible for secreting the components of the extracellular matrix?
Which cell type is responsible for secreting the components of the extracellular matrix?
What is the primary difference between holocrine and merocrine glands?
What is the primary difference between holocrine and merocrine glands?
How are multicellular exocrine glands classified based on duct structure?
How are multicellular exocrine glands classified based on duct structure?
Which statement best describes unicellular exocrine glands?
Which statement best describes unicellular exocrine glands?
Which gland type remains intact after secretion?
Which gland type remains intact after secretion?
What structural classifications are used for multicellular exocrine glands?
What structural classifications are used for multicellular exocrine glands?
What are the two types of serosa found in the abdominopelvic cavity?
What are the two types of serosa found in the abdominopelvic cavity?
Which statement correctly describes the role of the serosa in the body cavities?
Which statement correctly describes the role of the serosa in the body cavities?
What is the primary function of the visceral peritoneum?
What is the primary function of the visceral peritoneum?
How does the parietal peritoneum differ from the visceral peritoneum?
How does the parietal peritoneum differ from the visceral peritoneum?
What is a common characteristic of serous membranes?
What is a common characteristic of serous membranes?
Which layer of the serosa directly engages with abdominal organs?
Which layer of the serosa directly engages with abdominal organs?
Which tissue type is primarily found in the serous membrane?
Which tissue type is primarily found in the serous membrane?
What role does serous fluid play in the body cavities?
What role does serous fluid play in the body cavities?
What is the primary function of mucous membranes in the body?
What is the primary function of mucous membranes in the body?
What type of fluid do serous membranes secrete?
What type of fluid do serous membranes secrete?
Which layer sits below the epithelial layer in mucous membranes?
Which layer sits below the epithelial layer in mucous membranes?
In what locations would you typically find mucous membranes?
In what locations would you typically find mucous membranes?
Which of the following best describes the structure of serous membranes?
Which of the following best describes the structure of serous membranes?
What key term describes the outer layer of serous membranes that line the body cavities?
What key term describes the outer layer of serous membranes that line the body cavities?
What is the main purpose of the lubricating fluid secreted by serous membranes?
What is the main purpose of the lubricating fluid secreted by serous membranes?
Which type of membrane lines body cavities that are closed to the exterior?
Which type of membrane lines body cavities that are closed to the exterior?
What component of the mucous membrane is specifically responsible for mucus production?
What component of the mucous membrane is specifically responsible for mucus production?
Which of the following describes the structure of the lamina propria?
Which of the following describes the structure of the lamina propria?
What type of cartilage provides flexible support and is primarily found in the external ear?
What type of cartilage provides flexible support and is primarily found in the external ear?
What is the primary function of fibrocartilage?
What is the primary function of fibrocartilage?
What type of connective tissue is characterized by fibers arranged in parallel bundles?
What type of connective tissue is characterized by fibers arranged in parallel bundles?
Which location is primarily associated with hyaline cartilage?
Which location is primarily associated with hyaline cartilage?
Which type of tissue acts as a protective cushion and helps store energy in the body?
Which type of tissue acts as a protective cushion and helps store energy in the body?
What is the main role of synovial membranes?
What is the main role of synovial membranes?
Which of the following correctly describes elastic connective tissue?
Which of the following correctly describes elastic connective tissue?
What characterizes cutaneous membranes?
What characterizes cutaneous membranes?
What is the role of chondrocytes within cartilage?
What is the role of chondrocytes within cartilage?
Which function is NOT associated with mucous membranes?
Which function is NOT associated with mucous membranes?
Lacunae are defined as?
Lacunae are defined as?
Which type of connective tissue is classified as 'dense connective tissue'?
Which type of connective tissue is classified as 'dense connective tissue'?
In what manner do synovial membranes contribute to joint movement?
In what manner do synovial membranes contribute to joint movement?
Dense irregular connective tissue is designed to resist what force?
Dense irregular connective tissue is designed to resist what force?
Where is fibrocartilage primarily located?
Where is fibrocartilage primarily located?
Which attribute is typical of hyaline cartilage compared to elastic cartilage?
Which attribute is typical of hyaline cartilage compared to elastic cartilage?
The extracellular matrix of cartilage is primarily composed of?
The extracellular matrix of cartilage is primarily composed of?
What is the primary role of serous membranes?
What is the primary role of serous membranes?
Which connective tissue type is found within lymphoid organs and helps support blood cells?
Which connective tissue type is found within lymphoid organs and helps support blood cells?
Which of the following options correctly describes dense regular connective tissue?
Which of the following options correctly describes dense regular connective tissue?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Major Tissue Types
- Four major tissue types: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous tissue
- Tissue consists of similar cells functioning together.
Epithelial Tissue Characteristics
- Two main types: glandular and covering/lining epithelium
- Glandular epithelium specializes in secretion
- Covering and lining epithelium covers body surfaces both internally and externally
- Separated from connective tissue by a basement membrane
- Avascular: lacks blood vessels, but innervated: contains nerves
- Epithelial cells exhibit polarity with distinct apical and basal surfaces
- Rapid cell reproduction leads to quick healing and potential scarring
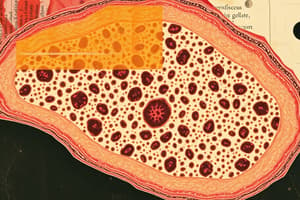
Classification of Epithelial Tissues
- Classified by layer number and cell shape
- Layer Number:
- Simple: single layer of cells
- Stratified: multiple layers of cells
- Cell Shape:
- Squamous: flat cells
- Cuboidal: square cells
- Columnar: rectangular cells
- Different arrangements of the same tissue type can perform distinct functions.
Locations and Functions of Epithelial Tissues
- Endothelium: lines blood vessels
- Alveoli: air sacs in the lungs for gas exchange
- Kidney Tubules: responsible for filtration
- Digestive Tract: can include goblet cells for mucus secretion
- Arrangement can include microvilli to enhance surface area
- Keratinized epithelium has dead, keratin-packed outer cells; found in skin.
- Non-keratinized type lines moist areas (mouth, esophagus) with living cells.
- Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium: appears stratified but is a single layer; functions in mucus secretion and ciliary movement in the respiratory tract.
Structure of the Basement Membrane
- Thin, acellular structure part of the extracellular matrix (ECM)
- Located between epithelium and connective tissue
- Composed of two layers:
- Basal Lamina: includes lamina lucida and lamina densa
- Reticular Lamina: supports the basement membrane and connects to connective tissue
Structural Elements of Connective Tissue
- Connective tissue consists of an extracellular matrix (ECM)
- ECM contains a limited number of cell types (matrix-secreting blast cells and mature cyte cells)
- Matrix consists of long, thin fibers forming networks:
- Collagen Fibers: the strongest fibers providing tensile strength
- Elastic Fibers: allow tissues to return to original shape
- ECM comprised of approximately 10% large organic molecules and 90% interstitial fluid
- Contains glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) and proteoglycans for structural support
- Adhesion proteins assist in connecting cells to ECM components
Body Cavities and Serous Membranes
- Serosa lines body cavities and the outer organs within them.
- In the abdominopelvic cavity, serosa is classified as either parietal peritoneum or visceral peritoneum.
Exocrine Glands
- Classified based on structure (multicellular vs. unicellular) and function (merocrine vs. holocrine).
- Multicellular glands can be simple or compound in duct structure and tubular, alveolar, or tubuloalveolar in secretory parts.
- Unicellular glands, like goblet cells, secrete mucus.
Connective Tissue
- Dense regular connective tissue features fibers arranged in parallel, resisting tension in one direction. Examples include tendons and ligaments.
- Dense irregular connective tissue has fibers arranged in various planes for multidirectional strength, found in the dermis and fibrous capsules of joints.
- Elastic connective tissue, with abundant elastic fibers, allows tissues to recoil after stretching, found in large arteries and certain ligaments.
Types of Loose Connective Tissue
- Areolar tissue supports and forms the lamina propria of mucous membranes lining various tracts.
- Adipose tissue provides cushioning, insulation, and energy storage.
- Reticular tissue supports blood cells in lymphoid organs like lymph nodes, bone marrow, and the spleen.
Cartilage Composition and Types
- Cartilage is dense connective tissue with cells called chondrocytes housed in lacunae within an extracellular matrix.
- Avascular with no nerve fibers, cartilage consists of collagen fibers and chondroitin sulfates.
- Types of cartilage include:
- Elastic cartilage, rich in elastic fibers for flexibility, found in the external ear.
- Fibrocartilage, tough and shock-absorbing, located between vertebrae.
- Hyaline cartilage, the most abundant, provides support and is found in costal cartilages, nose, trachea, and synovial joints.
Body Membranes
- Body membranes cover or line various parts, comprising an epithelial layer bonded to connective tissue.
- Synovial membranes line joints, providing lubrication and cushioning during movement.
- Cutaneous membranes (skin) are the only dry membranes covering external surfaces.
- Mucous membranes line open body cavities and are involved in producing mucus for protection and lubrication.
Serous Membranes
- Serous membranes line closed body cavities, composed of flat epithelial cells (mesothelium) and underlying connective tissue.
- Secrete serous fluid to reduce friction between organs.
- Classified into three types: pericardium (heart), pleural (lungs), and peritoneum (abdominal cavity).
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.